Abstract
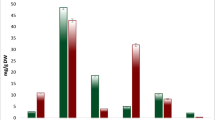
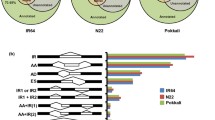
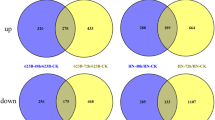
Salinity is one of the well-known abiotic stresses resulting in loss of wheat yield. The identification of differentially induced genes and then becoming aware of their function in salt-stressed wheat is imperative to enhance salinity resistance. To determine salt-responsive genes, we evaluated the transcriptome derived from control and stressed wheat by cDNA-AFLP procedure. A total of 31 transcript-derived fragments (TDFs) were sequenced with success. Most of the genes recognized herein, via BLASTX search of TDFs versus GenBank database, belonged to several functional groups such as transport, protein degradation, transcription regulation, signal transduction, cell defense, energy, and metabolism. Real-time PCR revealed that four TDFs were down-regulated and 18 were up-regulated of 22 TDFs. The HAK, CBL3, serine/threonine PK, cysteine proteinase, LTP, glutamine synthetase, PCAP, DNA glycosylase, PEPC, sulfate permease, and FRA2 genes were specified responsible for salinity stress tolerance. Further research on the new salt-responsive TDFs identified in our experiment can present useful information helping the improvement of wheat tolerance to a high level of salt in the field. These findings altogether improved our understanding of cellular mechanisms involved in wheat response to soil salinization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akladious SA, Mohamed HI (2018) Ameliorative effects of calcium nitrate and humic acid on the growth, yield component and biochemical attribute of pepper (Capsicum annuum) plants grown under salt stress. Sci Horticult 236:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.03.047
Berri S, Abbruscato P, Odile FR, Brasileiro ACM, Fumasoni I, Satoh K, Kikuchi S, Mizzi L, Morandini P, Pè ME, Piffanelli P (2009) Characterization of WRKY co-regulatory networks in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 9:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-9-120
Botha AM, Kunert KJ, Cullis CA (2017) Cysteine proteases and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under drought: A still greatly unexplored association. Plant Cell Environ 4:1679–1690. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12998
Chen H, Melis A (2004) Localization and function of SulP, a nuclear-encoded chloroplast sulfate permease in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta 220:198–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1331-5
Chen H, Chu P, Zhou Y, Li Y, Liu J, Ding Y, Tsang EWT, Jiang L, Wu Ke, Huang S (2012) Overexpression of AtOGG1, a DNA glycosylase/AP lyase, enhances seed longevity and abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 63:4107–4121. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers093
Cushman JC, Bohnert HJ (2000) Genomic approaches to plant stress tolerance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800876-8.00001-1
FAO (2015) World wheat, corn and rice. Oklahoma State University, FAO Statistics, Oklahoma
Feria AB, Bosch N, Sánchez A, Nieto-Ingelmo AI, de la Osa C et al (2016) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) and PEPC-kinase (PEPC-k) isoenzymes in Arabidopsis thaliana: role in control and abiotic stress conditions. Planta 244:901–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2556-9
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh003
Ghonaim MM, Mohamed HI, Omran AAA (2020) Evaluation of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) salt stress tolerance using physiological parameters and retrotransposon-based markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00981-w
Goudarzi M, Pakniyat H (2008) Evaluation of wheat cultivars under salinity stress based on some agronomic and physiological traits. J Agric Soc Sci 4:35–38
He H, Yajing N, Huawen C, Xingjiao T, Xinli X, Weilun Y, Silan D (2012) cDNA-AFLP analysis of salt-inducible genes expression in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under salt treatment. J Plant Physiol 169:410–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.09.013
Huang YP, Huang YW, Chen IH, Shenkwen LL, Hsu YH, Tsai CH (2017) Plasma membrane-associated cation-binding protein 1-like protein negatively regulates intercellular movement of BaMV. J Exp Bot 68:4765–4774. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx307
Jayaraman A, Puranik S, Rai NK, Vidapu S, Sahu PP, Lata C, Prasad M (2008) cDNA-AFLP analysis reveals differential gene expression in response to salt stress in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). Mol Biotechnol 40:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-008-9081-4
Kang H, Zhanga M, Zhou S, Guo Q, Chen F, Wu J, Wang W (2016) Overexpression of wheat ubiquitin gene, Ta-Ub2, improves abiotic stress tolerance of Brachypodium distachyon. Plant Sci 248:102–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.04.015
Kim DY, Hong MJ, Jang JH, Seo YW (2012) cDNA-AFLP analysis reveals differential gene expression in response to salt stress in Brachypodium distachyon. Genes Genomics 34:475–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-012-0067-z
Kumánovics A, Chen OS, Li L, Bagley D, Adkins EM, Lin H, Dingra NN et al (2008) Identification of FRA1 and FRA2 as genes involved in regulating the yeast iron regulon in response to decreased mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster synthesis. J Biol Chem 283:10276–10286. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M801160200
Liu L, Huang FL, Luo QX, Pang HY, Meng FJ (2012) cDNA- AFLP analysis of the response of tetraploid black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) to salt stress. Afr J Biotechnol 11:3116–3124. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3358
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆C T method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Melloul M, Iraqi D, Alaoui ME, Erba G, Alaoui S, Ibriz M, Elfahime E (2014) Identification of differentially expressed genes by cDNA-AFLP technique in response to drought stress in Triticum durum. Food Technol Biotechnol 52:479–488. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.52.04.14.3701
Mian AA, Senadheera P, Maathuis FJM (2009) Improving crop salt tolerance: anion and cation transporters as genetic engineering targets. Plant Stress 5:64–72
Munns R, James RA, Läuchli A (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J Exp Bot 5:1025–1043. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj100
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Reijans M, Lascaris R, Groeneger AO, Wittenberg A, Wesselink E, van Oeveren J et al (2003) Quantitative comparison of cDNA-AFLP, microarrays, and GeneChip expression data in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genomics 82:606–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0888-7543(03)00179-4
Roy SJ, Negrao S, Tester M (2014) Salt resistant crop plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 26:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.12.004
Sabzehzari M, Hoveidamanesh S, Modarresi M, Mohammadi V (2019) Morphological, anatomical, physiological, and cytological studies in diploid and tetraploid plants of Plantago Psyllium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 139:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01670-y
Sabzehzari M, Naghavi MR (2019a) Phyto-miRNAs-based regulation of metabolites biosynthesis in medicinal plants. Gene 682:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.049
Sabzehzari M, Naghavi MR (2019) Phyto-miRNA: a molecule with beneficial abilities for plant biotechnology. Gene 683:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.054
Sabzehzari M, Naghavi MR, Bozari M, Orafai H, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A (2020) Pharmacological and therapeutic aspects of plants from the genus Ferula: a comprehensive review. Mini Rev Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557520666200505125618
Sabzehzari M, Zeinali M, Naghavi MR (2020) Alternative sources and metabolic engineering of Taxol: advances and future perspectives. Biotechnol Adv 43:107569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107569
Sabzehzari M, Zeinali M, Naghavi MR (2020) CRISPR-based metabolic editing: next-generation metabolic engineering in plants. Gene 759:144993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144993
Sabzehzari M, Hoveidamanesh S, Modarresi M, Mohammadi V (2020d) Morphological, anatomical, physiological, and cytological studies in diploid and tetraploid plants of Ispaghul (Plantago ovata Forsk.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 67:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-019-00846-x
Safi H, Saibi W, Alaoui MM, Hmyene A, Masmoudi K, Hanin M, Brini F (2015) A wheat lipid transfer protein (TdLTP4) promotes tolerance to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 89:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.02.008
Sahin O, Karlik E, Meric S, Ari S, Gozukirmizi N (2020) Genome organization changes in GM and non-GM soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] under salinity stress by retro-transposition events. Genet Resour Crop Evol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00928-1
Šamajova O, Plihal O, Al-Yousif M, Hirt H, Šamaj J (2013) Improvement of stress tolerance in plants by genetic manipulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. Biotechnol Adv 31:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.12.002
Santos C, Pereira A, Pereira S, Teixeira J (2004) Regulation of glutamine synthetase expression in sunflower cells exposed to salt and osmotic stress. Sci Hortic 103:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2004.04.010
Tang R, Liu H, Yang Y, Yang L, Gao XS, Garcia VJ, Luan S, Zhang HX (2012) Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 22:1650–1665. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.161
Wang L, Zhou B, Wu L, Guo B, Jiang T (2011) Differentially expressed genes in Populus simonii × Populus nigra in response to NaCl stress using cDNA-AFLP. Plant Sci 180:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.02.001
Zhang X, Liu S, Takano T (2008) Two cysteine proteinase inhibitors from Arabidopsis thaliana, AtCYSa and AtCYSb, increasing the salt, drought, oxidation and cold tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 68:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9357-x
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Mohammad Sabzehzari, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran for providing the writing support to publish this research work.
Funding
This work was supported by Ahvaz Branch, Islamic Azad University, Ahvaz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamyab, S., Alami-Saeid, K., Eslahi, M. et al. cDNA-AFLP technique discloses differential gene expression in response to salinity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 68, 2299–2311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01098-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01098-w