Abstract
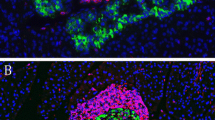
During type 1 diabetes, most beta cells die by immune processes. However, the precise fate and characteristics of beta cells and islet autoimmunity after onset are unclear. Here, the extent of beta cell survival was determined in the non-obese diabetic (NOD) mouse during increasing duration of disease and correlated with insulitis. Pancreata from female NOD mice at diagnosis and at 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks thereafter were analysed immunohistochemically for insulin, glucagon and somatostatin cells and glucose transporter-2 (glut2) and correlated with the degree of insulitis and islet immune cell phenotypes. Insulitis, although variable, persisted after diabetes and declined with increasing duration of disease. During this period, beta cells also declined sharply whereas glucagon and somatostatin cells increased, with occasional islet cells co-expressing insulin and glucagon. Glut2 was absent in insulin-containing cells from 1 week onwards. CD4 and CD8 T cells and macrophages persisted until 4 weeks, in islets with residual beta cells or extensive insulitis. We conclude that after diabetes onset, some beta cells survive for extended periods, with continuing autoimmunity and expansion of glucagon and somatostatin cells. The absence of glut2 in several insulin-positive cells suggests that some beta cells may be unresponsive to glucose.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assan R, Feutren G, Sirmai J, Laborie C, Boitard C, Vexiau P, Rostu HD, Rodier M, Figoni M, Vague P, Hors J, Bach J-F (1990) Plasma C-peptide levels and clinical remissions in recent-onset type 1 diabetic patients treated with cyclosporine A and insulin. Diabetes 39:768–774
Bonner-Weir S (2000) Islet growth and development in the adult. J Mol Endocrinol 24:297–302
Bottazzo GF, Dean BM, McNally JM, McKay EH, Swift PGF, Gamble DR (1985) In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. New Engl J Med 313:353–360
Charlton B, Bacelj A, Slattery RM, Mandel TE (1989) Cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD/WEHI mice: evidence for suppression in spontaneous autoimmune diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 38:441–447
Eisenbarth GS, Connelly J, Soeldner JS (1987) The “natural” history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev 3:873–891
Foulis AK, Stewart JA (1984) The pancreas in recent-onset Type 1(insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: insulin content of islets, insulitis and associated changes in the exocrine acinar tissue. Diabetologia 26:456–461
Foulis AK, Liddle CN, Farquharson MA, Richmond JA, Weir RS (1986) The histopathology of the pancreas in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: a 25-year review of deaths in patients under 20 years of age in the United Kingdom. Diabetologia 29:267–274
Foulis AK, McGill M, Farquharson MA (1991) Insulitis in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in man- macrophages, lymphocytes and interferon-γ containing cells. J Pathol 165:97–103
Gepts W (1965) Pathological anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 14:619–633
Gepts W, De Mey J (1978) Islet cell survival determined by morphology. An immunocytochemical study of the islets of Langerhans in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 27(Suppl 1):251–261
Hashimoto T, Kawano H, Daikoku S, Shima K, Taniguchi H, Baba S (1988) Transient co-appearance of glucagon and insulin in the progenitor cells of the rat pancreatic islets. Anat Embryol 178:489–497
Kano Y, Kanatsuna T, Nakamura N, Kitagawa Y, Mori H, Kajiyama S, Nakano K, Kondo M (1986) Defect of the first-phase insulin secretion to glucose stimulation in the perfused pancreas of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. Diabetes 35:486–490
Li Z, Karlsson FA, Sandler S (2000) Islet loss and alpha cell expansion in type 1 diabetes induced by multiple low-dose streptozotocin administration in mice. J Endocrinol 165:93–99
Lohr M, Kloppel G (1987) Residual insulin positivity and pancreatic atrophy in relation to duration of chronic Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus and microangiopathy. Diabetologia 30:757–762
Meier JJ, Bhushan A, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Butler PC (2005) Sustained beta cell apoptosis in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes: indirect evidence for islet regeneration? Diabetologia 48:2221–2228
O’Reilley LA, Gu D, Sarvetnick N, Edlund H, Phillips JM, Fulford T, Cooke A (1997) α-Cell neogenesis in an animal model of IDDM. Diabetes 46:599–606
Palmer JP, Fleming GA, Greenbaum CJ, Herold KC, Jansa LD, Kolb H, Lachin JM, Polonsky KS, Pozzilli P, Skyler JS, Steffes MW (2004) C-Peptide is the appropriate outcome measure for type 1 diabetes clinical trials to preserve β-cell function: Report of an ADA Workshop, 21–22 October 2001. Diabetes 53:250–264
Reddy S, Bibby NJ, Elliott RB (1988) Ontogeny of islet cell antibodies, insulin autoantibodies and insulitis in the non-obese diabetic mouse. Diabetologia 31:322–328
Reddy S, Wu D, Swinney C, Elliott RB (1995) Immunohistochemical analyses of pancreatic macrophages and CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets prior to and following diabetes in the NOD mouse. Pancreas 11:16–25
Reddy S, Young M, Poole CA, Ross JM (1998) Loss of glucose transporter-2 precedes insulin loss in the non-obese diabetic and the low-dose streptozotocin mouse models: a comparative immunohistochemical study by light and confocal microscopy. Gen Comp Endocrinol 111:9–19
Reddy S, Yip S, Karanam M, Poole CA, Ross JM (1999) An immunohistochemical study of macrophage influx and the co-localization of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the pancreas of non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice during disease acceleration with cyclophosphamide. Histochem J 31:303–314
Reddy S, Bradley J, Ginn S, Pathipati P, Ross JM (2003) Immunohistochemical study of caspase-3-expressing cells within the pancreas of non-obese diabetic mice during cyclophosphamide-accelerated diabetes. Histochem Cell Biol 119:451–461
Reddy S, Pathipathi P, Bai Y, Robinson E, Ross JM (2005) Histopathological changes in insulin, glucagon and somatostatin cells in the islets of NOD mice during cyclophosphamide-accelerated diabetes: a combined immunohistochemical and histochemical study. J Mol Histology 36:289–300
Thorens B (1992) Molecular and cellular physiology of GLUT-2, a high-Km facilitated diffusion glucose transporter. Int Rev Cytol 137A:209–238
Somoza N, Vargas F, Roura-Mir C, Vives-Pi M, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Ariza A, Gomis R, Bragado R, Marti M, Jaraquemada D, Pujol-Burel R (1994) Pancreas in recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Changes in HLA, adhesion molecules and autoantigens, restricted T cell receptor Vβ usage, and cytokine profile. J Immunol 153:1360–1377
Stefan Y, Orci L, Malaisse-Lagae F, Perrelet A, Patel A, Unger RH (1982) Quantitation of endocrine cell content in the pancreas of non-diabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes 31:694–700
Rahier J, Goebbels RM, Henquin JC (1983) Cellular composition of the human diabetic pancreas. Diabetologia 24:366–371
Suarez-Pinzon WL, Yan Y, Power R, Brand SJ, Rabinovitch A (2005) Combination therapy with epidermal growth factor and gastrin increases β-cell mass and reverses hyperglycaemia in diabetic NOD mice. Diabetes 54:2596–2601
Uno S, Imagagwa A, Okita K, Sayama K, Moriwaki M, Iwahashi J, Yamaga K, Tamura S, Matsuzawa Y, Hanafusa T, Miyagawa J, Shimomura I (2007) Macrophages and dendritic cells infiltrating islets with or without beta cells produce tumour necrosis factor-α in patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 50:596–601
Acknowledgements
We thank Beryl Davy and Lorraine Rolston for expert histological support and Jacqueline Ross for valuable advice on image preparation and Vernon Tintinger for assistance with the careful maintenance of the NOD mouse colony. Financial assistance from the Child Health Research Foundation, the Maurice & Phyllis Paykel Trust, University of Auckland School of Biological Sciences Summer Studentship Programme and the Auckland Medical Research Foundation is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, S., Chai, R., Rodrigues, J.A. et al. Presence of residual beta cells and co-existing islet autoimmunity in the NOD mouse during longstanding diabetes: a combined histochemical and immunohistochemical study. J Mol Hist 39, 25–36 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-007-9122-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-007-9122-5