Abstract
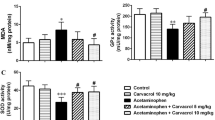
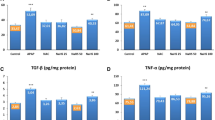
An overdose of acetaminophen (APAP) produces acute tubular necrosis. The aim of this study was to observe the effects of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) only and combined with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on inflammatory cytokines in kidney. Thirty-two male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into four groups: sham, control (APAP), NAC, and NAC + HBO. In the APAP, NAC, and NAC + HBO groups, renal injury was induced by oral administration of 1 g/kg APAP. The NAC group received NAC (100 mg/kg/day). NAC + HBO group received NAC (100 mg/kg/day) intraperitoneally and HBO underwent at 2.8 ATA pressure with 100 % oxygen inhalation for 90 min every 12 h for 5 days. Rats in the sham group received distilled water only by gastric tube. All animals were killed on 6 days after APAP or distilled water administration. Creatinine, urea, neopterin, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-6 levels were measured in sera. There was a significant increase in serum creatinine and urea levels in the control group compared to the sham group (in both, p = 0.001). NAC and NAC + HBO significantly decreased serum neopterin, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels compared to control group. APAP administration caused tubular necrosis in the renal. NAC and NAC + HBO treatments significantly reduced APAP-induced renal damage. The results of this study showed that renal dysfunction in APAP toxicity was attenuated by the use of HBO and NAC treatments. The combination of NAC and HBO treatments might be recommended as an effective treatment modality for APAP-induced nephrotoxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cakir, E., O.E. Akgul, I. Aydin, T. Cayci, Y.G. Kurt, O. Onguru, F.N. Aydin, M. Agilli, H. Yaman, N. Ersoz, S. Bilgic, A. Guven, T. Turker, C. Bilgi, and K.M. Erbil. 2010. The association between neopterin and acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity. Renal Failure 32: 740–746.
Demirbas, S., E. Cakir, E.O. Akgul, M. Seyrek, T. Cayci, Y.G. Kurt, B. Uysal, I. Aydin, B. Kurt, H. Yaman, and M.K. Erbil. 2011. Elevated serum neopterin levels in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 31: 165–170.
Gul, H., B. Uysal, E. Cakir, H. Yaman, E. Macit, A.O. Yildirim, Y.E. Eyi, U. Kaldirim, E. Oztas, E.O. Akgul, T. Cayci, M. Ozler, T. Topal, S. Oter, A. Korkmaz, M. Toygar, and S. Demirbag. 2012. The protective effects of ozone therapy in a rat model of acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 34: 81–86.
Yaman, H., S. Isbilir, E. Cakir, and B. Uysal. 2011. Current issues with paracetamol induced toxicity. Journal of Experimental and Integrative Medicine 1: 165–166.
Salhanick, S.D., B. Belikoff, D. Orlow, D. Holt, W. Reenstra, and J.A. Buras. 2006. Hyperbaric oxygen reduces acetaminophen toxicity and increases HIF-1alpha expression. Academic Emergency Medicine 13: 707–714.
Atasoyu, E.M., S. Yildiz, M. Cimsit, H. Cermik, T. Qyrdedi, T.R. Evrenkaya, S. Aktas, G. Uzun, O. Bilgi, and M. Gultepe. 2006. Investigation of the effect of hyperbaric oxygen on experimental cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 98: 150–154.
Tibbles, P.M., and J.S. Edelsberg. 1996. Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. The New England Journal of Medicine 334: 1642–1648.
Atasoyu, E.M., S. Yildiz, O. Bilgi, H. Cermik, R. Evrenkaya, S. Aktas, M. Gultepe, and E.G. Kandemir. 2005. Investigation of the role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Archives of Toxicology 79: 289–293.
Yasar, M., S. Yildiz, R. Mas, K. Dundar, A. Yildirim, A. Korkmaz, C. Akay, N. Kaymakcioglu, T. Ozisik, and D. Sen. 2003. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on oxidative stress in experimental acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Physiological Research 52: 111–116.
Chen, M.F., H.M. Chen, S.W. Ueng, and M.H. Shyr. 1998. Hyperbaric oxygen pretreatment attenuates hepatic reperfusion injury. Liver 18: 110–116.
Edremitlioglu, M., D. Kilic, S. Oter, U. Kisa, A. Korkmaz, O. Coskun, and O. Bedir. 2005. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on the renal functions in septic rats: relation to oxidative damage. Surgery Today 35: 653–661.
Yeh, C.H., Z.C. Chen, C.C. Hsu, M.T. Lin, and C.C. Chen. 2010. Protection in rats with heatstroke: hyperbaric oxygen vs activated protein C therapy. European Journal of Pharmacology 635: 103–108.
Al-Waili, N.S., G.J. Butler, B.Y. Lee, Z. Carrey, and R. Petrillo. 2009. Possible application of hyperbaric oxygen technology in the management of urogenital and renal diseases. Journal of Medical Engineering & Technology 33: 507–515.
Al-Waili, N.S., and G.J. Butler. 2006. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on inflammatory response to wound and trauma: possible mechanism of action. The Scientific World Journal 6: 425–441.
Rinaldi, B., S. Cuzzocrea, M. Donniacuo, A. Capuano, D. Di Palma, F. Imperatore, E. Mazzon, R. Di Paola, L. Sodano, and F. Rossi. 2011. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces the toll-like receptor signaling pathway in multiple organ failures. Intensive Care Medicine 37: 1110–1119.
Jain, K.K. 2004. Drug interactions with hyperbaric oxygen. In Textbook of hyperbaric oxygen, ed. K.K. Jain, 80–82. Cambridge: Hogrefe-Huber Publishers.
Caglikulekci, M., C. Pata, D.D. Apa, M. Dirlik, L. Tamer, F. Yaylak, A. Kanik, and S. Aydin. 2004. The effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on liver and renal tissue inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and tissue lipid peroxidation in obstructive jaundice stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Pharmacological Research 49: 227–238.
Hsu, B.G., R.P. Lee, F.L. Yang, H.J. Harn, and H.I. Chen. 2006. Post-treatment with N-acetylcysteine ameliorates endotoxin shock-induced organ damage in conscious rats. Life Sciences 79: 2010–2016.
Hsu, B.G., F.L. Yang, R.P. Lee, T.C. Peng, H.J. Harn, and H.I. Chen. 2004. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced organ damage in conscious rats. Journal of Biomedical Science 11: 152–162.
Altinel, O., S. Demirbas, E. Cakir, H. Yaman, I.H. Ozerhan, E. Duran, T. Cayci, E.O. Akgul, N. Ersoz, B. Uysal, B. Kurt, M. Yasar, S. Oter, and Y. Peker. 2011. Comparison of hyperbaric oxygen and medical ozone therapies in a rat model of experimental distal colitis. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 71: 185–192.
Yaman, H., E. Cakir, O. Ozcan, Z. Yesilova, A. Ozcan, E.O. Akgul, M.K. Erbil, S. Bagci, C. Bilgi, and K. Dagalp. 2005. Elevated urine neopterin levels in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinical Biochemistry 38: 187–190.
Agilli, M., H. Yaman, T. Cayci, I. Sener, M. Oztosun, I. Aydin, F.N. Aydin, Y.G. Kurt, E. Cakir, and E.O. Akgul. 2012. Comparison of two different HPLC methods and Elisa method for measurement of serum neopterin. Journal of Investigational Biochemistry 1: 43–47.
Yamanel, L., U. Kaldirim, Y. Oztas, O. Coskun, Y. Poyrazoglu, M. Durusu, T. Cayci, A. Ozturk, S. Demirbas, M. Yasar, O. Cinar, S.K. Tuncer, Y.E. Eyi, B. Uysal, T. Topal, S. Oter, and A. Korkmaz. 2011. Ozone therapy and hyperbaric oxygen treatment in lung injury in septic rats. International Journal of Medical Sciences 8: 48–55.
van der Poll, T., and S.J. van Deventer. 1999. Cytokines and anticytokines in the pathogenesis of sepsis. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America 13: 413–426.
Ruokonen, E., L. Ilkka, M. Niskanen, and J. Takala. 2002. Procalcitonin and neopterin as indicators of infection in critically ill patients. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 46: 398–404.
Weisz, G., A. Lavy, Y. Adir, Y. Melamed, D. Rubin, S. Eidelman, and S. Pollack. 1997. Modification of in vivo and in vitro TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-6 secretion by circulating monocytes during hyperbaric oxygen treatment in patients with perianal Crohn’s disease. Journal of Clinical Immunology 17: 154–159.
Nandi, J., B. Saud, J.M. Zinkievich, Z.J. Yang, and R.A. Levine. 2010. TNF-alpha modulates iNOS expression in an experimental rat model of indomethacin-induced jejunoileitis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 336: 17–24.
Lahat, N., H. Bitterman, N. Yaniv, A. Kinarty, and N. Bitterman. 1995. Exposure to hyperbaric oxygen induces tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) secretion from rat macrophages. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 102: 655–659.
Benson, R.M., L.M. Minter, B.A. Osborne, and E.V. Granowitz. 2003. Hyperbaric oxygen inhibits stimulus-induced proinflammatory cytokine synthesis by human blood-derived monocyte-macrophages. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 134: 57–62.
Pan, H.C., C.S. Chin, D.Y. Yang, S.P. Ho, C.J. Chen, S.M. Hwang, M.H. Chang, and F.C. Cheng. 2009. Human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells in combination with hyperbaric oxygen augment peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurochemical Research 34: 1304–1316.
Granowitz, E.V., E.J. Skulsky, R.M. Benson, J. Wright, J.L. Garb, E.R. Cohen, E.C. Smithline, and R.B. Brown. 2002. Exposure to increased pressure or hyperbaric oxygen suppresses interferon-gamma secretion in whole blood cultures of healthy humans. Undersea & Hyperbaric Medicine 29: 216–225.
Choudhury, D., and M. Levi. 2011. Kidney aging—inevitable or preventable? Nature Reviews Nephrology 7: 706–717.
Spapen, H., H. Zhang, C. Demanet, W. Vleminckx, J.L. Vincent, and L. Huyghens. 1998. Does N-acetyl-l-cysteine influence cytokine response during early human septic shock? Chest 113: 1616–1624.
Zafarullah, M., W.Q. Li, J. Sylvester, and M. Ahmad. 2003. Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 60: 6–20.
Luo, J., T. Tsuji, H. Yasuda, Y. Sun, Y. Fujigaki, and A. Hishida. 2008. The molecular mechanisms of the attenuation of cisplatin-induced acute renal failure by N-acetylcysteine in rats. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation 23: 2198–2205.
Mishima, K., A. Baba, M. Matsuo, Y. Itoh, and R. Oishi. 2006. Protective effect of cyclic AMP against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 40: 1564–1577.
Shalby, A.B., N. Assaf, and H.H. Ahmed. 2011. Possible mechanisms for N-acetyl cysteine and taurine in ameliorating acute renal failure induced by cisplatin in rats. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods 21: 538–546.
Abdel-Zaher, A.O., R.H. Abdel-Hady, M.M. Mahmoud, and M.M. Farrag. 2008. The potential protective role of alpha-lipoic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology 243: 261–270.
Abraham, P. 2005. Vitamin C may be beneficial in the prevention of paracetamol-induced renal damage. Clinical and Experimental Nephrology 9: 24–30.
Conflict of Interest.
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cermik, H., Taslipinar, M.Y., Aydin, I. et al. The Relationship Between N-acetylcysteine, Hyperbaric Oxygen, and Inflammation in a Rat Model of Acetaminophen-induced Nephrotoxicity. Inflammation 36, 1145–1152 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9649-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9649-4