Abstract
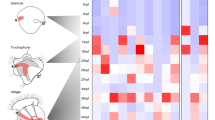
Penaeid shrimp embryos undergo holoblastic division, gastrulation by invagination, and hatching as a nauplius larva. Posterior segments form and differentiate during larval development. Hedgehog (Hh) pathway genes from penaeid shrimp and other pancrustaceans were identified by in silico analysis of genomes and transcriptomes, and mapped onto a recent pancrustacean phylogeny to determine patterns of intron gains and losses. Penaeus vannamei, P. japonicus, and P. monodon Hh proteins were encoded by four exons. Amphipod, isopod, and ostracod hh were also encoded by four exons, but hh from other arthropod groups contained three conserved exons. The novel hh intron is hypothesized to have arisen independently in the malacostracan ancestor and Ostracoda by a transposon insertion. Shared patterns of ptc, smo, and ci exon structure were found for Malacostraca, Branchiopoda + Hexapoda, Hexanauplia (Thecostraca + Copepoda), Multicrustacea (Thecostraca + Copepoda + Malacostraca), and Pancrustacea minus Oligostraca. mRNA expression of P. vannamei of hh, ptc, and ci from developmental transcriptomes of zygotes through postlarvae showed low expression from zygote to gastrula, which increased at limb bud, peaked at unhatched nauplius, and declined in nauplius and later larval stages. smo expression was found in zygotes, peaked in gastrula, and declined in limb bud and later stages. These results are consistent with a role for Hh signaling during segmentation in penaeid shrimp.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abzhanov A, Kaufman TC (2000) Evolution of distinct expression patterns for engrailed paralogues in higher crustaceans (Malacostraca). Dev Genes Evol 210:493–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004270000090
Alcedo J, Zyzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper JE (1996) The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell 86:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80094-x
Briscoe J, Thérond PP (2013) The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:416–429. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3598
Catania F (2017) From intronization to intron loss: how the interplay between mRNA-associated processes can shape the architecture and the expression of eukaryotic genes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 91:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.06.017
Dohle W, Scholtz G (1997) How far does cell lineage influence cell fate specification in crustacean embryos? Sem Cell Devel Biol 8:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1006/scdb.1997.0162
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacque B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP (1993) Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell 75:1417–1430. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90627-3
Gong X, Qian H, Cao P, Zhao X, Zhou Q, Lei J, Yan N (2018) Structural basis for the recognition of Sonic Hedgehog by human Patched1. Science 361:eaas8935. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aas8935
Hertzler PL (2005) Cleavage and gastrulation in the shrimp Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei (Malacostraca, Decapoda, Dendrobranchiata). Arthropod Struct Dev 34:455–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asd.2005.01.009
Hertzler PL, Clark WH (1992) Cleavage and gastrulation in the shrimp Sicyonia ingentis: invagination is accompanied by oriented cell division. Development 116:127–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-169X.2010.01205.x
Huerlimann R, Wade NM, Gordon L, Montenegro JD, Goodall J, McWilliam S, Tinning M, Siemering K, Giardina E, Donovan D et al (2018) De novo assembly, characterization, functional annotation and expression patterns of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) transcriptome. Sci Rep 8:13553. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31148-4
Hui C-C, Angers S (2011) Gli proteins in development and disease. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:513–537. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154048
Hui M, Cui ZX, Liu Y, Song CW (2017) Transcriptome profiles of embryos before and after cleavage in Eriocheir sinensis: identification of developmental genes at the earliest stages. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 35:770–781. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00191.2013
Irimia M, Rukov JL, Penny D, Vinther J, Garcia-Fernandez J, Roy SW (2008) Origin of introns by ‘intronization’ of exonic sequences. Trends Genet 24:378–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2008.05.007
Jamarillo ML, Guzman F, Paese CLB, Margis R, Nazari EM, Ammar D, Muller YMR (2016) Exploring developmental gene toolkit and associated pathways in a potential new model crustacean using transcriptomic analysis. Develop Genes Evol 226:325–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-016-0551-6
Li P, Wang Y, Wang Y, Guo H (2017) Whole transcriptome sequencing and analysis of gastrula embryos of Marsupenaeus japonicus (Bate, 1888) Madrige. J Aquac Res Dev 1:1000101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2007.01.010
Lozano-Fernandez JL, Giacomelli M, Fleming JF, Chen A, Vinther J, Thomsen PF, Glenner H, Palero F, Legg DA, Iliffe TM, Pisani D (2019) Pancrustacean evolution illuminated by taxon-rich genomic-scaled data sets with an expanded Remipede sampling. Genome Biol Evol 11:2055–2070. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evz097
Nüsslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980) Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287:795–801. https://doi.org/10.1038/287795a0
Parchem RJ, Poulin F, Stuart AB, Amemiya CT, Patel NH (2010) BAC library for the amphipod crustacean, Parhyale hawaiensis. Genomics 95:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.03.005
Porter JA, Ekker SG, Park W-J, von Kessler DP, Young EK, Chen C-H, Ma Y, Woods AS, Cotter RJ, Koonin EV, Beachy PA (1996) Hedgehog patterning activity: role of a lipophilic modification mediated by the carboxy-terminal autoprocessing domain. Cell 86:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80074-4
Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C (1993) Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell 75:1401–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2
Senapathy P (1988) Possible evolution of splice-junction signals in eukaryotic genes from stop codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1129–1133. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.85.4.1129
Simonnet F, Deutsch J, Quéinnec E (2004) hedgehog is a segment polarity gene in a crustacean and a chelicerate. Dev Genes Evol 214:537–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-004-0435-z
Wei J, Zhang X, Yu Y, Huang H, Li F, Ziang J (2014) Comparative transcriptomic characterization of the early development in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 9:e106201. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106201
Yuan J, Zhang X, Liu C, Yu Y, Wei J, Li F, Ziang J (2017) Genomic resources and comparative analyses of two economical penaeid shrimp species, Marsupenaeus japonicus and Penaeus monodon. Mar Genomics 39:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.09.004
Zhan L, Meng Q, Chen R, Yue Y, Jin Y (2014) Origin and evolution of a new retained intron on the Vulcan gene in Drosophila melanogaster subgroup species. Genome 57:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2014-0132
Zhang XJ, Yuan JB, Sun YM, Li SH, Gao Y, Yu Y, Liu CZ, Wang QC, Lv KJ, Zhang XX et al (2019) Penaeid shrimp genome provides insights into benthic adaptation and frequent molting. Nat Commun 10:356. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08197-4
Zilch R (1978) Embryologische Untersuchungen an der holoblastischen Ontogenes von Penaeus trisulcatus Leach (Crustacea, Decapoda). Zoomorphology 90:67–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00993744
Du J, Zhang X, Yuan J, Zhang X, Li F, Xiang J (2018) Wnt gene family members and their expression profiling in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immun 77:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.03.034
Tahiro S, Michiue T, Higashijima S, Zenno S, Ishimaru S, Takahashi F, Orihara M, Kojima T, Saigo K (1993) Structure and expression of hedghog, a Drosophila segment-polarity gene required for cell-cell communication. Gene 125:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(93)90392-g
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Central Michigan University Faculty Research and Creative Endeavors grant [48022].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Emma Devries analyzed the sequences of Cyprideis torosa Smo and Ci. Rachel DeBoer analyzed the sequence of penaeid shrimp Patched. Philip Hertzler performed all other analysis and writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hertzler, P.L., Devries, E.J. & DeBoer, R.A. The Hedgehog pathway in penaeid shrimp: developmental expression and evolution of splice junctions in Pancrustacea. Genetica 150, 87–96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00151-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00151-z