Abstract
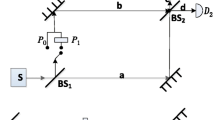
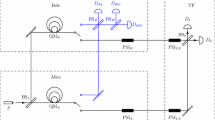
A quantum private comparison(QPC) protocol is proposed, in which the single photons are uesed as quantum resources and the private information of each participant is independently encoded on the global phase of the particle sequence. Compared with QPC protocols based on entangled states or high-dimensional quantum states, the protocols using single photons have the advantages of low cost and easy implementation, but the impact of noise on private comparison is a challenge. Aiming at the extreme sensitivity of information equality comparison to noise, analyze the influence of noise on the output of the parallel beam splitter, the classical linear block code are used to constructed the error correction code of this protocol, to achieve higher encoding efficiency than quantum error correction code and correct single-bit error in quantum transmission. Security analysis demonstrates that this protocol can resist various typical attacks from inside or outside.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05088-9
References
Yao, A.C.: Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceeding of 23Rd IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 160–164 (1982)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 42, 055305 (2009)
Chen, X.B., Xu, G., Niu, X.X., Wen, Q.Y., Yang, Y.X.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 283(7), 1561–1565 (2010)
Tseng, H.Y., Lin, J., Hwang, T.: New quantum private comparison protocol using epr pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 373–384 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Jiang, Z.T.: An efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with w state. Opt. Commun. 284(12), 3160–3163 (2011)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Jiang, Z.T., Cao, Y.Z.: A protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with χ-type state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51(1), 69–77 (2012)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Wang, X.M.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol using d-dimensional basis states without entanglement swapping. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(4), 1085–1091 (2014)
Lin, S., Sun, Y., Liu, X.F., Yao, Z.Q.: Quantum private comparison protocol with d-dimensional bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 559–568 (2013)
Huang, S.L., Hwang, T., Gope, P.: Multi-party quantum private comparison protocol with an almost-dishonest third party using ghz states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(6), 2969–2976 (2016)
Hung, S.M., Hwang, S.L., Hwang, T., Kao, S.H.: Multiparty quantum private comparison with almost dishonest third parties for strangers. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(2), 36 (2017)
Ye, T.Y., Ji, Z.X.: Multi-user quantum private comparison with scattered preparation and one-way convergent transmission of quantum states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 60(9), 090312 (2017)
Cao, H., Ma, W., Lyu, L., He, Y., Liu, G.: Multi-party quantum privacy comparison of size based on d-level ghz states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18 (9), 287 (2019)
Pan, H.M.: Quantum private comparison based on χ-type entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(10), 3340–3347 (2017)
Ye, T.Y., Ji, Z.X.: Two-party quantum private comparison with five-qubit entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(5), 1517–1529 (2017)
Zha, X.W., Yu, X.Y., Cao, Y., Wang, S.K.: Quantum private comparison protocol with five-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3874–3881 (2018)
Li, C.Y., Chen, X.B., Li, H.J., Yang, Y.G., Li, J.: Efficient quantum private comparison protocol based on the entanglement swapping between four-qubit cluster state and extended bell state. Quantum Inf. Process 18, 158 (2019)
Xu, Q.D., Chen, H.Y., Gong, L.H., Zhou, N.R.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on four-particle ghz states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(6), 1798–1806 (2020)
Wu, W.Q., Zhao, Y.X.: Quantum private comparison of size using d-level bell states with a semi-honest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 20(4), 155 (2021)
Yang, Y.G., Xia, J., Jia, X., Shi, L., Zhang, H.: New quantum private comparison protocol without entanglement. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 10(6), 1250065 (2012)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Jia, H.Y., Huang, W., Zhang, W.W., Wen, Q.Y.: Efficient quantum private comparison employing single photons and collective detection. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 887–897 (2013)
Liu, X.T., Zhang, B., Wang, J., Tang, C.J., Zhao, J.J.: Differential phase shift quantum private comparison. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(1), 71–84 (2014)
Li, Y.B., Ma, Y.J., Xu, S.W., Huang, W., Zhang, Y.S.: Quantum private comparison based on phase encoding of single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(9), 3191–3200 (2014)
Lin, P.H., Hwang, T., Tsai, C.W.: Efficient semi-quantum private comparison using single photons. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(7), 207 (2019)
Andersson, E., Curty, M., Jex, I.: Experimentally realizable quantum comparison of coherent states and its applications. Phys. Rev. A 74(2), 022304 (2006)
Kok, P., Nemoto, K., Ralph, T.C., Dowling, J.P., Milburn, G.J.: Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79(1), 135–135 (2007)
Macwilliams, F.J., Sloane, N.: The theory of Error-Correcting codes. The Nethertands, North-Holland (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for Publication
Informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Consent to participate
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, M., Ma, C. Fault-tolerant Quantum Private Comparison Protocol. Int J Theor Phys 61, 41 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05008-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05008-x