Abstract
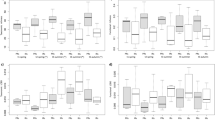
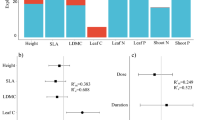
Functional traits of exotic species play an important role in their invasive process by enhancing their performance and promoting them as a potentially malignant invasive species. However, the interrelationship between functional traits and invasion capacity of exotic aquatic species is still not clear. Here, we selected two exotic aquatic species Egeria densa Planch. and Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. and two related native species Hydrilla verticillata (L. f.) Royle and Myriophyllum spicatum L. in China to reveal the potential invasiveness of exotic submerged macrophytes based on functional traits and their effects on sediment bacterial community. Our results showed that there was no significant competition between exotic species and related native species. Many functional traits of related native species H. verticillata performed significantly better than exotic species E. densa beside leaf area. Related native species M. spicatum also had obvious advantages in important functional traits such as relative growth rate and nutrient concentrations. The belowground part of two exotic species had significant effects on sediment bacterial community. Due to developed roots and their radial oxygen loss of exotic species E. densa and M. aquaticum, the diversity of sediment bacterial community positively correlated with exotic species ratio in treatment. Some dominant sediment bacteria, such as Streptomyces, might accelerate the invasion of exotic species through feedback effects. In general, compared with related native species, the competitive ability and functional traits of exotic plants did not show significant invasion ability. However, positive interaction with sediment bacteria and moderate interspecific relationships may promote the invasion of exotic submerged macrophyte species. Our results provide a theoretical basis for risk assessment and effective management of exotic aquatic plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data and materials availability
The data and materials used to support the findings of this study are shared by the requesting author.
References
Arnon, D. I., 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidases in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiology 24: 1–15.
Aschehoug, E. T., R. Brooker, D. Z. Atwater, J. L. Maron & R. M. Callaway, 2016. The mechanisms and consequences of interspecific competition among plants. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 47: 263–281.
Bains, G., A. S. Kumar, T. Rudrappa, E. Alff, T. E. Hanson & H. P. Bais, 2009. Native plant and microbial contributions to a negative plant-plant interaction. Plant Physiology 151: 2145–2151.
Bally, J., M. Nadai, M. Vitel, A. Rolland, R. Dumain & M. Dubald, 2009. Plant physiological adaptations to the massive foreign protein synthesis occurring in recombinant chloroplasts. Plant Physiology 150: 1474–1481.
Barnett, M. J. & R. F. Fisher, 2006. Global gene expression in the rhizobial-legume symbiosis. Symbiosis 42: 1–24.
Bezeng, S. B., J. T. Davies, K. Yessoufou, O. Maurin & M. Van der Bank, 2015. Revisiting Darwin’s naturalization conundrum: explaining invasion success of non-native trees and shrubs in southern Africa. Journal of Ecology 103: 871–879.
Bormann, F. H., 1953. Factors determining the role of loblolly pine and sweetgum in early Old-Field succession in the piedmont of North Carolina. Ecological Monographs 23: 339–358.
Bornette, G. & S. Puijalon, 2009. Macrophytes: ecology of aquatic plants Encyclopedia of Life Sciences. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester.
Boyle, S. A., R. R. Yarwood, P. J. Bottomley & D. D. Myrold, 2008. Bacterial and fungal contributions to soil nitrogen cycling under Douglas fir and red alder at two sites in Oregon. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 40: 443–451.
Brown, D. M., 1953. Conifer transplants to a grassy bald on Roan Mountain. Ecology 34: 614–617.
Callaway, R. M., D. Montesinos, K. Williams & J. L. Maron, 2013. Native congeners provide biotic resistance to invasive Potentilla through soil biota. Ecology 94: 1223–1229.
Callaway, R. M., G. C. Thelen, A. Rodriguez & W. E. Holben, 2004. Soil biota and exotic plant invasion. Nature 427: 731–733.
Caravaca, F., G. Rodriguez-Caballero, M. Campoy, P. M. Sanleandro & A. Roldan, 2020. The invasion of semiarid Mediterranean sites by Nicotiana glauca mediates temporary changes in mycorrhizal associations and a permanent decrease in rhizosphere activity. Plant and Soil 450: 217–229.
Carboni, M., S. W. Livingstone, M. E. Isaac & M. W. Cadotte, 2021. Invasion drives plant diversity loss through competition and ecosystem modification. Journal of Ecology 109: 3587–3601.
Caruso, C. M., H. Maherali & R. A. Martin, 2020. A meta-analysis of natural selection on plant functional traits. International Journal of Plant Sciences 181: 44–55.
Chaintreuil, C., E. Giraud, Y. Prin, J. Lorquin, A. Ba, M. Gillis, P. de Lajudie & B. Dreyfus, 2000. Photosynthetic bradyrhizobia are natural endophytes of the African wild rice Oryza breviligulata. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 66: 5437–5447.
Chen, L., K. Fang, J. Zhou, Z. P. Yang, X. F. Dong, G. H. Dai & H. B. Zhang, 2019. Enrichment of soil rare bacteria in root by an invasive plant Ageratina adenophora. Science of the Total Environment 683: 202–209.
Di Nino, F., G. Thiebaut & S. Muller, 2007. Phenology and phenotypic variation of genetically uniform populations of Elodea nuttallii (Planch.) H. St John at sites of different trophic states. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 168: 335–343.
Diagne, C., B. Leroy, A. C. Vaissiere, R. E. Gozlan, D. Roiz, I. Jaric, J. M. Salles, C. J. A. Bradshaw & F. Courchamp, 2021. High and rising economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Nature 592: 571–576.
Doornbos, R. F., L. C. van Loon & P. Bakker, 2012. Impact of root exudates and plant defense signaling on bacterial communities in the rhizosphere: a review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 32: 227–243.
Drenovsky, R. E., A. Khasanova & J. J. James, 2012. Trait convergence and plasticity among native and invasive species in resource-poor environments. American Journal of Botany 99: 629–639.
Drexler, J. Z., S. Khanna & J. R. Lacy, 2021. Carbon storage and sediment trapping by Egeria densa Planch, a globally invasive, freshwater macrophyte. Science of the Total Environment 755: 142602.
Ebina, J., T. Tsutsui & T. Shirai, 1983. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Water Research 17: 1721–1726.
Edwards, K. F., E. Litchman & C. A. Klausmeier, 2013. Functional traits explain phytoplankton responses to environmental gradients across lakes of the United States. Ecology 94: 1626–1635.
Efthymiou, A., B. Jensen & I. Jakobsen, 2018. The roles of mycorrhiza and Penicillium inoculants in phosphorus uptake by biochar-amended wheat. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 127: 168–177.
Elser, J. J., K. Acharya, M. Kyle, J. Cotner, W. Makino, T. Markow, T. Watts, S. Hobbie, W. Fagan, J. Schade, J. Hood & R. W. Sterner, 2003. Growth rate-stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota. Ecology Letters 6: 936–943.
Emery-Butcher, H. E., S. J. Beatty & B. J. Robson, 2020. The impacts of invasive ecosystem engineers in freshwaters: a review. Freshwater Biology 65: 999–1015.
Evangelista, H. B., T. S. Michelan, L. C. Gomes & S. M. Thomaz, 2017. Shade provided by riparian plants and biotic resistance by macrophytes reduce the establishment of an invasive Poaceae. Journal of Applied Ecology 54: 648–656.
Faust, K. & J. Raes, 2012. Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nature Reviews Microbiology 10: 538–550.
Fleming, J. P. & E. D. Dibble, 2015. Ecological mechanisms of invasion success in aquatic macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 746: 23–37.
Fornah, A., M. Anderson & J. Habiger, 2021. The relationship between rhizobacteria auxin production and wheat biomass productivity is negative. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 52: 985–997.
Fouqueray, M., J. L. Mouget, A. Morant-Manceau & G. Tremblin, 2007. Dynamics of short-term acclimation to UV radiation in marine diatoms. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 89: 1–8.
Fridley, J. D., I. Jo, P. E. Hulme & R. P. Duncan, 2021. A habitat-based assessment of the role of competition in plant invasions. Journal of Ecology 109: 1263–1274.
Fridley, J. D. & D. F. Sax, 2014. The imbalance of nature: revisiting a Darwinian framework for invasion biology. Global Ecology Biogeography 23: 1157–1166.
Fu, H., G. X. Yuan, Q. Lou, T. T. Dai, J. Xu, T. Cao, L. Y. Ni, J. Y. Zhong & S. W. Fang, 2018. Functional traits mediated cascading effects of water depth and light availability on temporal stability of a macrophyte species. Ecological Indicators 89: 168–174.
Funk, J. L. & P. M. Vitousek, 2007. Resource-use efficiency and plant invasion in low-resource systems. Nature 446: 1079–1081.
Gao, G. F., P. F. Li, J. X. Zhong, Z. J. Shen, J. Chen, Y. T. Li, A. Isabwe, X. Y. Zhu, Q. S. Ding, S. Zhang, C. H. Gao & H. L. Zheng, 2019. Spartina alterniflora invasion alters soil bacterial communities and enhances soil N2O emissions by stimulating soil denitrification in mangrove wetland. Science of the Total Environment 653: 231–240.
Getnet, H., D. Kifle & T. Fetahi, 2020. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) affects the composition and abundance of zooplankton in the littoral region of Koka Reservoir, Ethiopia. African Journal of Aquatic Science 45: 486–492.
Gillard, M., G. Thiebaut, N. Rossignol, S. Berardocco & C. Deleu, 2017. Impact of climate warming on carbon metabolism and on morphology of invasive and native aquatic plant species varies between spring and summer. Environmental and Experimental Botany 144: 1–10.
Gonzalez, A. L., J. S. Kominoski, M. Danger, S. Ishida, N. Iwai & A. Rubach, 2010. Can ecological stoichiometry help explain patterns of biological invasions? Oikos 119: 779–790.
Grace, J. B., 1995. On the measurement of plant competition intensity. Ecology 76: 305–308.
Grimshaw, H. J. & B. Sharfstein, 2008. The effects of shading on dioecious, pistillate Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle transplants from Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 173: 101–109.
Guan, B. H., X. Wang, C. Y. Yin, Z. W. Liu, Z. X. Wang & Y. M. Gao, 2018. Comparison of the morphological traits of the submerged macrophyte Potamogeton malaianus from turbid and clear waters in Lake Taihu. Hydrobiologia 813: 63–74.
Hao, B. B., H. P. Wu, Q. Shi, G. H. Liu & W. Xing, 2013. Facilitation and competition among foundation species of submerged macrophytes threatened by severe eutrophication and implications for restoration. Ecological Engineering 60: 76–80.
Hoffmann, M. & U. Raeder, 2016. Predicting the potential distribution of neophytes in Southern Germany using native Najas marina as invasion risk indicator. Environmental Earth Sciences 75: 1217.
Hung, N. T., T. Asaeda & J. Manatunge, 2007. Modeling interactions of submersed plant biomass and environmental factors in a stream using structural equation modeling. Hydrobiologia 583: 183–193.
Hussner, A., 2009. Growth and photosynthesis of four invasive aquatic plant species in Europe. Weed Research 49: 506–515.
Hussner, A., I. Stiers, M. Verhofstad, E. S. Bakker, B. M. C. Grutters, J. Haury, J. van Valkenburg, G. Brundu, J. Newman, J. S. Clayton, L. W. J. Anderson & D. Hofstra, 2017. Management and control methods of invasive alien freshwater aquatic plants: a review. Aquatic Botany 136: 112–137.
Kiers, E. T., M. Duhamel, Y. Beesetty, J. A. Mensah, O. Franken, E. Verbruggen, C. R. Fellbaum, G. A. Kowalchuk, M. M. Hart, A. Bago, T. M. Palmer, S. A. West, P. Vandenkoornhuyse, J. Jansa & H. Bucking, 2011. Reciprocal rewards stabilize cooperation in the mycorrhizal symbiosis. Science 333: 880–882.
Kim, Y. C., J. H. J. Leveau, B. B. M. Gardener, E. A. Pierson, L. S. Pierson & C. M. Ryu, 2011. The multifactorial basis for plant health promotion by plant-associated bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 77: 1548–1555.
Kunstler, G., D. Falster, D. A. Coomes, F. Hui, R. M. Kooyman, D. C. Laughlin, L. Poorter, M. Vanderwel, G. Vieilledent, S. J. Wright, M. Aiba, C. Baraloto, J. Caspersen, J. H. C. Cornelissen, S. Gourlet-Fleury, M. Hanewinkel, B. Herault, J. Kattge, H. Kurokawa, Y. Onoda, J. Penuelas, H. Poorter, M. Uriarte, S. Richardson, P. Ruiz-Benito, I. F. Sun, G. Stahl, N. G. Swenson, J. Thompson, B. Westerlund, C. Wirth, M. A. Zavala, H. C. Zeng, J. K. Zimmerman, N. E. Zimmermann & M. Westoby, 2016. Plant functional traits have globally consistent effects on competition. Nature 529: 204–207.
Kuznetsova, A. I., E. A. Ivanova, O. S. Samylina, F. G. Kurbanova, D. S. Gruzdev, T. A. Kanapatskiy & N. V. Pimenov, 2020. Prokaryotic communities in saline soils of the Lake Elton area in a soil catena along the Khara River. Microbiology 89: 670–684.
Latombe, G., D. M. Richardson, P. Pysek, T. Kucera & C. Hui, 2018. Drivers of species turnover vary with species commonness for native and alien plants with different residence times. Ecology 99: 2763–2775.
Li, J. M., A. M. O. Oduor, F. H. Yu & M. Dong, 2019. A native parasitic plant and soil microorganisms facilitate a native plant co-occurrence with an invasive plant. Ecology and Evolution 9: 8652–8663.
Li, S. P., M. W. Cadotte, S. J. Meiners, Z. S. Hua, H. Y. Shu, J. T. Li & W. S. Shu, 2015a. The effects of phylogenetic relatedness on invasion success and impact: deconstructing Darwin’s naturalisation conundrum. Ecology Letters 18: 1285–1292.
Li, W. H., J. N. Luo, X. S. Tian, W. S. Chow, Z. Y. Sun, T. J. Zhang, S. L. Peng & C. L. Peng, 2015b. A new strategy for controlling invasive weeds: selecting valuable native plants to defeat them. Scientific Reports 5: 11004.
Liu, H., G. H. Liu & W. Xing, 2021. Functional traits of submerged macrophytes in eutrophic shallow lakes affect their ecological functions. Science of the Total Environment 760: 143332.
Liu, H., W. Zhou, X. W. Li, Q. S. Chu, N. Tang, B. Z. Shu, G. H. Liu & W. Xing, 2020. How many submerged macrophyte species are needed to improve water clarity and quality in Yangtze floodplain lakes? Science of the Total Environment 724: 138267.
Lodge, A. G., T. J. S. Whitfeld, A. M. Roth & P. B. Reich, 2018. Invasive plants in Minnesota are “joining the locals”: A trait-based analysis. Journal of Vegetation Science 29: 746–755.
Lv, X. F., B. Ma, J. B. Yu, S. X. Chang, J. M. Xu, Y. Z. Li, G. M. Wang, G. X. Han, G. Bo & X. J. Chu, 2016. Bacterial community structure and function shift along a successional series of tidal flats in the Yellow River Delta. Scientific Reports 6: 36550.
Ma, C., S. P. Li, Z. C. Pu, J. Q. Tan, M. Q. Liu, J. Zhou, H. X. Li & L. Jiang, 2016. Different effects of invader-native phylogenetic relatedness on invasion success and impact: a meta-analysis of Darwin’s naturalization hypothesis. Proceedings of the Royal Society Biological Sciences 283: 1838.
Macauley, J. M., J. R. Clark & W. A. Price, 1988. Seasonal changes in the standing crop and chlorophyll content of Thalassia testudinum Banks ex Knig and its epiphytes in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Aquatic Botany 31: 277–287.
Moorhouse, T. P. & D. W. Macdonald, 2015. Are invasives worse in freshwater than terrestrial ecosystems? Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water 2: 1–8.
Murchie, E. H. & T. Lawson, 2013. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: a guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. Journal of Experimental Botany 64: 3983–3998.
O’Hare, M. T., A. Baattrup-Pedersen, I. Baumgarte, A. Freeman, I. D. M. Gunn, A. N. Lazar, R. Sinclair, A. J. Wade & M. J. Bowes, 2018. Responses of aquatic plants to eutrophication in rivers: A revised conceptual model. Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 451.
Ochs, K., R. P. Rivaes, T. Ferreira & G. Egger, 2018. Flow management to control excessive growth of macrophytes - An assessment based on habitat suitability modeling. Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 356.
Pearson, D. E., Y. K. Ortega, J. Runyon & J. L. Butler, 2018. Secondary invasion re-redefined: The distinction between invader-facilitated and invader-contingent invasions as subclasses of secondary invasion. Ecology and Evolution 8: 5185–5187.
Perez-Harguindeguy, N., S. Diaz, E. Garnier, S. Lavorel, H. Poorter, P. Jaureguiberry, M. S. Bret-Harte, W. K. Cornwell, J. M. Craine, D. E. Gurvich, C. Urcelay, E. J. Veneklaas, P. B. Reich, L. Poorter, I. J. Wright, P. Ray, L. Enrico, J. G. Pausas, A. C. de Vos, N. Buchmann, G. Funes, F. Quetier, J. G. Hodgson, K. Thompson, H. D. Morgan, H. ter Steege, M. G. A. van der Heijden, L. Sack, B. Blonder, P. Poschlod, M. V. Vaieretti, G. Conti, A. C. Staver, S. Aquino & J. H. C. Cornelissen, 2013. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Australian Journal of Botany 61: 167–234.
Perkins, R. G., J. L. Mouget, S. Lefebvre & J. Lavaud, 2006. Light response curve methodology and possible implications in the application of chlorophyll fluorescence to benthic diatoms. Marine Biology 149: 703–712.
Poorter, H., U. Niinemets, N. Ntagkas, A. Siebenkas, M. Maenpaa, S. Matsubara & T. L. Pons, 2019. A meta-analysis of plant responses to light intensity for 70 traits ranging from molecules to whole plant performance. New Phytologist 223: 1073–1105.
Powell, K. I., J. M. Chase & T. M. Knight, 2013. Invasive plants have scale-dependent effects on diversity by altering species-area relationships. Science 339: 316–318.
Pysek, P., V. Jarosik, P. E. Hulme, J. Pergl, M. Hejda, U. Schaffner & M. Vila, 2012. A global assessment of invasive plant impacts on resident species, communities and ecosystems: the interaction of impact measures, invading species’ traits and environment. Global Change Biology 18: 1725–1737.
Qin, T. J., J. Zhou, Y. Sun, H. Muller-Scharer, F. L. Luo, B. C. Dong, H. L. Li & F. H. Yu, 2020. Phylogenetic diversity is a better predictor of wetland community resistance to Alternanthera philoxeroides invasion than species richness. Plant Biology 22: 591–599.
Quan, W. M., H. Zhang, Z. L. Wu, S. F. Jin, F. H. Tang & J. B. Dong, 2016. Does invasion of Spartina alterniflora alter microhabitats and benthic communities of salt marshes in Yangtze River estuary? Ecological Engineering 88: 153–164.
Redekop, P., D. Hofstra & A. Hussner, 2016. Elodea canadensis shows a higher dispersal capacity via fragmentation than Egeria densa and Lagarosiphon major. Aquatic Botany 130: 45–49.
Ribas, L. G. D., C. de Cassia-Silva, D. K. Petsch, M. J. Silveira & M. S. Lima-Ribeiro, 2018. The potential invasiveness of an aquatic macrophyte reflects founder effects from native niche. Biological Invasions 20: 3347–3355.
Riis, T., B. Olesen, J. S. Clayton, C. Lambertini, H. Brix & B. K. Sorrell, 2012. Growth and morphology in relation to temperature and light availability during the establishment of three invasive aquatic plant species. Aquatic Botany 102: 56–64.
Robinson, T. B., N. Martin, T. G. Loureiro, P. Matikinca & M. P. Robertson, 2020. Double trouble: the implications of climate change for biological invasions. NeoBiota. https://doi.org/10.3897/neobiota.62.55729.
Rodriguez-Echeverria, S. & A. Traveset, 2015. Putative linkages between below- and aboveground mutualisms during alien plant invasions. Aob Plants 7: plv1062.
Salvucci, M. E. & G. Bowes, 1981. Induction of reduced photorespiratory activity in submersed and amphibious aquatic macrophytes. Plant Physiology 67: 335–340.
Santos, M. J., E. L. Hestir, S. Khanna & S. L. Ustin, 2012. Image spectroscopy and stable isotopes elucidate functional dissimilarity between native and nonnative plant species in the aquatic environment. New Phytologist 193: 683–695.
Shea, K. & P. Chesson, 2002. Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 17: 170–176.
Sielaff, A. C., R. N. Upton, K. S. Hofmockel, X. Xu, H. W. Polley & B. J. Wilsey, 2018. Microbial community structure and functions differ between native and novel (exotic-dominated) grassland ecosystems in an 8-year experiment. Plant and Soil 432: 359–372.
Simberloff, D., 2006. Invasional meltdown 6 years later: important phenomenon, unfortunate metaphor, or both? Ecology Letters 9: 912–919.
Stanek, M., S. Zubek & A. M. Stefanowicz, 2021. Differences in phenolics produced by invasive Quercus rubra and native plant communities induced changes in soil microbial properties and enzymatic activity. Forest Ecology and Management 482: 118901.
Suding, K. N., W. S. Harpole, T. Fukami, A. Kulmatiski, A. S. MacDougall, C. Stein & W. H. van der Putten, 2013. Consequences of plant-soil feedbacks in invasion. Journal of Ecology 101: 298–308.
Szabo, S., E. Peeters, G. Varbiro, G. Borics & B. A. Lukacs, 2019. Phenotypic plasticity as a clue for invasion success of the submerged aquatic plant Elodea nuttallii. Plant Biology 21: 54–63.
Tan, B., H. He, J. Gu & K. Li, 2018. Eutrophic water or fertile sediment: which is more important for the growth of invasive aquatic macrophyte Myriophyllum aquaticum? Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 2018(419): 3.
Tang, X. J., L. N. Zou, S. M. Su, Y. H. Lu, W. W. Zhai, M. Manzoor, Y. L. Liao, J. Nie, J. Y. Shi, L. Q. Ma & J. M. Xu, 2021. Long-Term manure application changes bacterial communities in rice rhizosphere and arsenic speciation in rice grains. Environmental Science & Technology 55: 1555–1565.
van der Putten, W. H. 2010. Impacts of soil microbial communities on exotic plant invasions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 25: 512–519.
van Kleunen, M., W. Dawson & N. Maurel, 2015. Characteristics of successful alien plants. Molecular Ecology 24: 1954–1968.
van Kleunen, M., W. Dawson, D. Schlaepfer, J. M. Jeschke & M. Fischer, 2010a. Are invaders different? A conceptual framework of comparative approaches for assessing determinants of invasiveness. Ecology Letters 13: 947–958.
van Kleunen, M., E. Weber & M. Fischer, 2010b. A meta-analysis of trait differences between invasive and non-invasive plant species. Ecology Letters 13: 235–245.
Van, T. K., W. T. Haller & G. Bowes, 1976. Comparison of the photosynthetic characteristics of three submersed aquatic plants. Plant Physiology 58: 761–768.
Vila, M., J. L. Espinar, M. Hejda, P. E. Hulme, V. Jarosik, J. L. Maron, J. Pergl, U. Schaffner, Y. Sun & P. Pysek, 2011. Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: a meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology Letters 14: 702–708.
Waller, L. P., W. J. Allen, B. I. P. Barratt, L. M. Condron, F. M. Franca, J. E. Hunt, N. Koele, K. H. Orwin, G. S. Steel, J. M. Tylianakis, S. A. Wakelin & I. A. Dickie, 2020. Biotic interactions drive ecosystem responses to exotic plant invaders. Science 368: 967–972.
Wang, H., Q. Wang, P. A. Bowler & W. Xiong, 2016. Invasive aquatic plants in China. Aquatic Invasions 11: 1–9.
Wang, W. Q., Y. Wang, X. X. Li, Y. Liu & Q. Q. Huang, 2021. Individual growth, competitive ability and stand-level biomass production of invasive Sorghum halepense populations on Hainan island, China. Journal of Plant Ecology 14: 793–804.
Wilkes, M. A., F. Edwards, J. I. Jones, J. F. Murphy, J. England, N. Friberg, D. Hering, N. L. Poff, P. Usseglio-Polatera, W. Verberk, J. Webb & L. E. Brown, 2020. Trait-based ecology at large scales: Assessing functional trait correlations, phylogenetic constraints and spatial variability using open data. Global Change Biology 26: 7255–7267.
Woitke, M., W. Hartung, H. Gimmler & H. Heilmeier, 2004. Chlorophyll fluorescence of submerged and floating leaves of the aquatic resurrection plant Chamaegigas intrepidus. Functional Plant Biology 31: 53–62.
Yang, W., D. Zhang, X. W. Cai, L. Xia, Y. Q. Luo, X. L. Cheng & S. Q. An, 2019. Significant alterations in soil fungal communities along a chronosequence of Spartina alterniflora invasion in a Chinese Yellow Sea coastal wetland. Science of the Total Environment 693: 133548.
You, W. H., D. Yu, D. Xie, L. F. Yu, W. Xiong & C. M. Han, 2014. Responses of the invasive aquatic plant water hyacinth to altered nutrient levels under experimental warming in China. Aquatic Botany 119: 51–56.
You, Y., L. J. Liu, Y. Wang, J. X. Li, Z. N. Ying, Z. L. Hou, H. J. Liu & S. T. Du, 2021. Graphene oxide decreases Cd concentration in rice seedlings but intensifies growth restriction. Journal of Hazardous Materials 417: 125958.
Yu, H. W., N. Shen, X. Guan, S. Q. Yu, D. Yu & C. H. Liu, 2019. Influence of soil nutrient heterogeneity and competition on sprouting and ramets growth of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Clean-Soil Air Water 47: 1800182. .
Zaiko, A., D. Minchin & S. Olenin, 2014. “The day after tomorrow”: anatomy of an ‘r’ strategist aquatic invasion. Aquatic Invasions 9: 145–155.
Zervas, D., V. Tsiaoussi, A. S. Kallimanis, P. Dimopoulos & I. Tsiripidis, 2019. Exploring the relationships between aquatic macrophyte functional traits and anthropogenic pressures in freshwater lakes. Acta Oecologica-International Journal of Ecology 99: 103443.
Zhang, L. M., H. Cheng, D. Pan, Y. R. Wu, R. T. Ji, W. Li, X. Jiang & J. G. Han, 2021a. One-pot pyrolysis of a typical invasive plant into nitrogen-doped biochars for efficient sorption of phthalate esters from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 280: 130712.
Zhang, P., M. Nie, B. Li & J. H. Wu, 2017. The transfer and allocation of newly fixed C by invasive Spartina alterniflora and native Phragmites australis to soil microbiota. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 113: 231–239.
Zhang, X. L., H. W. Yu, H. H. Yu, C. H. Liu, S. F. Fan & D. Yu, 2021b. Highly competitive native aquatic species could suppress the growth of invasive aquatic species with similar traits. Biological Invasions 23: 267–280.
Zhang, Z. J., Y. J. Liu, C. Brunel & M. van Kleunen, 2020. Soil-microorganism-mediated invasional meltdown in plants. Nature Ecology & Evolution 4: 1612–1621.
Zhang, Z. J. & M. van Kleunen, 2019. Common alien plants are more competitive than rare natives but not than common natives. Ecology Letters 22: 1378–1386.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870346, 32170375), Wuhan Application Foundation Frontier Project (2020020601012287) and SAJOREC, CAS (SAJC202102). Hirpa Abduro Ogo was sponsored by CAS “the Belt and Road” Master Fellowship Program and CAS President’s International Fellowship Initiative’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL and QC processed and analyzed the functional traits and sediment bacterial data and were major contributors in writing the manuscript. XL and WX designed the experiment scheme and the structure of the paper and were also the major contributors in writing the manuscript. NT and HAO analyzed the competition index in all the treatments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to participate
All authors consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors carefully revised and improved the article. All authors consent to publish.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling editor: Stefano Amalfitano
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Chu, Q., Tang, N. et al. Functional trait-based potential invasiveness of exotic submerged macrophytes and their effects on sediment bacterial community. Hydrobiologia 849, 3061–3077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-04914-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-04914-9