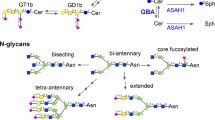
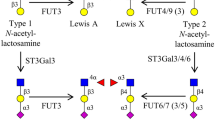
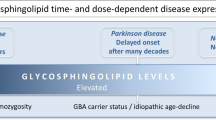
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects over 10 million aging people worldwide. This condition is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta region of the substantia nigra (SNpc) and by aggregation of proteins, commonly α-synuclein (SNCA). The formation of Lewy bodies that encapsulate aggregated proteins in lipid vesicles is a hallmark of PD. Glycosylation of proteins and neuroinflammation are involved in the pathogenesis. SNCA has many posttranslational modifications and interacts with components of membranes that affect aggregation. The large membrane lipid dolichol accumulates in the brain upon age and has a significant effect on membrane structure. The replacement of dopamine and dopaminergic neurons are at the forefront of therapeutic development. This review examines the role of membrane lipids, glycolipids, glycoproteins and dopamine in the aggregation of SNCA and development of PD. We discuss the SNCA-dopamine-neuromelanin-dolichol axis and the role of membranes in neuronal stem cells that could be a regenerative therapy for PD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gai, W.P., Yuan, H.X., Li, X.Q., Power, J.T., Blumbergs, P.C., Jensen, P.H.: In situ and in vitro study of colocalization and segregation of alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin, and lipids in Lewy bodies. Exp Neurol. 166(2), 324–333 (2000)
Stefanis, L.: α-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2(2), a009399 (2012)
Dehay, B., Bourdenx, M., Gorry, P., Przedborski, S., Vila, M., Hunot, S., et al.: Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 14(8), 855–866 (2015)
Videira, P.A.Q., Castro-Caldas, M.: Linking Glycation and Glycosylation With Inflammation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 12, 381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00381
Li, J., Uversky, V.N., Fink, A.L.: Conformational behavior of human alpha-synuclein is modulated by familial Parkinson’s disease point mutations A30P and A53T. Neurotoxicology 23(4–5), 553–567 (2002)
Ulrih, N.P., Barry, C.H., Fink, A.L.: Impact of Tyr to Ala mutations on alpha-synuclein fibrillation and structural properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1782, 581–585 (2008)
Dettmer, U., Newman, A.J., von Saucken, V.E., Bartels, T., Selkoe, D.: J. KTKEGV repeat motifs are key mediators of normal α-synuclein tetramerization: their mutation causes excess monomers and neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112, 9596–9601 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1505953112
Nuytemans, K., Theuns, J., Cruts, M.V., Broeckhoven, C.: Genetic etiology of Parkinson disease associated with mutations in the SNCA, PARK2, PINK1, PARK7, and LRRK2 genes: A mutation update. Hum Mutat. 31, 763–780 (2010)
Alcalay, R.N., Levy, O.A., Waters, C.C., Fahn, S., Ford, B., Kuo, S.H., et al.: Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson’s disease with and without GBA mutations. Brain 138(Pt 9), 2648–2658 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv179
Do, J., McKinney, C., Sharma, P., Sidransky, E.: Glucocerebrosidase and its relevance to Parkinson disease. Mol Neurodegener. 14(1), 36 (2019)
Yap, T.L., Gruschus, J.M., Velayati, A., Westbroek, W., Goldin, E., Moaven, N., et al.: Alpha-synuclein interacts with Glucocerebrosidase providing a molecular link between Parkinson and Gaucher diseases. J Biol Chem. 286(32), 28080–28088 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.237859
López, G.H., Ilincheta de Boschero, M.G., Castagnet, P.I., Giusto, N.M.: Age-associated changes in the content and fatty acid composition of brain glycerophospholipids. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem. 112, 331–343 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(95)00079-8
Ledesma, M.D., Martin, M.G., Dotti, C.G.: Lipid changes in the aged brain: effect on synaptic function and neuronal survival. Prog Lipid Res. 51, 23–35 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2011.11.004
Andersson, M., Appelkvist, E.L., Kristensson, K., Dallner, G.: Distribution of Dolichol and Dolichyl Phosphate in Human Brain. J Neurochem. 49, 685–691 (1987)
Lai, C.S., Schutzbach, J.S.: Localization of Dolichols in Phospholipid Membranes. An ESR Spin Label Study. FEBS Lett 203, 153–156 (1986)
Schutzbach, J.S., Jensen, J.W., Lai, C.S., Monti, J.A.: Membrane Structure and Mannosyltransferase Activities: The Effect of Dolichols on Membranes. Chem. Scr. 27, 109–118 (1987)
Ward, W.C., Guan, Z., Zucca, F.A., et al.: Identification and quantification of dolichol and dolichoic acid in neuromelanin from substantia nigra of the human brain. J Lipid Res. 48(7), 1457–1462 (2007)
Engelen, M., Vanna, R., Bellei, C., et al.: Neuromelanins of human brain have soluble and insoluble components with dolichols attached to the melanic structure. PLoS One. 7(11), e48490 (2012)
Ono, K.: The Oligomer Hypothesis in α-Synucleinopathy. Neurochem Res. 42(12), 3362–3371 (2017)
Ugalde, C.L., Lawson, V.A., Finkelstein, D.I., Hill, A.F.: The role of lipids in α-synuclein misfolding and neurotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 294(23), 9016–9028 (2019)
Singleton, A.B., Farrer, M., Johnson, J., Singleton, A., Hague, S., Kachergus, J., et al.: α-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302, 841 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1090278
Oliveira, L.M., Falomir-Lockhart, L.J., Botelho, M.G., Lin, K.H., Wales, P., Koch, J.C., et al.: Elevated α-synuclein caused by SNCA gene triplication impairs neuronal differentiation and maturation in Parkinson’s patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 6(11), e1994 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.318
Sandal, M., Valle, F., Tessari, I., Mammi, S., Bergantino, E., Musiani, F., et al.: Conformational equilibria in monomeric alpha-synuclein at the single-molecule level. PLoS Biol. 6(1), e6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060006
Galvagnion, C., Topgaard, D., Makasewicz, K., Buell, A.K., Linse, S., Sparr, E., Dobson, C.M.: Lipid Dynamics and Phase Transition within α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils. J Phys Chem Lett. 10(24), 7872–7877 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b03005
α-Synuclein membrane interactions and lipid specificity: Jo, E., McLaurin, J. A., Yip, C. M., St. George-Hyslop, P. Fraser, P. E. J Biol Chem. 275, 34328–34334 (2000)
Lee, H.J., Choi, C., Lee, S.J.: Membrane-bound alpha-synuclein has a high aggregation propensity and The ability to seed the aggregation of the cytosolic form. J Biol Chem. 277(1), 671–678 (2002)
Wu, G., Lu, Z.H., Kulkarni, N., Ledeen, R.W.: Deficiency of ganglioside GM1 correlates with Parkinson’s disease in mice and humans. J Neurosci Res. 90(10), 1997–2008 (2012)
Kubo, S.I.: Membrane lipids as therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease: a possible link between Lewy pathology and membrane lipids. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20(11), 1301–1310 (2016)
Galvagnion, C.: The Role of Lipids Interacting with α-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 7(3), 433–450 (2017)
Hartl, F.U.: Protein Misfolding Diseases. Annu Rev Biochem. 86, 21–26 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044518
Brummel, B.E., Braun, A.R., Sachs, J.N.: Polyunsaturated chains in asymmetric lipids disorder raft mixtures and preferentially associate with α-Synuclein. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1859(4), 529–536 (2017)
Banks, W.A.: Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier. BMC Neurol. 9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S3 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-9-S1-S3
Parmar, M.: Towards stem cell based therapies for Parkinson's disease. Development. 145(1), dev156117 (2018).
Reddy, A.P., Ravichandran, J., Carkaci-Salli, N.: Neural regeneration therapies for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease-related disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1866(4), 165506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.020
Falkenburger, B.H., Saridaki, T., Dinter, E.: Cellular models for Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 139 Suppl 1, 121–130 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13618
Lotharius, J., Falsig, J., van Beek, J., Payne, S., Dringen, R., Brundin, P., Leist, M.: Progressive degeneration of human mesencephalic neuron-derived cells triggered by dopamine-dependent oxidative stress is dependent on the mixed-lineage kinase pathway. J Neurosci. 25(27), 6329–6342 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1746-05.2005
Wu, G., Lu, Z.H., Seo, J.H., Alselehdar, S.K., DeFrees, S., Ledeen, R.W.: Mice deficient in GM1 manifest both motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease; successful treatment with synthetic GM1 ganglioside. Exp Neurol. 329, 113284 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113284
Mesa-Herrera, F., Taoro-González, L., Valdés-Baizabal, C., Diaz, M., Marín, R.: Lipid and Lipid Raft Alteration in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Window for the Development of New Biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 20(15), 3810 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153810
Fabelo, N., Martín, V., Santpere, G., Marín, R., Torrent, L., Ferrer, I., Díaz, M.: Severe alterations in lipid composition of frontal cortex lipid rafts from Parkinson’s disease and incidental Parkinson’s disease. Mol Med. 17(9–10), 1107–1118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2011.00119
Powers, R., Lei, S., Anandhan, A., Marshall, D.D., Worley, B., Cerny, R.L., et al.: Metabolic Investigations of the Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Metabolites 7(2), 22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020022
Viana, S.D., Valero, J., Rodrigues-Santos, P., Couceiro, P., Silva, A.M., Carvalho, F., et al.: Regulation of striatal astrocytic receptor for advanced glycation end-products variants in an early stage of experimental Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 138(4), 598–609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13682
Padmaraju, V., Bhaskar, J.J., Prasada Rao, U.J., Salimath, P.V., Rao, K.S.: Role of advanced glycation on aggregation and DNA binding properties of alpha-synuclein. J Alzheimers Dis. 24(Suppl 2), 211–221 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-101965
Russell, A.C., Šimurina, M., Garcia, M.T., Novokmet, M., Wang, Y., Rudan, I., et al.: The N-glycosylation of immunoglobulin G as a novel biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Glycobiology 27(5), 501–510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwx022
Le Grand, J.N., Gonzalez-Cano, L., Pavlou, M.A., Schwamborn, J.C.: Neural stem cells in Parkinson’s disease: a role for neurogenesis defects in onset and progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72(4), 773–797 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1774-1
Alza, N.P., Iglesias González, P.A., Conde, M.A., Uranga, R.M., Salvador, G.A.: Lipids at the Crossroad of α-Synuclein Function and Dysfunction: Biological and Pathological Implications. Front Cell Neurosci. 13, 175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00175
Giasson, B.I., Duda, J.E., Quinn, S.M., Zhang, B., Trojanowski, J.Q., Lee, V.M.: Neuronal alpha-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human alpha-synuclein. Neuron 34(4), 521–533 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00682-7
Jankovic, J., Tan, E.K.: Parkinson’s disease: etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 91(8), 795–808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-322338
Bendor, J., Logan, T., Edward, R.H.: The Function of α-Synuclein. Neuro 79(6), 1044–1066 (2013)
Caputi, V., Giron, M.C.: Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis and Toll-Like Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 19(6), 1689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061689
Liddle, R.A.: Parkinson’s disease from the gut. Brain Res. 1693(Pt B), 201–206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.01.010
Elfil, M., Kamel, S., Kandil, M., Koo, B.B., Schaefer, S.M.: Implications of the Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease Mov Disord. 35(6), 921–933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28004
Herath, M., Hosie, S., Bornstein, J.C., Franks, A.E., Hill-Yardin, E.L.: The Role of the Gastrointestinal Mucus System in Intestinal Homeostasis: Implications for Neurological Disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10, 248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00248
Fusco, G., Sanz-Hernandez, M., De Simone, A.: Order and disorder in the physiological membrane binding of α-synuclein. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 48, 49–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2017.09.004
Badawy, M.M.S., Okada, T., Kajimoto, T., Hirase, M., Matovelo, S., Nakamura, S., et al.: Extracellular α-Synuclein Drives Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Subtype 1 out of Lipid Rafts, Leading to Impaired Inhibitory G-Protein Signaling. J Biol Chem. 293, 8208–8216 (2018)
Rasheed, M., Liang, J., Wang, C., Deng, Y., Chen, Z.: Epigenetic Regulation of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 22(9), 4956 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094956
MacMahon Copas, A.N., McComish, S.F., Fletcher, J.M., Caldwell, M.A.: The Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease: A Complex Interplay Between Astrocytes, Microglia, and T Lymphocytes? Front Neurol. 12, 666737 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.666737
Ma, J., Gao, J., Wang, J., Xie, A.: Prion-Like Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 13, 552 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00552
Cohlberg, J.A., Li, J., Uversky, V.N., Fink, A.L.: Heparin and other glycosaminoglycans stimulate the formation of amyloid fibrils from alpha-synuclein in vitro. Biochemistry 41(5), 1502–1511 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/bi011711s
Desplats, P., Lee, H.-J., Bae, E.-J., Patrick, C., Rockenstein, E., Crews, L., et al.: Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 13010–13015 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903691106
Liu, I.H., Uversky, V.N., Munishkina, L.A., Fink, A.L., Halfter, W., Cole, G.J.: Agrin binds alpha-synuclein and modulates alpha-synuclein fibrillation. Glycobiology 15(12), 1320–1331 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwj014
Surmeier, D.J.: Determinants of dopaminergic neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 285(19), 3657–3668 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14607
Wong, Y.C., Luk, K., Purtell, K., Burke Nanni, S., Stoessl, A.J., Trudeau, L.E., et al.: Neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease: Should the focus be on axons and synaptic terminals? Mov Disord. 34(10), 1406–1422 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27823
Karpowicz, R.J., Jr., Trojanowski, J.Q., Lee, V.M.: Transmission of α-synuclein seeds in neurodegenerative disease: recent developments. Lab Invest. 99(7), 971–981 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-019-0195-z
Weber, A.N., Morse, M.A., Gay, N.J.: Four N-linked glycosylation sites in human toll-like receptor 2 cooperate to direct efficient biosynthesis and secretion. J Biol Chem. 279(33), 34589–34594 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M403830200
Hughes, C.D., Choi, M.L., Ryten, M., Hopkins, L., Drews, A., Botía, J.A., et al.: Picomolar concentrations of oligomeric alpha-synuclein sensitizes TLR4 to play an initiating role in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 137(1), 103–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1907-y
Amith, S.R., Jayanth, P., Franchuk, S., Finlay, T., Seyrantepe, V., Beyaert, R., Pshezhetsky, A.V., Szewczuk, M.R.: Neu1 desialylation of sialyl alpha-2,3-linked beta-galactosyl residues of TOLL-like receptor 4 is essential for receptor activation and cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 22(2), 314–324 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.038
Voutilainen, M.H., Arumäe, U., Airavaara, M., Saarma, M.: Therapeutic potential of the endoplasmic reticulum located and secreted CDNF/MANF family of neurotrophic factors in Parkinson's disease. FEBS Lett. 589(24 Pt A), 3739–3748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.09.031
Perez, R.G., Waymire, J.C., Lin, E., Liu, J.J., Guo, F., Zigmond, M.J.: A role for alpha-synuclein in the regulation of dopamine biosynthesis. J Neurosci. 22(8), 3090–3099 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-08-03090.2002
Venda, L.L., Cragg, S.J., Buchman, V.L., Wade-Martins, R.: α-Synuclein and dopamine at the crossroads of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 33(12), 559–568 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.09.004
Butler, B., Sambo, D., Khoshbouei, H.: Alpha-synuclein modulates dopamine neurotransmission. J Chem Neuroanat. 83–84, 41–49 (2017)
Itäaho, K., Court, M.H., Uutela, P., Kostiainen, R., Radominska-Pandya, A., Finel, M.: Dopamine is a low-affinity and high-specificity substrate for the human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A10. Drug Metab Dispos. 37(4), 768–775 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.108.025692
Piras, S., Furfaro, A.L., Domenicotti, C., Traverso, N., Marinari, U.M., Pronzato, M.A., Nitti, M.: RAGE Expression and ROS Generation in Neurons: Differentiation versus Damage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016, 9348651 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9348651
Segura-Aguilar, J., Paris, I., Muñoz, P., Ferrari, E., Zecca, L., Zucca, F.A.: Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 129(6), 898–915 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12686
Man, W.K., Tahirbegi, B., Vrettas, M.D. et al. The docking of synaptic vesicles on the presynaptic membrane induced by α-synuclein is modulated by lipid composition. Nat Commun 12, 927 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21027-4
Fountaine, T.M., Venda, L.L., Warrick, N., Christian, H.C., Brundin, P., Channon, K.M., Wade-Martins, R.: The effect of alpha-synuclein knockdown on MPP+ toxicity in models of human neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 28(12), 2459–2473 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06527.x
Rilstone, J.J., Alkhater, R.A., Minassian, B.A.: Brain dopamine-serotonin vesicular transport disease and its treatment. N Engl J Med. 368(6), 543–550 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1207281
Afonso-Oramas, D., Cruz-Muros, I., Alvarez de la Rosa, D., Abreu, P., Giráldez, T., Castro-Hernández, J., et al.: Dopamine transporter glycosylation correlates with the vulnerability of midbrain dopaminergic cells in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 36(3), 494–508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.09.002
Burré, J., Sharma, M., Tsetsenis, T., Buchman, V., Etherton, M.R., Südhof, T.C.: Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329(5999), 1663–1667 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195227
Dearry, A., Gingrich, J.A., Falardeau, P., Fremeau, R.T., Jr., Bates, M.D., Caron, M.G.: Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor. Nature 347(6288), 72–76 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/347072a0
Villar, V.A., Jones, J.E., Armando, I., Palmes-Saloma, C., Yu, P., Pascua, A.M., Keever, L., et al.: G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4 (GRK4) regulates the phosphorylation and function of the dopamine D3 receptor. J Biol Chem. 284(32), 21425–21434 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.003665
Albizu, L., Holloway, T., González-Maeso, J., Sealfon, S.C.: Functional crosstalk and heteromerization of serotonin 5-HT2A and dopamine D2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 61(4), 770–777 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.05.023
Beaulieu, J.M., Gainetdinov, R.R.: The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 63(1), 182–217 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.002642
Li, A., Mishra, Y., Malik, M., Wang, Q., Li, S., Taylor, M., et al.: Evaluation of N-phenyl homopiperazine analogs as potential dopamine D3 receptor selective ligands. Bioorg Med Chem. 21(11), 2988–2998 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.03.074
Fishburn, C.S., Elazar, Z., Fuchs, S.: Differential glycosylation and intracellular trafficking for the long and short isoforms of the D2 dopamine receptor. J Biol Chem. 270(50), 29819–29824 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.50.29819
Min, C., Zheng, M., Zhang, X., Guo, S., Kwon, K.J., Shin, C.Y., et al.: N-linked Glycosylation on the N-terminus of the dopamine D2 and D3 receptors determines receptor association with specific microdomains in the plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853(1), 41–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.024
Marotta, N.P., Lin, Y.H., Lewis, Y.E., et al.: O-GlcNAc modification blocks the aggregation and toxicity of the protein α-synuclein associated with Parkinson’s disease. Nat Chem. 7(11), 913–920 (2015)
Karube, H., Sakamoto, M., Arawaka, S., Hara, S., Sato, H., Ren, C.H., et al.: N-terminal region of α-synuclein is essential for the fatty acid-induced oligomerization of the molecules. FEBS Lett. 582, 3693–3700 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.10.001
Giasson, B.I., Murray, I.V., Trojanowski, J.Q., Lee, V.M.: A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J Biol Chem. 276(4), 2380–2386 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008919200
Afitska, K., Fucikova, A., Shvadchak, V.V., Yushchenko, D.A.: Modification of C Terminus Provides New Insights into the Mechanism of α-Synuclein Aggregation. Biophys J. 113(10), 2182–2191 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2017.08.027
Jo, E., Fuller, N., Rand, R.P., St George-Hyslop, P., Fraser, P.E.: Defective membrane interactions of familial Parkinson’s disease mutant A30P alpha-synuclein. J Mol Biol. 315(4), 799–807 (2002)
Ghosh, D., et al.: alpha-synuclein aggregation and its modulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 100, 37–54 (2017)
Wang, W., Perovic, I., Chittuluru, J., Kaganovich, A., Nguyen, L.T., Liao, J., et al.: A soluble α-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 108(43), 17797–17802 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1113260108
Trexler, A.J., Rhoades, E.: N-Terminal acetylation is critical for forming a-helical oligomer of a-synuclein. Protein Sci. 21, 601–605 (2012)
Zhu, M., Li, J., Fink, A.L.: The association of alpha-synuclein with membranes affects bilayer structure, stability, and fibril formation. J Biol Chem. 278(41), 40186–40197 (2003)
Zhu, M., Fink, A.L.: Lipid binding inhibits alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J Biol Chem. 278(19), 16873–16877 (2003)
Arawaka, S., Sato, H., Sasaki, A., Koyama, S., Kato, T.: Mechanisms underlying extensive Ser129-phosphorylation in α-synuclein aggregates. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 5(1), 48 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0452-6
Paleologou, K.E., Oueslati, A., Shakked, G., Rospigliosi, C.C., Kim, H.-Y., Lamberto, G.R., et al.: Phosphorylation at S87 is enhanced in synucleinopathies, inhibits alpha-synuclein oligomerization, and influences synuclein-membrane interactions. J Neurosci. 30, 3184–3198 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5922-09.2010
O’Leary, E.I., Jiang, Z., Strub, M.P., Lee, J.C.: Effects of phosphatidylcholine membrane fluidity on the conformation and aggregation of N-terminally acetylated α-Synuclein. J Biol Chem. 293, 11195–11205 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002780
O’Leary, E.I., Lee, J.C.: Interplay between α-synuclein amyloid formation and membrane structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 1867, 483–491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.09.012
Bartels, T., Kim, N.C., Luth, E.S., Selkoe, D.J.: N-alpha-acetylation of α-synuclein increases its helical folding propensity, GM1 binding specificity and resistance to aggregation. PLoS ONE 9, e103727 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103727
König, A., Vicente Miranda, H., Outeiro, T.F.: Alpha-Synuclein Glycation and the Action of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 8(1), 33–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-171285
Guerrero, E., Vasudevaraju, P., Hegde, M.L., Britton, G.B., Rao, K.S.: Recent advances in α-synuclein functions, advanced glycation, and toxicity: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol. 47(2), 525–536 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8328-z
Vicente Miranda, H., Szego, É.M., Oliveira, L.M.A., Breda, C., Darendelioglu, E., de Oliveira, R.M., et al.: Glycation potentiates α-synuclein-associated neurodegeneration in synucleinopathies. Brain. 140(5), 1399–1419 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx056
Jin, Q., Chen, H., Luo, A., Ding, F., Liu, Z.: S100A14 stimulates cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis at different concentrations via receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE). PLoS ONE 6(4), e19375 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019375
De Oliveira, R.M., Vicente Miranda, H., Francelle, L., Pinho, R., Szegö, É.M., Martinho, R., et al.: The mechanism of sirtuin 2-mediated exacerbation of alpha-synuclein toxicity in models of Parkinson disease. PLoS Biol. 15(3), e2000374 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2000374
He, Y., Yu, Z., Chen, S.: Alpha-Synuclein Nitration and Its Implications in Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 10(2), 777–782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00288
Cole, R.N., Hart, G.W.: Cytosolic O-glycosylation is abundant in nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 79(5), 1080–1089 (2001)
Gao, Y., Wells, L., Comer, F.I., Parker, G.J., Hart, G.W.: Dynamic O-glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins: cloning and characterization of a neutral, cytosolic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from human brain. J Biol Chem. 276(13), 9838–9845 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010420200
Kang, L., Moriarty, G.M., Woods, L.A., Ashcroft, A.E., Radford, S.E., Baum, J.: N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein induces increased transient helical propensity and decreased aggregation rates in the intrinsically disordered monomer. Protein Sci. 21(7), 911–917 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2088
Levine, P.M., et al.: A-Synuclein O-GlcNAcylation alters aggregation and toxicity, revealing certain residues as potential inhibitors of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116(5), 1511–1519 (2019)
Banerjee, P.S., Lagerlöf, O., Hart, G.W.: Roles of O-GlcNAc in chronic diseases of aging. Mol Aspects Med. 51, 1–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.05.005
Wang, A.C., Jensen, E.H., Rexach, J.E., Vinters, H.V., Hsieh-Wilson, L.C.: Loss of O-GlcNAc glycosylation in forebrain excitatory neurons induces neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 113, 15120–15125 (2016)
Sipione, S., Monyror, J., Galleguillos, D., Steinberg, N., Kadam, V.: Gangliosides in the Brain: Physiology. Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Applications. Front Neurosci. 14, 572965 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.572965
Seyfried, T.N., Choi, H., Chevalier, A., Hogan, D., Akgoc, Z., Schneider, J.S.: Sex-Related Abnormalities in Substantia Nigra Lipids in Parkinson’s Disease. ASN Neuro 10, 1759091418781889 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091418781889
Huebecker, M., Moloney, E.B., van der Spoel, A.C., Priestman, D.A., Isacson, O., Hallett, P.J., Platt, F.M.: Reduced sphingolipid hydrolase activities, substrate accumulation and ganglioside decline in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 14, 40 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0339-z
Lai, C.S., Schutzbach, .JS.: Dolichol Induces Membrane Leakage of Liposomes Composed of Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylcholine. FEBS Lett. 169, 279–282 (1984)
Egawa, J., Pearn, M.L., Lemkuil, B.P., Patel, P.M., Head, B.P.: Membrane lipid rafts and neurobiology: age-related changes in membrane lipids and loss of neuronal function. J Physiol. 594(16), 4565–4579 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270590
Fecchio, C., Palazzi, L., Polverino de Laureto, P.: α-Synuclein and polyunsaturated fatty acids: molecular basis of the interaction and implication in neurodegeneration. Molecules. 23, E1531 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071531
Tettamanti, G., Preti, A., Cestaro, B., Venerando, B., Lombardo, A., Ghidoni, R., Sonnino, S.: Gangliosides, neuraminidase and sialyltransferase at the nerve endings. Adv Exp Med Biol. 125, 263–281 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-7844-0_25
Angata, K., Fukuda, M.: Roles of polysialic acid in migration and differentiation of neural stem cells. Methods Enzymol. 479, 25–36 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(10)79002-9
Hildebrandt, H., Dityatev, A.: Polysialic Acid in Brain Development and Synaptic Plasticity. Top Curr Chem. 366, 55–96 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2013_446
Schiff, M., Weinhold, B., Grothe, C., Hildebrandt, H.: NCAM and polysialyltransferase profiles match dopaminergic marker gene expression but polysialic acid is dispensable for development of the midbrain dopamine system. J Neurochem. 110(5), 1661–1673 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06267.x
Gao, Y., Luan, X., Melamed, J., Brockhausen, I. Role of Glycans on Key Cell Surface Receptors That Regulate Cell Proliferation and Cell Death. Cells. 10(5), 1252 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051252
Woronowicz, A., Amith, S.R., De Vusser, K., Laroy, W., Contreras, R., Basta, S., Szewczuk, M.R.: Dependence of neurotrophic factor activation of Trk tyrosine kinase receptors on cellular sialidase. Glycobiology 17(1), 10–24 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwl049
Ledeen, R.W., Wu, G.: Gangliosides, α-Synuclein, and Parkinson’s Disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 156, 435–454 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.12.009
Comoletti, D., Flynn, R., Jennings, L.L., Chubykin, A., Matsumura, T., Hasegawa, H., Südhof, T.C., Taylor, P.: Characterization of the interaction of a recombinant soluble neuroligin-1 with neurexin-1beta. J Biol Chem. 278(50), 50497–50505 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306803200
Birol, M., Wojcik, S.P., Miranker, A.D., Rhoades, E.: Identification of N-linked glycans as specific mediators of neuronal uptake of acetylated α-Synuclein. PLoS Bio 17(6), e3000318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000318
Dikiy, I., Eliezer, D.: Folding and misfolding of alpha-synuclein on membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818, 1013–1018 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.09.008
Terakawa, M.S., Lee, Y.H., Kinoshita, M., Lin, Y., Sugiki, T., Fukui, N., et al.: Membrane-induced initial structure of α-synuclein control its amyloidogenesis on model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860, 757–766 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.12.011
Lorenzen, N., Lemminger, L., Pedersen, J.N., Nielsen, S.B., Otzen, D.E.: The N-terminus of α-synuclein is essential for both monomeric and oligomeric interactions with membranes. FEBS Lett. 588(3), 497–502 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.12.015
Starheim, K.K., Arnesen, T., Gromyko, D., Ryningen, A., Varhaug, J.E., Lillehaug, J.R.: Identification of the human N(alpha)-acetyltransferase complex B (hNatB): a complex important for cell-cycle progression. Biochem J. 415(2), 325–331 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20080658
Fusco, G., Chen, S.W., Williamson, P.T.F., Cascella, R., Perni, M., Jarvis, J.A., et al.: Structural basis of membrane disruption and cellular toxicity by α-synuclein oligomers. Science 358, 1440–1443 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan6160
Shvadchak, V.V., Yushchenko, D.A., Pievo, R., Jovin, T.M.: The mode of α-synuclein binding to membranes depends on lipid composition and lipid to protein ratio. FEBS Lett. 585(22), 3513–3519 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2011.10.006
Mizuno, S., Sasai, H., Kume, A., et al.: Dioleoyl-phosphatidic acid selectively binds to αsynuclein and strongly induces its aggregation. FEBS Lett. 591(5), 784–791 (2017)
Carroll, C.B., Wyse, R.K.H.: Simvastatin as a Potential Disease-Modifying Therapy for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: Rationale for Clinical Trial, and Current Progress. J Parkinsons Dis. 7(4), 545–568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-171203
Perrin, R.J., Woods, W.S., Clayton, D.F., George, J.M.: Exposure to long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids triggers rapid multimerization of synucleins. J Biol Chem. 276(45), 41958–41962 (2001)
De Franceschi, G., Frare, E., Pivato, M., Relini, A., Penco, A., Greggio, E., et al.: Structural and morphological characterization of aggregated species of α-synuclein induced by docosahexaenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 286(25), 22262–22274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.202937
De Franceschi, G., Fecchio, C., Sharon, R., Schapira, A.H.V., Proukakis, C., Bellotti, V., et al.: α-Synuclein structural features inhibit harmful polyunsaturated fatty acid oxidation, suggesting roles in neuroprotection. J Biol Chem. 292, 6927–6937 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.765149
Davidson, W.S., Jonas, A., Clayton, D.F., George, J.M.: Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J Biol Chem. 273(16), 9443–9449 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.16.9443
Martinez, Z., Zhu, M., Han, S., Fink, A.L.: GM1 Specifically Interacts with Alpha-Synuclein and Inhibits Fibrillation. Biochem Pharmacol. 46, 1868–1877 (2007)
Schneider, J.S.: Altered expression of genes involved in ganglioside biosynthesis in substantia nigra neurons in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 13(6), e0199189 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199189
Ledeen, R., Wu, G.: New findings on nuclear gangliosides: overview on metabolism and function. J Neurochem. 116(5), 714–720 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07115.x
Chiricozzi, E., Di Biase, E., Lunghi, G., Fazzari, M., Loberto, N., Aureli, M., Mauri, L., Sonnino, S.: Turning the spotlight on the oligosaccharide chain of GM1 ganglioside. Glycoconj J. 38(1), 101–117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-021-09974-y
Galvagnion, C., Buell, A.K., Meisl, G., Michaels, T.C., Vendruscolo, M., Knowles, T.P., Dobson, C.M.: Lipid vesicles trigger α-synuclein aggregation by stimulating primary nucleation. Nat Chem Biol. 11(3), 229–234 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1750
Jensen, J.W., Schutzbach, J.S.: Activation of Mannosyltranferase II by Nonbilayer Phospholipids Biochemistry. 23, 1115–1119 (1984)
Monti, J.A., Christian, S.T., Schutzbach, J.S.: Effects of Dolichol on Membrane Properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 905, 133–142 (1987)
Adair, W.L. Jr., Keller, R.K.: Dolichol metabolism in rat liver. Determination of the subcellular distribution of dolichyl phosphate and its site and rate of de novo biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 257(15):8990–8996 (1982)
Rip, J.W., Rupar, C.A., Ravi, K., Carroll, K.K.: Distribution, metabolism and function of dolichol and polyprenols. Prog Lipid Res. 24(4), 269–309 (1985)
Edlund, C., Söderberg, M., Kristensson, K.: Isoprenoids in aging and neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int. 25(1), 35–38 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(94)90050-7
Daniels, I., Hemming, F.W.: Changes in murine tissue concentrations of dolichol and dolichol derivatives associated with age. Lipids 25(10), 586–593 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536006
Ward, W.C., Zucca, F.A., Bellei, C., Zecca, L., Simon, J.D.: Neuromelanins in various regions of human brain are associated with native and oxidized isoprenoid lipids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 484(1), 94–99 (2009)
Bergamini, E., Bizzarri, R., Cavallini, G., Cerbai, B., Chiellini, E., Donati, A., et al.: Ageing and oxidative stress: a role for dolichol in the antioxidant machinery of cell membranes? J Alzheimers Di 6(2), 129–135 (2004). https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2004-6204
Schutzbach, J.S., Jensen, J.W.: Bilayer Membrane Destabilization Induced by DolichylPhosphate. Chem Phys Lipids. 51, 213–218 (1989)
Buczkowska, A., Swiezewska, E., Lefeber, D.J.: Genetic defects in dolichol metabolism J Inherit Metab Dis. 38, 157–169 (2015)
Bar-On, P., Crews, L., Koob, A.O., Mizuno, H., Adame, A., Spencer, B., et al.: Statins reduce neuronal α-synuclein aggregation in in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 105, 1656–1667 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05254.x
Atil, B., Berger-Sieczkowski, E., Bardy, J., Werner, M., Hohenegger, M.: In vitro and in vivo downregulation of the ATP binding cassette transporter B1 by the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 389(1), 17–32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1169-3
Grabinska, K., A., et al.: cis-Prenyltransferase: New Insights into Protein Glycosylation, Rubber Synthesis, and Human Diseases, J Biol Chem. 219(35), 18582–18590 (2016)
Kharel, Y., Takahashi, S., Yamashita, S., Koyama, T.: In vivo interaction between the human dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase and the Niemann-Pick C2 protein revealed by a yeast two-hybrid system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 318(1), 198–203 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.007
Morava, E., Wevers, R.A., Cantagrel, V., Hoefsloot, L.H., Al-Gazali, L., Schoots, J., et al.: A novel cerebello-ocular syndrome with abnormal glycosylation due to abnormalities in dolichol metabolism. Brain 133(11), 3210–3220 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq261
Rush, E.T., Baker, C.V., Rizzo, W.B.: Dolichol kinase deficiency (DOLK-CDG): Two new cases and expansion of phenotype. Am J Med Genet A. 173(9), 2428–2434 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.38287
Van Dessel, G., Lagrou, A., Hilderson, H.J., Dierick, W.: Characterization of the in vitro conversion of dolichol to dolichoate in bovine thyroid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1167(3), 307–315 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(93)90234-z
Vila, M.: Neuromelanin, aging, and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 34(10), 1440–1451 (2019)
Fedorow, H., Pickford, R., Hook, J.M., et al.: Dolichol is the major lipid component of human substantia nigra neuromelanin. J Neurochem. 92(4), 990–995 (2005)
Conway, K.A., Rochet, J.C., Bieganski, R.M., Lansbury, P.T., Jr.: Kinetic stabilization of the alpha-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-alpha-synuclein adduct. Science 294(5545), 1346–1349 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1063522
Greggio, E., Bergantino, E., Carter, D., Ahmad, R., Costin, G.E., Hearing, V.J., et al.: Tyrosinase exacerbates dopamine toxicity but is not genetically associated with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 93(1), 246–256 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03019.x
Hasegawa, T.: Tyrosinase-expressing neuronal cell line as in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 11(3), 1082–1089 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11031082
Carballo-Carbajal, I., Laguna, A., Romero-Giménez, J., et al.: Brain tyrosinase overexpression implicates age-dependent neuromelanin production in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Nat Commun. 10, 973 (2019)
Haining, R.L., Achat-Mendes, C.: Neuromelanin, one of the most overlooked molecules in modern medicine, is not a spectator. Neural Regen Res. 12(3), 372–375 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.202928
Zucca, F.A., Vanna, R., Cupaioli, F.A., Bellei, C., De Palma, A., Di Silvestre, D.: Neuromelanin organelles are specialized autolysosomes that accumulate undegraded proteins and lipids in aging human brain and are likely involved in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 4, 17 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41531-018-0050-8
da Silva, F.L., Coelho Cerqueira, E., de Freitas, M.S., Gonçalves, D.L., Costa, L.T., Follmer, C.: Vitamins K interact with N-terminus α-synuclein and modulate the protein fibrillization in vitro. Exploring the interaction between quinones and α-synuclein. Neurochem Int. 62(1), 103–112 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.10.001
Oliveri, V.: Toward the discovery and development of effective modulators of α-synuclein amyloid aggregation. Eur J Med Chem. 167, 10–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.01.045
Reglodi, D., Renaud, J., Tamas, A., Tizabi, Y., Socías, S.B., Del-Bel, E., Raisman-Vozari, R.: Novel tactics for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease: Role of antibiotics, polyphenols and neuropeptides. Prog Neurobiol. 155, 120–148 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.10.004
Norris, E.H., Giasson, B.I., Hodara, R., Xu, S., Trojanowski, J.Q., Ischiropoulos, H., Lee, V.M.: Reversible inhibition of alpha-synuclein fibrillization by dopaminochrome-mediated conformational alterations. J Biol Chem. 280(22), 21212–21219 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M412621200
Tagliafierro, L., Chiba-Falek, O.: Up-regulation of SNCA gene expression: implications to synucleinopathies. Neurogenetics 17(3), 145–157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-016-0478-0
Bonuccelli, U., Pavese, N.: Role of dopamine agonists in Parkinson’s disease: an update. Expert Rev Neurother. 7(10), 1391–1399 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.7.10.1391
Liu, Y., Hao, S., Yang, B., Fan, Y., Qin, X., Chen, Y., Hu, J.: Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays an essential role in α7 nicotinic receptor-mediated neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons in a mouse Parkinson’s disease model. Biochem Pharmacol. 140, 115–123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.05.017
Magistretti, P.J., Geisler, F.H., Schneider, J.S., Li, P.A., Fiumelli, H., Sipione, S.: Gangliosides: Treatment Avenues in Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Neurol. 10, 859 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00859
Sidorova, Y.A., Volcho, K.P., Salakhutdinov, N.F.: Neuroregeneration in Parkinson’s Disease: From Proteins to Small Molecules. Curr Neuropharmacol. 17(3), 268–287 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180905094123
Jang, S.E., Qiu, L., Chan, L.L., Tan, E.K., Zeng, L.: Current Status of Stem Cell-Derived Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease: From Cell Assessment and Imaging Modalities to Clinical Trials. Front Neurosci. 14, 558532 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.558532
Chia, Y.C., Anjum, C.E., Yee, H.R., Kenisi, Y., Chan, M.K.S., Wong, M.B.F., Pan, S.Y.: Stem Cell Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases: How Do Stem Cells Bypass the Blood-Brain Barrier and Home to the Brain? Stem Cells International. e8889061 (2020)
Goncharova, V., Das, S., Niles, W., Schraufstatter, I., Wong, A.K., Povaly, T., et al.: Homing of neural stem cells from the venous compartment into a brain infarct does not involve conventional interactions with vascular endothelium. Stem Cells Transl Med. 3(2), 229–240 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2013-0052
Yagi, H., Kato, K.: Functional roles of glycoconjugates in the maintenance of stemness and differentiation process of neural stem cells. Glycoconj J. 34(6), 757–763 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9707-x
Yu, R.K., Yanagisawa, M.: Glycobiology of neural stem cells. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 5(4), 415–423 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2174/187152706777950675
Yanagisawa, M., Yu, R.K.: The expression and functions of glycoconjugates in neural stem cells. Glycobiology 17, 57R-74R (2007)
Yuan, S.H., Martin, J., Elia, J., Flippin, J., Paramban, R.I., Hefferan, M.P., et al.: Cell-Surface Marker Signatures for the Isolation of Neural Stem Cells, Glia and Neurons Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. PLoS One. 6, e17540 (2011)
Yale, A.R., Nourse, J.L., Lee, K.R., Ahmed, S.N., Arulmoli, J., Jiang, A.Y.L., et al.: Cell Surface N-Glycans Influence Electrophysiological Properties and Fate Potential of Neural Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 11, 869–882 (2018)
Murrell, M.P., Yarema, K.J., Levchenko, A.: The systems biology of glycosylation. ChemBioChem 5(10), 1334–1347 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200400143
Krasnova, L., Wong, C.H.: Exploring human glycosylation for better therapies. Mol Aspects Med. 51, 125–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.05.003
Iqbal, S., Ghanimi Fard, M., Everest-Dass, A., Packer, N.H., Parker, L.M.: Understanding cellular glycan surfaces in the central nervous system. Biochem Soc Trans. 47(1), 89–100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20180330
Cummings, R.D.: Stuck on sugars - how carbohydrates regulate cell adhesion, recognition, and signaling. Glycoconj. J 36(4), 241–257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-019-09876-0
Kirkeby, A., Grealish, S., Wolf, D.A., Nelander, J., Wood, J., Lundblad, M., et al.: Generation of regionally specified neural progenitors and functional neurons from human embryonic stem cells under defined conditions. Cell Rep. 1(6), 703–714 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.04.009
Takahashi, J.: Preparing for first human trial of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cells for Parkinson’s disease: an interview with Jun Takahashi. Regen Med. 14(2), 93–95 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2018-0158
Schweitzer, J.S., Song, B., Herrington, T.M., Park, T.-Y., Lee, N., Ko, S., et al.: Personalized iPSC-Derived Dopamine Progenitor Cells for Parkinson’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 382(20), 1926–1932 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1915872
Venkataramana, N.K., Kumar, S.K., Balaraju, S., Radhakrishnan, R.C., Bansal, A., Dixit, A., et al.: Open-labeled study of unilateral autologous bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in Parkinson’s disease. Transl Res. 155(2), 62–70 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2009.07.006
Lanctot, P.M., Gage, F.H., Varki, A.P.: The Glycans of Stem Cells. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 11, 373–380 (2007)
Breimer, M.E., Säljö, K., Barone, A., Teneberg, S.: Glycosphingolipids of human embryonic stem cells. Glycoconj J. 34(6), 713–723 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9706-y
Terashima, M., Amano, M., Onodera, T., Nishimura, S.-I., Iwasaki, N.: Quantitative glycomics monitoring of induced pluripotent- and embryonic stem cells during neuronal differentiation. Stem Cell Research. 13, 454–464 (2014)
Hennen, E., Czopka, T., Faissner, A.: Structurally Distinct LewisX Glycans Distinguish Subpopulations of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. J Biol Chem. 286, 16321–16331 (2011)
An, H.J., Gip, P., Kim, .J, Wu, S., Park, K.W., McVaugh, C.T., et al.: Extensive determination of glycan heterogeneity reveals an unusual abundance of high mannose glycans in enriched plasma membranes of human embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11(4), M111.010660 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M111.010660
Yu, R.K., Suzuki, Y., Yanagisawa, M.: Membrane Glycolipids in Stem Cells. FEBS Lett. 584, 1694–1699 (2010)
Li, Y.L., Wu, G.Z., Zeng, L., Dawe, G.S., Sun, L., Loers, G., et al.: Cell surface sialylation and fucosylation are regulated by the cell recognition molecule L1 via PLCgamma and cooperate to modulate embryonic stem cell survival and proliferation. FEBS Lett. 583(4), 703–710 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.013
Doherty, P., Cohen, J., Walsh, F.S.: Neurite outgrowth in response to transfected N-CAM changes during development and is modulated by polysialic acid. Neuron 5(2), 209–219 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(90)90310-c
El Maarouf, A., Yaw, D.M., Rutishauser, U.: Improved stem cell-derived motoneuron survival, migration, sprouting, and innervation with enhanced expression of polysialic acid. Cell Transplant. 24(5), 797–809 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3727/096368914X679228
He, H., Nilsson, C.L., Emmett, M.R., Marshall, A.G., Kroes, R.A., Moskal, J.R., et al.: Glycomic and transcriptomic response of GSC11 glioblastoma stem cells to STAT3 phosphorylation inhibition and serum-induced differentiation. J Proteome Res. 9(5), 2098–2108 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/pr900793a
Itokazu, Y., Tsai, Y.T., Yu, R.K.: Epigenetic regulation of ganglioside expression in neural stem cells and neuronal cells. Glycoconj J. 34(6), 749–756 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-016-9719-6
Brawner, A.T., Xu, R., Liu, D., Jiang, P.: Generating CNS organoids from human induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling neurological disorders. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 9(3), 101–111 (2017)
Jo, J., Xiao, Y., Sun, A.X., Cukuroglu, E., Tran, H.D., Göke, J., et al.: Midbrain-like Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Contain Functional Dopaminergic and Neuromelanin-Producing Neurons. Cell Stem Cell 19(2), 248–257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.07.005
Kriks, S., Shim, J.W., Piao, J., Ganat, Y.M., Wakeman, D.R., Xie, Z., et al.: Dopamine neurons derived from human ES cells efficiently engraft in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 480(7378), 547–551 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10648
Steinbeck, J.A., Studer, L.: Moving stem cells to the clinic: potential and limitations for brain repair. Neuron 86(1), 187–206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.002
Tagliafierro, L., Zamora, M.E., Chiba-Falek, O.: Multiplication of the SNCA locus exacerbates neuronal nuclear aging. Hum Mol Genet. 28(3), 407–421 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy355
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brockhausen, I., Schutzbach, J., Wang, J. et al. Glycoconjugate journal special issue on: the glycobiology of Parkinson’s disease. Glycoconj J 39, 55–74 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-021-10024-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-021-10024-w