Abstract
This study aimed to experimentally examine how riverbed drying and different rates of water level reduction influenced the vertical movement of amphipods of various sizes into different subsurface sediment compositions. Using sediment columns (mesocosms) filled with different sized transparent substrates, we explored how varying speeds of drawdown affected vertical movement and stranding of individuals. We hypothesised that: (1) larger individuals would be less able to migrate within subsurface sediments compared to smaller ones; (2) smaller sediment particles would lead to more individuals becoming stranded and; (3) faster rates of water level drawdown would increase the likelihood of individuals becoming stranded above the waterline. Body size significantly influenced the final position of an individual, with smaller individuals accessing deeper sediments more readily. Larger amphipods were more likely to become stranded above the waterline. Amphipods migrated to greater depths during faster water level reduction rates with smaller individuals displaying greater overall movement. Sediment particle size did not influence the ability of amphipods to move vertically into subsurface sediments in response to water level reduction. The results indicate that subsurface sediments may serve as a refuge from surface drying but that both the size of individual invertebrates influences their ability to migrate vertically.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The dewatering of benthic sediments has increased globally due to natural events and anthropogenic activities (e.g., Pyne & Poff, 2016; Stubbington et al., 2017; Datry et al., 2018). Flow decrease and cessation can occur naturally, either seasonally or during drought (Bogan et al., 2017; Aspin et al., 2019), or anthropogenically, associated with river management activities such as hydropeaking for power generation (Richards et al., 2013; Holzapfel et al., 2017; Lange et al., 2019). The loss of surface water can have important effects on the fluxes of organic matter and lead to modified faunal community structure both during and post-drying (e.g., Hill et al., 2018; Pařil et al., 2019). Moreover, the legacies of such events may influence subsequent recolonization and recovery patterns of fauna and flora (Piano et al., 2019). Given the increasing pressures associated with surface and groundwater abstraction and diversion for anthropogenic use (White et al., 2018; Mihalicz et al., 2019), and the predicted increase in the frequency and duration of droughts (Prudhomme et al., 2014; Manning et al., 2019), there is a pressing need to understand how freshwater organisms respond to riverbed drying events.
A key driver of aquatic macroinvertebrate community structure is channel dewatering and drying of benthic sediments (Bogan et al., 2015; Rosset et al., 2017). As drying occurs, waterbodies lose their connectivity with the landscape through the loss of lateral (i.e. riparian zone and floodplain), longitudinal (upstream-downstream) and vertical (surface-subsurface) dimensions (Lake, 2003; Chadd et al., 2017). Channel drying and loss of surface water results in distinct species assemblages (Leigh et al., 2016; Bogan et al., 2017; Mathers et al., 2019a), characterised by fauna exhibiting resistance and resilience traits to surface water drying such as use of atmospheric oxygen (Stanley et al., 1994), desiccation-resistant life stages (Stubbington et al., 2016), or the ability to rapidly recolonize following the rewetting and resumption of favourable conditions (Vander Vorste et al., 2016a; Pařil et al., 2019). Although surface water may not be available, water may persist in subsurface sediments (hyporheic zone) which may provide a potential refuge for macroinvertebrates (Williams & Hynes, 1974; Vadher et al., 2018a). However, the refuge potential may be highly variable depending on water table depth (Vander Vosrte et al., 2016b) and the nature of surface-groundwater exchange (Folegot et al., 2018).
The ability of fauna to access the subsurface habitat reflects both sedimentary characteristics (Gayraud & Philippe, 2003; Vadher et al., 2018b) and faunal traits (Wickson et al., 2012; Loskotová et al., 2019). Sediment characteristics such as pore size, ratio of gravel framework to fine sediment matrix, and particle size and heterogeneity have been highlighted as key abiotic factors affecting the ability of invertebrate fauna to access subsurface sediments (Mathers et al., 2014; 2019b; Vadher et al., 2017; Loskotová et al., 2019). A reduction in sediment pore space due to excessive deposition of fine sediments and clogging may limit the ability of macroinvertebrates to move vertically through interstitial pathways and access subsurface habitats (Navel et al., 2010; Vadher et al., 2015; 2017). These abiotic factors operate in conjunction with faunal traits that may facilitate resistance to drying and dewatering including behavioural adaptations (Lytle et al., 2008), vermiform body morphology (Vadher et al., 2017; Loskotová et al., 2019) and physiological traits (Wickson et al., 2012; Stubbington et al., 2016). Recent research has also demonstrated how the vertical movement of macroinvertebrates may be influenced by their relative body size within sediments of varying heterogeneity (Mathers et al., 2019b). However, current knowledge of the relationship between body size and the ability to access subsurface habitats during dewatering of sediments is limited.
In this study, we experimentally examined how the rate of water level reduction for different sediment grain sizes and an individual’s body size influences organismal vertical movement into subsurface sediments using laboratory mesocosms. We used two amphipod species with comparable morphology to provide a body size continuum (ca. 5–30 mm in size), Gammarus pulex (Linnaeus, 1758) (Amphipoda: Gammaridae) and Dikerogammarus villosus (Sowinsky, 1894) (Amphipoda: Gammaridae), and employed transparent sediments to enable direct observations (sensu Vadher et al., 2017). Specifically, we hypothesised that: (1) larger individuals of both species would be less able to migrate within the subsurface compared to smaller ones; (2) smaller sediment grain sizes and pore space would result in greater potential for individuals to become stranded and; (3) faster water level reduction would enhance the likelihood of organismal stranding above the waterline.
Materials and methods
Experimental set-up
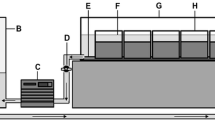
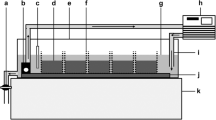
Ten sediment column mesocosms were constructed using transparent acrylic pipes (60 cm × 4.6 cm internal diameter), each filled with 50 cm of transparent sediments (adapted from Vadher et al., 2017; Fig. 1) and filled to a depth of 55 cm with pre-treated tap water (AquaSafe®- Tetra®; OxyTabs®- JBL®, Germany). To control water level reduction accurately (0.5 mm accuracy), sediment columns were sealed at the base using a rubber bung with a 5 mm glass tube (3 mm internal diameter) through the centre to act as a drain (Fig. 1). A silicone tube, secured with a Hoffman clip (Fig. 1), was fitted around the glass drain. Sediment columns were mounted side by side onto a horizontal rack using clamps and black cloth was placed over the columns to provide complete darkness analogous to subsurface streambed sediments.
Cross-section through transparent sediment column mesocosms: (1) Dimensions of a sediment column; (2) Rubber bung; (3) 5 mm diameter glass tube; (4) Hoffman clip to control water drainage. (a) Large sediment treatment (14–20 mm particles); (b) Mixed sediment treatment of 50% large particles (14–20 mm) and 50% small particles (10–15 mm); (c) Small sediment treatment (10–15 mm particles); (i) Start of experiment (50 mm surface water); (ii) After water level reduction (35 cm below sediment surface)
Treatments
Three sediment treatments were employed (large, small and mixed) to cover varying particle and pore sizes (but not pore volume / porosity). The large sediment treatment comprised rounded gravel sized particles of 14–20 mm in diameter with an average interstitial volume of 311 ml (± 1.87 ml—total of 194 particles per column). The small sediment treatment comprised angular particles 10–15 mm in diameter with an average interstitial volume of 303.2 ml (± 1.30 ml—total of 816 particles per column) and the mixed sediment treatment comprised a 50–50% mix of large and small particles creating an interstitial volume of 304.4 ml (± 1.65 ml—total of 408 small particles and 97 large particles). The fine gravel-sized particles used in the study are typical of those recorded in the surface and subsurface substrates of lowland streams in the area where organisms were collected (Mathers & Wood, 2016). Four water level reduction treatments were employed: very slow (3.75 cm/h), slow (7.5 cm/h), fast (15 cm/h) and very fast (30 cm/h). These treatments reflect rapid reductions in water level associated with drying events downstream of small weirs in lowland rivers (Hill et al., 2019), as well the very rapid variability in flow due to hydropeaking reservoir operations (Lange et al., 2019).
Test Amphipods
Two freshwater amphipod species were employed in the study, G. pulex and D. villosus. Both are predominantly benthic organisms and have comparable body morphology but vary in their maximal sizes, with G. pulex reaching up to 21 mm body length (Pinkster, 1970) and D. villosus reaching 30 mm (Rewicz et al., 2014). Both amphipod species typically dominate macroinvertebrate community biomass in temperate European rivers where they occur and display overlapping habitat preferences (McGrath et al., 2007; De Gelder et al., 2016). Individuals of both G. pulex and D. villous have been recorded inhabiting gravel (2–64 mm) and cobble (64–256 mm) substrates (Dahl & Greenberg, 1996; Clinton et al., 2018).
Specimens were collected by gently disturbing benthic sediments and catching individuals downstream in a standard kick net (1 mm mesh, 230 mm × 255 mm frame, 275 mm bag depth) before being placed in 5 l buckets of stream water at least 12 h prior to experimental runs commencing. Specimens were returned to the laboratory, placed in aerated holding tanks containing stream water and allowed to acclimate to water temperatures of 18–20 °C (reflecting the ambient air temperatures when experiments were conducted during May-July in England). A surplus of food was provided in the form of raw carrot and aquarium crayfish food pellets. G. pulex were collected from Burleigh Brook, Loughborough (52°45050.5″N, 1°14028.6″W) and D. villosus from Pitsford Reservoir, Northamptonshire (52° .323629″ N, − 0°.88302501″ W). Juvenile individuals less than 5 mm total body length in size were not used in experimental trials (as determine by allowing juveniles with smaller heads to pass through a 2 mm sieve at the field site).
Experimental procedure
One individual was left to acclimate for 20 min in the pre-prepared sediment column before the start of each experiment (time = 0; sensu Vadher et al., 2015; 2017). Only one individual was used in each column so that vertical distance moved could be accurately recorded throughout the experimental period. Prior to the reduction of water every 20 min, the depth position of each individual relative to the sediment surface was recorded using a small LED light. LED was used to minimise light disturbance during observations and eliminate photophobic behaviour often observed in gammarids (Lagrue et al., 2011). An individual’s depth position from the sediment surface (depth = 0) was recorded to 5 mm accuracy and individuals observed on the sediment surface or in the water column were recorded to have a depth position of 0 mm. Water levels were reduced every 20 min until a 15 cm water refuge was retained (35 cm below the sediment surface; Fig. 1). It should be noted that the duration of water level reduction (time) varied due to the differing water level reduction rates (very slow, 3.75 cm/h; slow, 7.5 cm/h; fast, 15 cm/h; very fast, 30 cm/h), ranging from 10 h 40 min (3.75 cm/h) to 1 h 20 min (30 cm/h). Each experimental trial was replicated 10 times for each of the three sediment mixtures, four water level reduction rates and two amphipod species providing a total n of 240 experiments (G. pulex n =120 and D. villosus n = 120).
Once a 15 cm refuge was retained, the column was left for 24 h (from the start of the experiment) to allow for any individuals stranded above, but close to the water line, to migrate into the water. Individuals above the water line at the end of experiments were classified as stranded organisms. After 24 h, the mesocosms were deconstructed to remove amphipods and sediments washed thoroughly to remove biological waste. Individual amphipods were preserved using 70% industrial methylated spirit (IMS) to enable an individual’s head size to be measured. Head size was employed as a standardised proxy for the body size of individuals (Kokkotis & McLaughlin 2002) as body size may vary depending on body posture even when preserved. Standardized measurements of head size for both G. pulex and D. villosus were taken from the base of the antenna to the posterior margin of the head carapace using a light microscope fitted with a calibrated eye-piece graticule.
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted in R version 3.6.0 (R Development Core Team, 2019). Three metrics were extracted from the experimental data for statistical analysis; final vertical position after 24 h, mean distance moved between each 20 min observation period and stranding of an individual above the waterline at the end of the experimental period. As vertical positions were calculated to a 5 mm accuracy (i.e. 5–10 mm, 10–15 mm), the midpoint was taken and used in subsequent analyses. Preliminary analyses were conducted to confirm that head sizes differed statistically between species. A Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric test confirmed that the head sizes differed statistically between the two species and that D. villosus individuals (mean head size: 1.36 mm ± 0.02 mm, range 0.70–1.98 mm) were significantly larger than G. pulex individuals (mean head size—0.92 mm ± 0.03 mm—range 0.4–1.33 mm) (x2 =105.25, P ≤ 0.001).
To test whether an individual’s final position or the mean distance moved per 20-min observation period differed, a Generalised Linear Model (GLM) was fitted using a Gaussian error distribution and identity link using the glm function in the ‘stats’ package. The model was fitted with the terms water level reduction rate, sediment treatment, head size and all interactions of these factors. To test the likelihood of individuals being stranded above the water line at the end of the 24-hour experiment a binary response characterising stranded and not stranded as “1” or “0” respectively was employed. A GLM was subsequently fitted using a binomial error distribution and logit link and fitted with the terms water level reduction rate, sediment treatment, head size and the interaction of these factors.
Results
Head size was significantly associated with an individual’s final position, with smaller G. pulex individuals accessing deeper sediments more readily (Fig. 2; Table 1). There were no significant effects of sediment treatment, water level reduction rate or the interaction of these factors on the final position recorded (Table 1). Head size and water level reduction rate were significantly associated with the mean distance moved during each 20-min observation period (Table 2; Fig. 3). More amphipods of both species migrated into deeper sediments during the faster water level reduction treatments (very fast and fast) than the slower water level reductions (slow and very slow), and smaller G. pulex individuals displayed greater overall vertical movement (Figs. 3, 4). Larger head sizes were significantly associated with an individual’s likelihood of stranding for both D. villosus (not stranded mean head size 1.18 mm ± 0.03 mm vs stranded mean head size 1.50 mm ± 0.03 mm) and G. pulex (note stranded mean head size 0.91 mm ± 0.02 mm vs stranded mean head size 1.03 mm ± 0.04 mm; Fig. 4). In particular, larger D. villosus individuals became stranded above the water line more readily (Table 3; Fig. 5). Across all experimental trials, 55% of D. villosus and 12.5% of G. pulex individuals became stranded (see Table 4 for a breakdown of stranding by experiment). However, there were no other significant effects of water level reduction rate, sediment treatment or the interaction of factors on the likelihood of individuals stranding.
Mean (± 1 SE) final vertical position (mm) of amphipod individuals within subsurface sediments at the end of experiment (24 h) as a function of water level reduction rate and amphipod species. Note amphipod species are presented to allow visual comparison with G. pulex being smaller than D. villosus
Discussion
Our findings support our first hypothesis that the vertical movement of G. pulex and D. villosus would vary as a function of their relative body size, with larger individuals being less able to move through subsurface sediments compared to smaller individuals. G. pulex and D. villosus have a comparable body morphology but differ in their overall body size, with adult D. villosus being larger than G. pulex (Pinkster, 1970; Rewicz et al., 2014). Our results demonstrate that larger amphipod individuals have a reduced ability to access and move through subsurface sediments. In agreement with previous studies (Gayraud & Philippe, 2001; Loskotová et al., 2019; Mathers et al., 2019b), these results indicate that body size is a key factor influencing an individual’s ability to access subsurface sediment. Furthermore, we found clear evidence that larger individuals of both amphipod species were more susceptible to stranding during water level reduction, whereas smaller individuals readily accessed deeper subsurface sediments. We hypothesise that individuals smaller than interstitial pore size openings may be able to move more freely through the sediment, whereas individuals of a similar size or larger than the sediment pore size are more likely to become stranded during water level reduction (Vadher et al., 2017; Loskotová et al., 2019); although direct measurement of pore size openings would be required to verify this.
The experimental results did not support our second hypothesis that vertical movement of amphipods would vary as a function of sediment size, given that the migration of amphipods through the three sediment treatments followed comparable trends. This finding may reflect the open sediment framework and relatively large number of interstitial spaces available for all sediment treatments (i.e. total pore volume was comparable among the three treatments). Previous studies have shown that in the presence of increased fine sediment deposition (< 2 mm in size), macroinvertebrates are less able to access and move through subsurface sediments (e.g. Bo et al., 2007; Vadher et al., 2015; Korbel et al, 2019; Mathers et al., 2019b). The absence of interstitial fine sediment in our experiments suggests that maintaining an open framework will facilitate the downward migration to subsurface sediments during drying for macroinvertebrates with similar or smaller body sizes to that of the interstitial openings.
Our findings partially support the third hypothesis that the vertical movement of amphipods would vary as a function of the rate of water level reduction. In fact, the rate of water level reduction influenced the speed and ability of amphipod individuals to migrate vertically but did not influence the final vertical position or likelihood of being stranded above the waterline. G. pulex displayed greater movement in all water level reduction treatments compared to D. villosus which probably reflects average differences in body size and therefore the ability to freely move within interstitial spaces of saturated sediments. Vertical migration into deeper interstitial sediments by G. pulex and D. villosus in response to faster water level reduction rates indicates the ability of amphipods to respond to rapid water level reductions and to actively migrate vertically into the subsurface sediment to avoid surface drying and stranding; although the movement of other faunal groups, such as Gastropoda, may be highly variable (e.g. Poznańska et al., 2015a; 2015b). The use of transparent sediments in laboratory mesocosms has facilitated the direct observation of the vertical migration of organisms of varying sizes in subsurface sediments in response to water level drawdown and drying (Stumpp & Hose, 2013; Vadher et al., 2017; 2018). This study confirms that larger individual macroinvertebrates were more likely to become stranded than smaller individuals, even in a relatively open subsurface framework, and supports the inferred responses to drying proposed in previous field studies (e.g. Fenoglio et al., 2006; Pařil et al., 2019).
Drying events, whether seasonal (Pinna et al., 2016; Bogan et al., 2017), supra-seasonal (Bogan et al., 2015; Hill et al., 2019) or anthropogenically driven such as dynamic fluctuations during hydropeaking events (Lange et al., 2019; Mihalicz et al., 2019), typically leads to shifts in macroinvertebrate community compositions. The findings of this study provide further evidence that subsurface sediments can act as a refuge during drying events if taxa are not limited by body size and if an open sediment framework exists (i.e. free of fine sediment particles). The ability of macroinvertebrates to access the subsurface habitat when sediment is comprised of more heterogeneous particles or where enhanced sedimentation occurs has been shown to be greatly reduced (Vadher et al., 2015, 2018b). It is widely recognised that disturbance/bioturbation activities of small bodied vermiform (long and thin) invertebrates within benthic and subsurface sediments help maintain open subsurface pore spaces and pathways that in turn can facilitate biogeochemical processing of nutrients and potential pollutants (e.g., Nogaro et al., 2006; Mermillod-Blondin, 2011). There is also growing evidence that larger macrofauna, including amphipod shrimps, can maintain subsurface sediment pathways, pore spaces and hydraulic properties within the subsurface sediments (Hose & Stump, 2019). Future laboratory and field-based research should consider the interactions between channel drying, benthic and subsurface sedimentary characteristics (e.g., grain size distribution, porosity and fine sediment content) and the faunal communities present in aquatic ecosystems subject to regular or irregular drying. This is essential to help predict and manage the effects of anthropogenically enhanced drying and determine the ability of ecosystems to recover following such events. Our findings also demonstrate the value of mesocosm and laboratory-based experiments in answering broader ecological questions. Future research should therefore use a combination of laboratory mesocosm approaches to validate field observations to facilitate a greater understanding of macroinvertebrate responses to drying.
References
Aspin, T. W. H., K. Khamis, T. J. Matthews, A. M. Milner, M. J. O’Callaghan, M. Trimmer, G. Woodward & M. E. Ledger, 2019. Extreme drought pushes stream invertebrate communities over functional thresholds. Global Change Biology 25: 230–244.
Bo, T., S. Fenoglio, G. Malacarne, M. Pessino & F. Sgariboldi, 2007. Effects of clogging on stream macroinvertebrates: an experimental approach. Limnologica 37: 186–192.
Bogan, M. T., K. S. Boersma & D. A. Lytle, 2015. Resistance and resilience of invertebrate communities to seasonal and supraseasonal drought in arid-land headwater streams. Freshwater Science 60: 2547–2558.
Bogan, M. T., J. L. Hwan, K. Cervantes-Yoshida, J. Ponce & S. M. Carlson, 2017. Aquatic invertebrate communities exhibit both resistance and resilience to seasonal drying in an intermittent coastal stream. Hydrobiologia 799: 123–133.
Chadd, R. P., J. A. England, D. Constable, M. J. Dunbar, C. A. Extence, D. J. Leeming, J. A. Murray-Bligh & P. J. Wood, 2017. An index to track the ecological effects of drought development and recovery on riverine invertebrate communities. Ecological Indicators 82: 344–356.
Clinton, K. E., K. L. Mathers, D. Constable, C. Gerrard & P. J. Wood, 2018. Substrate preferences of coexisting invasive amphipods, Dikerogammarus villosus and Dikerogammarus haemobaphes, under field and laboratory conditions. Biological Invasions 20: 2187–2196.
Dahl, J. & L. Greenberg, 1996. Effects of habitat structure on habitat use by Gammarus pulex in artificial streams. Freshwater Biology 36: 487–495.
Datry, T., A. J. Boulton, N. Bonada, K. Fritz, C. Leigh, E. Sauquet, K. Tockner, B. Hugueny & C. N. Dahm, 2018. Flow intermittence and ecosystem services in rivers of the Anthropocene. Journal of Applied Ecology 55: 353–364.
De Gelder, S., G. van der Velde, D. Platvoet, N. Leung, M. Dorenbosch, H. W. M. Hendriks & R. S. E. W. Leuven, 2016. Competition for shelter sites: testing a possible mechanism for gammarid species displacements. Basic Applied Ecology 17: 455–462.
Fenoglio, S., T. Bo & G. Bosi, 2006. Deep interstitial habitat as a refuge for Agabus paludosus (Fabricus) (Coleoptera: Dytiscidae) during summer droughts. The Coleopterists Bulletin 60: 37–41.
Folegot, S., S. Krause, R. Mons, D. M. Hannah & T. Datry, 2018. Mesocosm experiments reveal the direction of groundwater-surface water exchange alters the hyporheic refuge capacity under warming scenarios. Freshwater Biology 63: 165–177.
Gayraud, S. & M. Philippe, 2001. Does subsurface interstitial space influence general features and morphological traits of the benthic macroinvertebrate community in streams? Archiv für Hydrobiologie 151: 667–686.
Gayraud, S. & M. Philippe, 2003. Influence of bed-sediment features on the interstitial habitat available for macroinvertebrates in 15 French streams. Hydrobiologia 88: 77–93.
Hill, M. J. & V. S. Milner, 2018. Ponding in intermittent streams: A refuge for lotic taxa and a habitat for newly colonising taxa. Science of the Total Environment 628: 1308–1316.
Hill, M. J., K. L. Mathers, S. Little, T. Worrall, J. Gunn & P. J. Wood, 2019. Ecological effects of a supra-seasonal drought on macroinvertebrate communities differ between near-perennial and ephemeral river reaches. Aquatic Sciences 81: 62.
Holzapfel, P., P. Leitner, H. Habersack, W. Graf & C. Hauer, 2017. Evaluation of hydropeaking impacts on the food web in alpine streams based on modelling of fish- and macroinvertebrate habitats. Science of the Total Environment 575: 1489–1502.
Hose, G. C. & C. Stumpp, 2019. Architects of the underworld: bioturbation by groundwater invertebrates influences aquifer hydraulic properties. Aquatic sciences 81: 20.
Kokkotis, A. T. & J. D. McLaughlin, 2002. Instar-specific head and body lengths of Hyalella (Amphipoda): criteria for starting and endpoints in experimental studies. Hydrobiologia 474: 223–227.
Korbel, K. L., S. Stephenson & G. C. Hose, 2019. Sediment size influences habitat selection and use by groundwater macrofauna and meiofauna. Aquatic Sciences 81: 39.
Lagrue, C., N. Kaldonski, S. Motreuil, T. Lefèvre, O. Blatter, P. Giraud & L. Bollache, 2011. Interspecific differences in drift behaviour between the native Gammarus pulex and the exotic Gammarus roeseli and possible implications for the invader’s success. Biological Invasions 13: 1409–1421.
Lake, P. S., 2003. Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshwater Biology 48: 1161–1172.
Lange, K., B. Wehrli, U. Åberg, N. Bätz, J. Brodersen, M. Fischer & C. Weber, 2019. Small hydropower goes unchecked. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 17: 256–258.
Leigh, C., N. Bonada, A. J. Boulton, B. Hugueny, S. T. Larned, R. Vander Vorste & T. Datry, 2016. Invertebrate assemblage responses and the dual roles of resistance and resilience to drying in intermittent rivers. Aquatic Sciences 78: 291–301.
Loskotová, B., M. Straka & P. Pařil, 2019. Sediment characteristics influence benthic macroinvertebrate vertical migrations and survival under experimental water loss conditions. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 193: 39–49.
Lytle, D. A., J. D. Olden & L. E. McMullen, 2008. Drought escape behaviours of aquatic insects may be adaptations to highly variable flow regimes characteristic of desert rivers. The Southwestern Naturalist 53: 399–402.
Manning, C., M. Widmann, E. Bevacqua, A. F. Van Loon, D. Maraun & M. Vrac, 2019. Increased probability of compound long-duration dry and hot events in Europe during summer (1950–2013). Environmental Research Letters 14: 094006.
Mathers, K. L. & P. J. Wood, 2016. Fine sediment deposition and interstitial flow effects on macroinvertebrate community composition within riffle heads and tails. Hydrobiologia 776: 147–160.
Mathers, K. L., J. Millett, A. L. Robertson, R. Stubbington & P. J. Wood, 2014. Faunal response to benthic and hyporheic sedimentation varies with direction of vertical hydrological exchange. Freshwater Biology 59: 2278–2289.
Mathers, K. L., R. Stubbington, D. Leeming, C. Westwood & J. England, 2019a. Structural and functional responses of macroinvertebrate assemblages to long-term flow variability at perennial and nonperennial sites. Ecohydrology 12: e2112.
Mathers, K. L., M. J. Hill, C. D. Wood & P. J. Wood, 2019b. The role of fine sediment characteristics and body size on the vertical movement of a freshwater amphipod. Freshwater Biology 64: 152–163.
McGrath, K. E., E. T. H. M. Peeters, J. A. J. Beijer & M. Scheffer, 2007. Habitat-mediated cannibalism and microhabitat restriction in the stream invertebrate Gammarus pulex. Hydrobiologia 589: 155–164.
Mermillod-Blondin, F., 2011. The functional significance of bioturbation and biodeposition on biogeochemical processes at the water–sediment interface in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 30: 770–778.
Mihalicz, J. E., T. D. Jardine, H. M. Baulch & I. D. Phillips, 2019. Seasonal effects of a hydropeaking dam on a downstream benthic macroinvertebrate community. River Research and Applications 35: 714–724.
Navel, S., F. Mermillod-Blondin, B. Montuelle, E. Chauvet, L. Simon, C. Piscart & P. Marmonier, 2010. Interactions between fauna and sediment control the breakdown of plant matter in river sediments. Freshwater Biology 55: 753–766.
Nogaro, G., F. Mermillod-Blondin, F. François-Carcaillet, J. P. Gaudet, M. Lafont & J. Gibert, 2006. Invertebrate bioturbation can reduce the clogging of sediment: an experimental study using infiltration sediment columns. Freshwater Biology 51: 1458–1473.
Pařil, P., C. Leigh, M. Polášek, R. Sarremejane, P. Řezníková, A. Dostálová & R. Stubbington, 2019. Short-term streambed drying events alter amphipod population structure in a central European stream. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 193: 51–64.
Piano, E., A. Doretto, E. Falasco, S. Fenoglio, L. Gruppuso, D. Nizzoli, P. Viaroli & F. Bona, 2019. If Alpine streams run dry: the drought memory of benthic communities. Aquatic Sciences 81: 32.
Pinkster, S., 1970. Redescription of Gammarus pulex (Linnaeus, 1758) based on neotype material (Amphipoda). Crustaceana 18: 177–186.
Pinna, M., G. Marini, G. Cristiano, L. Mazzotta, P. Vignini, B. Cicolani & A. Di Sabatino, 2016. Influence of aperiodic summer droughts on leaf litter breakdown and macroinvertebrate assemblages: testing the drying memory in a Central Apennines River (Aterno River, Italy). Hydrobiologia 782: 111–126.
Poznańska, M., D. Goleniewska, T. Gulanicz, T. Kakareko, Ł. Jermacz & J. Kobak, 2015a. Effect of substratum drying on the survival and migrations of a freshwater pulmonate snail Planorbarius corneus (Linnaeus, 1758). Hydrobiologia 747: 177–188.
Poznańska, M., T. Kakareko, T. Gulanicz, Ł. Jermacz & J. Kobak, 2015b. Life on the edge: survival and behavioural responses of freshwater gill-breathing snails to declining water level andsubstratum drying. Freshwater Biology 60: 2379–2391.
Prudhomme, C., I. Giuntoli, E. L. Robinson, D. B. Clark, N. W. Arnell, R. Dankers, B. M. Fekete, W. Franssen, D. Gerten, S. N. Gosling, S. Hagemann, D. M. Hannah, H. Kim, Y. Masaki, Y. Satoh, T. Stacke, Y. Wada & D. Wisser, 2014. Hydrological droughts in the 21st century, hotspots and uncertainties from a global multimodel ensemble experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111: 3262–3267.
Pyne, M. I. & N. L. Poff, 2016. Vulnerability of stream community composition and function to projected thermal warming and hydrologic change across ecoregions in the western United States. Global Change Biology 23: 77–93.
R Development Core Team. 2019. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rewicz, T., M. Grabowski, C. MacNeil & K. Bącela-Spychalska, 2014. The profile of a ‘perfect’ invader – the case of killer shrimp, Dikerogammarus villosus. Aquatic Invasions 9: 267–288.
Richards, R. R., K. K. Gates & B. L. Kerans, 2013. Effects of simulated rapid water level fluctuations (hydropeaking) on survival of sensitive benthic species. River Research and Applications 30: 954–963.
Rosset, V., A. Ruhi, M. T. Bogan & T. Datry, 2017. Do lentic and lotic communities respond similarly to drying? Ecosphere 8: e01809.
Stanley, E. H., D. L. Buschman, A. J. Boulton, N. B. Grimm & S. G. Fisher, 1994. Invertebrate resistance and resilience to intermittency in a desert stream. The American Midland Naturalist 131: 288–300.
Stubbington, R., J. Gunn, S. Little, T. P. Worrall & P. J. Wood, 2016. Macroinvertebrate seedbank composition in relation to antecedent duration of drying and multiple wet-dry cycles in a temporary stream. Freshwater Biology 61: 1293–1307.
Stubbington, R., J. England, P. J. Wood & C. E. Sefton, 2017. Temporary streams in temperate zones: recognizing, monitoring and restoring transitional aquatic-terrestrial ecosystems. WIREs Water 4: e1223.
Stumpp, C. & G. C. Hose, 2013. The impact of water table drawdown and drying on subterranean aquatic fauna in in-vitro experiments. PLoS one: 8 (11).
Vadher, A. N., R. Stubbington & P. J. Wood, 2015. Fine sediment reduces vertical migrations of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea: Amphipoda) in response to surface water loss. Hydrobiologia 753: 61–71.
Vadher, A. N., C. Leigh, J. Millett, R. Stubbington & P. J. Wood, 2017. Vertical movements through subsurface stream sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates during experimental drying are influenced by sediment characteristics and species traits. Freshwater Biology 62: 1730–1740.
Vadher, A. N., J. Millett, R. Stubbington & P. J. Wood, 2018a. Drying duration and stream characteristics influence macroinvertebrate survivorship within the sediments of a temporary channel and exposed gravel bars of a connected perennial stream. Hydrobiologia 814: 121–132.
Vadher, A. N., J. Millett & P. J. Wood, 2018b. Direct observations on the effect of fine sediment deposition on the vertical movement of Gammarus pulex (Amphipoda: Gammaridae) during substratum drying. Hydrobiologia 815: 73–82.
Vander Vorste, R., F. Malard & T. Datry, 2016a. Is drift the primary process promoting the resilience of river invertebrate communities? A manipulative field experiment in an intermittent alluvial river. Freshwater Biology 61: 1276–1292.
Vander Vorste, R., F. Mermillod-Blondin, F. Hervant, R. Mons, M. Forcellini & T. Datry, 2016b. Increased depth to the water table during river drying decreases the resilience of Gammarus pulex and alters ecosystem function), and to the direction of groundwater-surface water exchange. Ecohydrology 9: 1177–1186.
White, J. C., A. House, N. Punchard, D. M. Hannah, N. A. Wilding & P. J. Wood, 2018. Macroinvertebrate community responses to hydrological controls of groundwater abstraction effects across intermittent and perennial headwater streams. Science of the Total Environment 610: 1514–1526.
Wickson, S., E. T. Chester & B. J. Robson, 2012. Aestivation provides flexible mechanisms for survival of stream drying in a larval trichopteran (Leptoceridae). Marine and Freshwater Research 63: 821–826.
Williams, D. D. & H. B. N. Hynes, 1974. The occurrence of benthos in the substratum of a stream. Freshwater Biology 4: 233–256.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the support of the site rangers at Pitsford Reservoir and in particular, Chris Gerrard and Angela Tarry at Anglian Water for granting access to the site to collect specimens. Charlie Patel would like to acknowledge the support of Richard Harland and Dr. Rebecca McKenzie in providing technical support to undertake the experiments. The authors gratefully acknowledged the helpful and constructive comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript of three anonymous reviewers and the associate editor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: María del Mar Sánchez-Montoya.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, C., Vadher, A.N., Mathers, K.L. et al. Body size affects the vertical movement of benthic amphipods through subsurface sediments in response to drying. Hydrobiologia 848, 1015–1025 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04500-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04500-x