Abstract
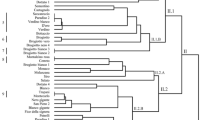
Fig (Ficus carica L.) tree is cultivated worldwide and is highly appreciated for its fruit, which is consumed fresh or dried, having high nutritional and pharmaceutical value and for these reasons there is an increasing interest for its cultivation. In the present study, an ex situ collection of 60 fig accessions (41 indigenous Greek and 19 from other Mediterranean countries) was established and its diversity was analyzed using eight simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci. Greek fig genotypes showed relatively low allelic variation (the average number of SSR alleles per locus was 3.75), an excess of heterozygosity (mean He = 0.489 and Ho = 0.557), and extensive outbreeding (mean F index − 0.151). Cluster analysis showed that the established fig population exhibited weak genetic structure, with most of the genetic variation (89%) being present within individual members of the clusters. Both cluster and principal coordinate analysis confirmed that there is little correlation between genetic makeup and geographical origin of the fig accessions. Polymorphism information content with an average of 0.421 was reasonably informative. An identification key scheme for fig cultivars that will be useful in cultivar discrimination and intellectual property protection was developed. This work will contribute to a sustainable fig production regionally and worldwide, through the establishment and conservation of a reference fig collection, providing germplasm for future breeding efforts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtak H, Oukabli A, Ater M, Santoni S, Khadari B (2009) Microsatellite markers as reliable tools for fig cultivar identification. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 134:624–631
Amos WJ, Hoffman I, Frodsham A, Zhang L, Best S, Hill AV (2007) Automated binning of microsatellite alleles: problems and solutions. Mol Ecol Notes 7:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01560.x
Aradhya MK, Stover ED, Velasco D, Koehmstedt A (2010) Genetic structure and differentiation in cultivated fig (Ficus carica L.). Genetica 138:681–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9442-3
Boudchicha RH, Hormaza JI, Benbouza H (2018) Diversity analysis and genetic relationships among local Algerian fig cultivars (Ficus carica L.) using SSR markers. S Afr J Bot 116:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2018.03.015
Caliskan O, Polat AA, Celikkol P, Bakir M (2012) Molecular characterization of autochthonous Turkish fig accessions. Span J Agric Res 10:130–140. https://doi.org/10.5424/sjar/2012101-094-11
Chapuis M-P, Estoup A (2007) Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Μol Biol Evol 24:621–631. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl191
Chatti K, Baraket G, Ben Abdelkrim A, Saddoud O, Mars M, Trifi M, Salhi Hannachi AC (2010) Development of molecular tools for characterization and genetic diversity analysis in Tunisian fig (Ficus carica) cultivars. Biochem Genet 48:789–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-010-9360-1
Condit IJ (1955) Fig varieties: a monograph. Hilgardia 23:323–538
Ergül A, Büyük BP, Hazrati N, Yılmaz F, Kazan K, Arslan N, Özmen CY, Aydin SS, Bakir M, Tan N, Kösoğlu I, Çobanoğlu F (2021) Genetic characterisation and population structure analysis of Anatolian figs (Ficus carica L.) by SSR markers. Folia Hortic 33:49–78. https://doi.org/10.2478/fhort-2021-0005
Ewen KR, Bahlo M, Treloar SA, Levinson DF, Mowry B, Barlow JW, Foote SJ (2000) Identification and analysis of error types in high-throughput genotyping. Am J Hum Genet 67:727–736. https://doi.org/10.1086/303048
Flaishman Μ, Radov V, Stover ED (2008) The fig: botany, horticulture, and breeding. In: Jules J (ed) Horticultural reviews, vol 34. John Wiley & Sons Ed., Inc., New Jersey, pp 113–1967
Ganopoulos I, Xanthopoulou A, Molassiotis A, Karagiannis E, Mousiadis T, Katsaris P, Aravanopoulos F, Tsaftaris A, Kalivas A, Madesis P (2015) Mediterranean basin Ficus carica L.: from genetic diversity and structure to authentication of a protected designation of origin cultivar using microsatellite markers. Trees 29:1959–1971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1276-2
Ghosh S, Karanjawala ZE, Hauser ER, Ally D, Knapp JI, Rayaman JB, Musick A, Tannenbaum J, Te C, Shapiro S, Eldridge W, Musick T, Martin C, Smith JR, Carpten JD, Brownstein MJ, Powell JI, Whiten R, Chines P, Nylund SJ, Magnuson VL, Boehnke M, Collins FS (1997) Methods for precise sizing, automated binning of alleles, and reduction of error rates in large-scale genotyping using fluorescently labeled dinucleotide markers. FUSION (Finland–US Investigation of NIDDM Genetics) Study Group. Genome Res 7:165–178. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.7.2.165
Giraldo E, Viruel MA, Lopez-Corrales M, Hormaza JI (2005) Characterisation and cross-species transferability of microsatellites in the common fig tree (Ficus carica L.). J Horticult Sci Biotechnol 80:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2005.11511920
Giraldo E, Lopez-Corrales M, Hormaza JI (2008) Optimization of the management of an ex-situ germplasm bank in common fig with SSRs. J Am Soc Horticult Sci 133:69–77. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.133.1.69
Gupta PK, Varshney RK (2000) The development and use of microsatellite markers for genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica 113:163–185. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003910819967
Hoffman JI, Amos W (2005) Microsatellite genotyping errors: detection approaches, common sources and consequences for paternal exclusion. Mol Ecol 14:599–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02419.x
Ikegami H, Nogata H, Hirashima K, Awamura M, Nakahara T (2009) Analysis of genetic diversity among European and Asian Fig varieties (Ficus carica L.) using ISSR, RAPD and SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-008-9355-5
Jombart T, Devillard S, Balloux F (2010) Discriminant analysis of principal components: a new method for the analysis of genetically structured populations. BMC Genet 11:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-11-94
Khadari B, Hochu I, Santoni S, Kjellberg F (2001) Identification and characterization of microsatellite loci in the common fig (Ficus carica L.) and representative species of the genus Ficus. Mol Ecol Notes 1:191–193. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8278.2001.00072.x
Khadari B, Hochu I, Bouzid L, Roger JP, Kjellberg F (2003) The use of microsatellite markers for identification and genetic diversity evaluation of the fig collection in CBNMP. Acta Horticult 605:77–86. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2003.605.10
Klekowski EJ (1988) Genetic load and its causes in long-lived plants. Trees 2:195–203
Lachance J (2016) Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium and random mating. In: Encyclopedia of evolutionary biology, pp. 208–211. ISBN 978-0-12-800426-5
Mondini L, Noorani A, Pagnotta MA (2009) Assessing plant genetic diversity by molecular tool. Diversity 1:19–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/d1010019
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Nagy S, Poczai P, Cernak I, Gorji AM, Hegedus G, Taller J (2012) PICcalc: An online program to calculate polymorphic information content for molecular genetic studies. Biochem Genet 50:670–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-012-9509-1
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1086/282771
Ntanos EK, Roussos PA, Sklavounos A, Voloudakis A, Assimakoroulou A (2015) Phenotypic characteristics of various fig genotypes. In: 27th conference of the Greek Society for horticultural science. Volos
Papadopoulou K, Ehaliotis C, Tourna M, Kastanis P, Karydis I, Zervakis G (2002) Genetic relatedness among dioecious Ficus carica L. cultivars by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis, and evaluation of agronomic and morphological characters. Genetica 114:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015126319534
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155.x
Perez-Jiminez M, Lopez B, Dorado G, Pujadas-Salva A, Guzman G, Hernandez P (2012) Analysis of genetic diversity of southern Spain fig tree (Ficus carica L.) and reference materials as a tool for breeding and conservation. Hereditas 149:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2012.02154.x
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin Software. http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6:847–859. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1707
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rodolfi M, Ganino T, Chiancone B, Petrucelli R (2018) Identification and characterization of Italian common figs (Ficus carica) using nuclear microsatellite markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 65:1337–1348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-018-0617-6
Roy S, Tyagi A, Shukla V, Kumar A, Singh UM, Chaudhary LB, Datt B, Bag SK, Singh PK, Nair NK, Husain NT, Tuli R (2010) Universal plant DNA barcode loci may not work in complex groups: a case study with Indian Berberis species. PLoS ONE 5:e13674. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013674
Saddoud O, Chatti K, Salhi-Hannachi A, Mars M, Rhouma A, Marrakchim M, Trifi M (2007) Genetic diversity of Tunisian figs (Ficus carica L.) as revealed by nuclear microsatellites. Hereditas 144:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2007.0018-0661.01967.x
Stover Ε, Aradhya Μ, Ferguson L, Crisosto CH (2007) The fig: overview of an ancient fruit. HortScience 42:1083–1087
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tessier C, David J, This P, Boursiquot JM, Charrier A (1999) Optimization of the choice of molecular markers for varietal identification in Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 98:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051054
UPOV/INF/17/1, 2010. Guidelines for DNA-profiling: molecular marker selection and database construction (“BMT guidelines”)
Van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) Μicro-checker: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol Ecol Notes 4:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00684.x
Vavilov NI (1951) The origin, variation, immunity and breeding of cultivated plants. The Ronald Press Company, NY
Vinson JA, Zubik L, Bose P, Samman N, Proch J (2005) Dried fruits: excellent in vitro and in vivo antioxidants. J Am Coll Nutr 24:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2005.10719442
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Mike Roose for critically reviewing of the manuscript.
Funding
We would like to thank the Department of Crop Sciences of the Agricultural University of Athens, Greece, and the Department of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences of the University of Milano, Italy for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10722_2022_1509_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Figure S1: Electrophoresis of PCR products for some of the fig accession per microsatellite. Accession numbers are shown on top. Electrophoreses were done in 12% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels. M: DNA ladder (50 bp GeneRuler, Thomas Scientific, USA). M+: DNA ladder as in M with the addition of a known size SSR PCR product. SSR: A known size SSR PCR product. (DOCX 201 KB)
10722_2022_1509_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Figure S2: Dendrogram showing genetic relationship of 60 Fig accessions per country of origin based on SSR data. The dendrogram constructed in MEGA11 with WNJ using the Nei’s genetic distance calculated by GenAlex. (PDF 17 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sclavounos, A., Roussos, P., Milla, S. et al. Genetic diversity of fig (Ficus carica L.) germplasm from the Mediterranean basin as revealed by SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 70, 1395–1406 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01509-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-022-01509-0