Abstract
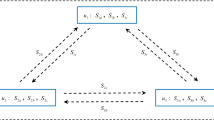
Utilizing the advantage of quantum entanglement swapping, a multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with authentication is proposed. In this protocol, a semi-trusted third party is introduced, who prepares Bell states, and sends one particle to multiple participants respectively. After that the participants can share a Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state by entanglement swapping. Finally, these participants measure the particles in their hands and obtain an agreement key. Here, classical hash function and Hadamard operation are utilized to authenticate the identity of participants. The correlations of GHZ states ensure the security of the proposed protocol. To illustrated it detailly, the security of this protocol against common attacks is analyzed, which shows that the proposed protocol is secure in theory.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing[C]. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661 (1991)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648–651 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting[J]. Phys. Rev. A 59, 162–168 (1999)
Hsu, L.Y.: Quantum secret-sharing protocol based on Grover’s algorithm[J]. Phys. Rev. A 68, 022306 (2003)
Liu, W., Wang, Y.B., Cui, W.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on Bell entangled states[J]. Commun. Theor. Phys. 57, 583–588 (2012)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., et al.: Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels[J]. Sci. China(Phys. Mech. Astronomy) 56, 1670–1678 (2013)
Liu, W.J., Liu, C., Chen, H.W., et al.: An efficient protocol for the quantum private comparison of equality with W state[J]. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 12, 1450001 (2014)
Yang, G., Wen, Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement.[J]. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. (2009)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with x-type entangled states[J]. Phys. Rev. A 78, 064304 (2008)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Multi-step quantum secure direct communication using multi-particle Green-Horne-Zeilinger state[J]. Optics Commun. 253, 15–20 (2005)
Wang, C., Deng, F.G., Li, Y.S., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding[J]. Phys. Rev. A 71, 44305 (2005)
Wang, S.A., Lu, C.Y.: Quantum secure direct communication network[J]. IEEE 752–755 (2013)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Li, C.Y., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication network with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs[J]. Phys. Lett. A 359, 359–365 (2016)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol[J]. Electron. Lett. 40(18), 1149–1150 (2004)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with Bell states and Bell measurements[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 12, 921–932 (2013)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., et al.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Sun, Z.W., Zhang, C., Wang, B.H., et al.: Improvements on ‘Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles’[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 12, 3411–3420 (2013)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., et al.: Cryptanalysis of a multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with single particles[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 13, 1651–1657 (2014)
Xu, G.B., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., et al.: Novel multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with GHZ states[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 13, 2587–2594 (2014)
Shukla, C., Alam, N., Pathak, A.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 13, 2391–2405 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement based on four-particle GHZ states[J]. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 14, 1650007 (2016)
Sun, Z.W., Zhang, C., Wang, P., et al: Multi-party quantum key agreement by an entangled six-qubit state[J]. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 1920–1929 (2016)
Liu, B., Xiao, D., Jia, H.Y., et al.: Collusive attacks to ‘circle-type’ multi-party quantum key agreement protocols[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 15, 2113–2124 (2016)
Cao, H., Ma, W.P.: Multiparty quantum key agreement based on quantum search algorithm[J]. Sci. Rep. 7, 45046 (2017)
Cao, H., Ma, W.P.: Multi-party traveling-mode quantum key agreement protocols immune to collusive attack[J]. Quantum Inf. Process 17, 219 (2018)
Huang, W.C., Yang, Y.K., Jiang, D., et al.: Efficient travelling-mode quantum key agreement against participant’s attacks[J]. Sci. Rep. 9, 16421 (2019)
Sun, Z.W., Wu, C.H., Zheng, S.G., et al.: Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement with a single d-level quantum system secure against collusive attack[J]. IEEE Access 7, 102377–102385 (2019)
Abulkasim, H., Mashatan, A., Ghose, S.: Secure multiparty quantum key agreement against collusive attacks. Sci. Rep. 11, 9456 (2021)
Pieprzyk, J, Hardjono, T, Seberry, J.: Key establishment protocols[M]. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Lee, H., Lim, J., Yang, H.: Quantum direct communication with authentication[J]. Phys. Rev. A 73, 042305 (2005)
Lin, S., Wang, H., Guo, G.D., et al.: Authenticated multi-user quantum key distribution with single particles[J]. Int. J. Quantum Inform. 14, 1650002 (2016)
Sun, Y., Du, J.Z., Qin, S.J., et al.: Quantum secret sharing with bidirectional authentication[J]. Acta Phys. Sin. 57, 46894694 (2008)
Xu, G., Jiang, D.: Novel methods to construct nonlocal sets of orthogonal product states in an arbitrary bipartite high-dimensional system[J]?. Quantum Inform. Proc. 20, 128 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 61772134 and No. 61976053), Fujian Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018J01776), and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, YT., Chang, H., Guo, GD. et al. Multi-party Quantum Key Agreement Protocol with Authentication. Int J Theor Phys 60, 4066–4077 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04954-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04954-2