Abstract
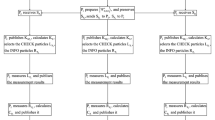
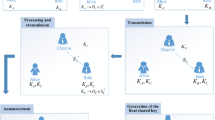
A new three-party quantum key agreement protocol based on seven-qubit states is proposed. In this protocol, each participant adopts different encryption methods to transmit a secret key of the same length. Subsequently, the participants utilize joint measurement to gain the ultimate shared secret key. No participant can determine the ultimate shared key by himself/herself. In addition, the proposed three-party quantum key agreement protocol could resist several well-known attacks. Compared with typical quantum key agreement protocols, our proposed three-party quantum key agreement protocol is more efficient.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40, 1149–1150 (2004)
Hsueh, C.C., Chen, C.Y.: Quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. Proc. Inf. Sec Conf. In: Proceedings of the 14th Information Security Conference, pp 236–242. National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei (2004)
Tsai, C.W., Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Comment on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. In: Proceedings of the 20th Cryptology and Information Security Conference, pp 210–213. National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu (2010)
Chong, S.K., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Improvement on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1793–1802 (2011)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Comm. 283, 1192–1195 (2010)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Wang, Y., Xiao, L.: Increasing the efficiencies of random-choice-based quantum communication protocols with delayed measurement. Chin. Phys. Lett. 21, 2097 (2004)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 921–932 (2013)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.-Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.-Y., Liu, B., Su, Q., Gao, F.: Cryptanalysis of a multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1651–1657 (2014)
Shukla, C., Alam. N., Pathak, A.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2391–2405 (2014)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Zhu, Z.C., Hu, A.Q., Fu, A.M.: Improving the security of protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 4245–4254 (2015)
Huang, W., Su, Q., Xu, B.: Improved multiparty quantum key agreement in travelling mode. Sci. China. Phys: Mech. Astron. 59, 120311 (2016)
Sun, Z.W., Zhang, C., Wang, P., Yu, J.P., Zhang, Y., Long, D.Y.: Multi-party quantum key agreement by an entangled six-qubit state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 1920–1929 (2016)
Shen, D.S., Ma, W.P., Wang, L.L.: Two-party quantum key agreement with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2313–2324 (2014)
Sun, Z.W., Yu, J.P., Wang, P.: Efficient multi-party quantum key agreement by cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 373–384 (2016)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Quantum key agreement protocols with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3483–3498 (2015)
Xu, G.B., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., Qin, S.J.: Novel multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2587–2594 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement based on four-particle GHZ states. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 14, 1650007 (2016)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement with five-particle entangled states. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15, 1750018 (2017)
Xu, L., Zhao, Z.: Quantum private comparison protocol based on the entanglement swapping between χ + state and W-Class state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1–15 (2017)
Min, S.Q., Chen, H.Y., Gong, L.H.: Novel multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with G-Like states and Bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 1811–1822 (2018)
Chou, Y.H., Zeng, G.J., Chang, Z.H.: Dynamic group multi-party quantum key agreement. Sci. Rep. 8, 4633 (2018)
Zha, X., Song, H., Qi, J.: A maximally entangled seven-qubit state. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 45, 255302 (2012)
Zha, X., Yuan, C., Zhang, Y.: Generalized criterion for a maximally multi-qubit entangled state. Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 045201 (2013)
Borras, A., Plastino, A.R., Batle, J.: Multiqubit systems: highly entangled states and entanglement distribution. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 40, 13407 (2007)
Gisin, N., Fasel, S., Kraus, B., et al.: Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022320 (2006)
Cai, Q.Y.: Eavesdropping on the two-way quantum communication protocols with invisible photons. Phys. Lett. A 351, 23–25 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., et al.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054302 (2006)
Ma, H., Huang, P., Bao, W., et al.: Continuous-variable quantum identity authentication based on quantum teleportation. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 2605–2620 (2016)
Hong, C., Heo, J., Jang, J.G., et al.: Quantum identity authentication with single photon. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 236 (2017)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5633–5638 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61561033), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20171BAB202002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, NR., Min, SQ., Chen, HY. et al. Three-Party Quantum Key Agreement Protocol with Seven-Qubit Entangled States. Int J Theor Phys 57, 3505–3513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3865-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3865-5