Abstract
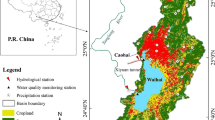
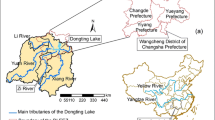
Lake Baiyangdian provides water in northern China. Agriculture contributes to nutrient pollution in this lake. This especially holds for livestock production with poor nutrient and manure management. Furthermore, a new urban area is currently developing in the basin. This increases demand for food in cities and feed for animals. This study aims to explore sustainable options to reduce nutrient losses from livestock production systems to Lake Baiyangdian between 2012 and 2050, taking urbanization into account. We used the MARINA-Lakes model to analyze future trends in nutrient pollution at the sub-basin scale, using four scenarios that consider nutrient management and intensified crop and animal production. Model results show that between 2012 and 2050, river export of nutrients to Lake Baiyangdian almost doubled in our baseline scenario without improved nutrient and manure management. As a result, the lake is expected to receive 9623 Mg of total dissolved nitrogen and 448 Mg of total dissolved phosphorus in 2050. Additional restrictions to livestock production did not reduce the projected river export of nutrients to the lake much. Increased recycling of manure could decrease the river export of nutrients by 40% by 2050. The river export of all nutrients is projected to decrease to one-third to half of the 2012 export in our optimistic nutrient management scenario, which assumes that the available animal manure is reallocated to areas where crop demand for nutrients is high. This avoids direct discharges of animal manure to rivers. Our study shows that additional policies are needed to effectively recycle animal manure in crop production systems. Effective sewage treatment is also important for pollution control in the lake, given the anticipated urbanization.

Source: MARINA-Lakes model (see “Scenario description” section)

Source: MARINA-Lakes model (see “Scenario description” section)

Source: MARINA-Lakes model (see “Scenario description” section)

Source: MARINA-Lakes model (see “Scenario description” section)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Z, Ma L, Jin S, Ma W, Velthof GL, Oenema O, Liu L, Chadwick D, Zhang F (2016a) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium flows through the manure management chain in China. Environ Sci Technol 50(24):13409–13418. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03348
Bai Z, Ma L, Ma W, Qin W, Velthof GL, Oenema O, Zhang F (2016b) Changes in phosphorus use and losses in the food chain of China during 1950–2010 and forecasts for 2030. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 104(3):361–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-015-9737-y
Bai Z, Ma L, Qin W, Chen Q, Oenema O, Zhang F (2014) Changes in pig production in china and their effects on nitrogen and phosphorus use and losses. Environ Sci Technol 48(21):12742–12749. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502160v
Bai Z, Ma W, Ma L, Velthof GL, Wei Z, Havlík P, Oenema O, Lee MRF, Zhang F (2018) China’s livestock transition: driving forces, impacts, and consequences. Sci Adv 4(7):8534. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar8534
Bai Z, Zhao J, Wei Z, Jin X, Ma L (2019) Socio-economic drivers of pig production and their effects on achieving sustainable development goals in China. J Integr Environ Sci 16(1):141–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/1943815X.2019.1671463
BDMGOV (2017) Water system protection plan of Baoding City. Baoding Municipal People's Government. http://www.bdhb.gov.cn/eportal3/cms/jsp/site001/article.jsp?fchannelidenty=402882163b3f8f26013b3f988bf004eb&articleId=8aa7976162effef7016300d4b7ec0148
Chen X, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Supit I, Wang M, Ma L, Chen X, Shi X (2020) Modeling the contribution of crops to nitrogen pollution in the Yangtze river. Environ Sci Technol 54(19):11929–11939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01333
Chen X, Strokal M, Van Vliet MTH, Stuiver J, Wang M, Bai Z, Ma L, Kroeze C (2019) Multi-scale modeling of nutrient pollution in the rivers of China. Environ Sci Technol 53(16):9614–9625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07352
Cheng H, Narindri B, Chu H, Whang L (2020) Recent advancement on biological technologies and strategies for resource recovery from swine wastewater. Biores Technol 303:122861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122861
Data on administrative boundaries of Towns in China (2015) Resource and Environment Science Data Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences. http://www.resdc.cn/data.aspx?DATAID=203
Feng Z, Yang Y, You Z (2017) The population and water and land resource carrying capacity of Xiongan new area. Bull Chinese Acad Sci 32(11):1216–1223. https://doi.org/10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.2017.11.006
Gao J, Zhao J, Sun X, Tang X, Zhang W (2002–2018) Hebei province Environment bulletin Hebei provincial Enviornmental Protection Bureau Shi Jiazhuang
Goshu G, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Koelmans AA, de Klein JJM (2020) Assessing seasonal nitrogen export to large tropical lakes. Sci Total Environ 731:139199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139199
Hou Y, Velthof GL, Lesschen JP, Staritsky IG, Oenema O (2017) Nutrient recovery and emissions of ammonia, nitrous oxide, and methane from animal manure in Europe: effects of manure treatment technologies. Environ Sci Technol 51(1):375–383. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b04524
Ji N, Zou R, Jiang Q, Liang Z, Hu M, Liu Y, Yu Y, Wang Z, Wang H (2021) Internal positive feedback promotes water quality improvement for a recovering hyper-eutrophic lake: a three-dimensional nutrient flux tracking model. Sci Total Environ 772:145505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145505
Jin S, Zhang B, Wu B, Han D, Hu Y, Ren C, Zhang C, Wei X, Wu Y, Mol APJ, Reis S, Gu B, Chen J (2020a) Decoupling livestock and crop production at the household level in China. Nat Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-00596-0
Jin X, Bai Z, Oenema O, Winiwarter W, Velthof G, Chen X, Ma L (2020) Spatial planning needed to drastically reduce nitrogen and phosphorus surpluses in China’s agriculture. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00781
Khoshnevisan B, Duan N, Tsapekos P, Awasthi MK, Liu Z, Mohammadi A, Angelidaki I, Tsang DCW, Zhang Z, Pan J, Ma L, Aghbashlo M, Tabatabaei M, Liu H (2021) A critical review on livestock manure biorefinery technologies: sustainability, challenges, and future perspectives. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 135:110033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110033
Lehner B, Grill G (2013) Global river hydrography and network routing: baseline data and new approaches to study the world’s large river systems. Hydrol Process 27(15):2171–2186. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9740
Li A, Strokal M, Bai Z, Kroeze C, Ma L (2019a) How to avoid coastal eutrophication-a back-casting study for the North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 692:676–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.306
Li X, Janssen ABG, de Klein JJM, Kroeze C, Strokal M, Ma L, Zheng Y (2019b) Modeling nutrients in Lake Dianchi (China) and its watershed. Agric Water Manag 212:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.023
Lourinho G, Rodrigues LFTG, Brito PSD (2020) Recent advances on anaerobic digestion of swine wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02793-y
Ma L, Fanghao W, Weifeng Z, Wenqi M, Gerard V, Wei Q, Oene O, Fusuo Z (2013) Environmental assessment of management options for nutrient flows in the food chain in China. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7260–7268. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400456u
Ma L, Guo J, Velthof GL, Li Y, Chen Q, Ma W, Oenema O, Zhang F (2014) Impacts of urban expansion on nitrogen and phosphorus flows in the food system of Beijing from 1978 to 2008. Glob Environ Change 28:192–204
Ma L, Velthof GL, Wang FH, Qin W, Zhang WF, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wei J, Lesschen JP, Ma WQ (2012) Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies and losses in the food chain in China at regional scales in 1980 and 2005. Sci Total Environ 434(18):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.028
MOA (2015a) Zero Growth” policy aims at zero growth in the use of synthetic fertilizers from the year 2020. Ministry of agriculture of People's republic of China. http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/ZZYGLS/2015a03/t2015a0318_4444765.htm
MOA (2015b) National agricultural sustainable development plan (2015b-2030). vol 2015b. Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China
Montalvo S, Huiliñir C, Castillo A, Pagés-Díaz J, Guerrero L (2020) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from liquid swine wastes: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 95(9):2335–2347. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6336
Nancharaiah YV, Venkata Mohan S, Lens PNL (2016) Recent advances in nutrient removal and recovery in biological and bioelectrochemical systems. Bioresour Technol 215:173–185
Oenema O, Tamminga S (2005) Nitrogen in global animal production and management options for improving nitrogen use efficiency. Science in China Series C, Life sciences/Chinese Academy of Sciences 48 Spec No:871–887. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03187126
Qiao S, Yamamoto T, Misaka M, Isaka K, Sumino T, Bhatti Z, Furukawa K (2009) High-rate nitrogen removal from livestock manure digester liquor by combined partial nitritation–anammox process. Biodegradation 21(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9277-8
Rosemarin A, Macura B, Carolus J, Barquet K, Ek F, Järnberg L, Lorick D, Johannesdottir S, Pedersen SM, Koskiaho J, Haddaway NR, Okruszko T (2020) Circular nutrient solutions for agriculture and wastewater—a review of technologies and practices. Current Opin Environ Sustain 45:78–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2020.09.007
SCPRC (2015) Action Plan for Prevention and Control of Water Pollution. The State Council of the People's Republic of China. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2015-04/16/content_9613.htm. Accessed 02–04 2015
SCPRC (2019) The overall development plan for Xiongan New Area (2018–2035). The State Council of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing
Strokal M, Kroeze C, Wang M, Bai Z, Ma L (2016a) The MARINA model (Model to Assess River Inputs of Nutrients to seAs): model description and results for China. Sci Total Environ 562:869–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.071
Strokal M, Kroeze C, Wang M, Ma L (2017) Reducing future river export of nutrients to coastal waters of China in optimistic scenarios. Sci Total Environ 579:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.065
Strokal M, Ma L, Bai Z, Luan S, Kroeze C, Oenema O, Velthof G, Zhang F (2016b) Alarming nutrient pollution of Chinese rivers as a result of agricultural transitions. Environ Res Lett 11:024014. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/2/024014
Strokal M, Kahil T, Wada Y, Albiac J, Bai Z, Ermolieva T, Langan S, Ma L, Oenema O, Wagner F, Zhu X, Kroeze C (2020) Cost-effective management of coastal eutrophication: a case study for the Yangtze river basin. Res Conserv Recycl 154104635-S0921344919305415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104635
Tervahauta T, van der Weijden RD, Flemming RL, Hernández Leal L, Zeeman G, Buisman CJN (2014) Calcium phosphate granulation in anaerobic treatment of black water: a new approach to phosphorus recovery. Water Res 48:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.012
Tong Y, Wang M, Peñuelas J, Liu X, Paerl HW, Elser JJ, Sardans J, Couture R-M, Larssen T, Hu H, Dong X, He W, Zhang W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zeng S, Kong X, Janssen ABG, Lin Y (2020) Improvement in municipal wastewater treatment alters lake nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in populated regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1920759117
Tong Y, Zhang W, Wang X, Couture R-M, Larssen T, Zhao Y, Li J, Liang H, Liu X, Bu X, He W, Zhang Q, Lin Y (2017) Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006. Nat Geosci 10(7):507–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2967
van Puijenbroek PJTM, Beusen AHW, Bouwman AF (2019) Global nitrogen and phosphorus in urban waste water based on the Shared Socio-economic pathways. J Environ Manag 231:446–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.048
Wang C, Liu JX, Makkar HPS, Wei NB, Xu QM (2014) Production level, feed conversion efficiency, and nitrogen use efficiency of dairy production systems in China. Trop Anim Health Prod 46(4):669–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-014-0550-4
Wang M, Kroeze C, Strokal M, van Vliet MT, Ma L (2020) Global change can make coastal eutrophication control in China more difficult. Earth’s Future. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EF001280
Wang M, Ma L, Strokal M, Chu Y, Kroeze C (2018) Exploring nutrient management options to increase nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies in food production of China. Agric Syst 163:58–72
Wang M, Ma L, Strokal M, Ma W, Liu X, Kroeze C (2018b) Hotspots for nitrogen and phosphorus losses from food production in China: a county-scale analysis. Environ Sci Technol 52(10):5782–5791. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06138
Wang M, Strokal M, Burek P, Kroeze C, Ma L, Janssen ABG (2019) Excess nutrient loads to Lake Taihu: opportunities for nutrient reduction. Sci Total Environ 664:865–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.051
Wang Y, Xie Z, Liu S, Wang L, Li R, Chen S, Jia B, Qin P, Xie J (2020b) Effects of anthropogenic disturbances and climate change on riverine dissolved inorganic nitrogen transport. J Adv Model Earth Syst. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002234
Willems J, van Grinsven HJM, Jacobsen BH, Jensen T, Dalgaard T, Westhoek H, Kristensen IS (2016) Why Danish pig farms have far more land and pigs than Dutch farms? Implications for feed supply, manure recycling and production costs. Agric Syst 144:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2016.02.002
Wu L, Liu D, Chen X, Ma C, Wang H, Zhang Y, Xu X, Zhou Y (2021) Nutrient flows in the crop-livestock system in an emerging county in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 120(2):243–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10147-4
Yang J, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Chen X, Bai Z, Li H, Wu Y, Ma L (2021) Seasonal river export of nitrogen to guanting and baiyangdian lakes in the hai he basin. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 126(10):e2020JG005689. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JG005689
Yang J, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Chen X, Bai Z, Li H, Wu Y, Ma L (2021b) Seasonal River Export of Nitrogen to Guanting and Baiyangdian Lakes in the Hai He Basin (have accepted). JGR: Biogeosciences
Yang J, Strokal M, Kroeze C, Wang M, Wang J, Wu Y, Bai Z, Ma L (2019) Nutrient losses to surface waters in Hai He basin: a case study of Guanting reservoir and Baiyangdian lake. Agric Water Manag 213:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.022
Yu J, Ding S, Zhong J, Fan C, Chen Q, Yin H, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2017) Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci Total Environ 592:662–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.219
Yu J, Fan C, Zhong J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Zhang L (2016) Evaluation of in situ simulated dredging to reduce internal nitrogen flux across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Pollut 214:866–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.062
Zhang C (2019) Rebuilding the linkage between livestock and cropland to mitigate agricultural pollution in China. Resources, Conservation & Recycling: 9
Zhang C, Liu S, Wu S, Jin S, Reis S, Liu H, Gu B (2019) Rebuilding the linkage between livestock and cropland to mitigate agricultural pollution in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 144:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.01.011
Zhang X, Zhi X, Chen L, Shen Z (2020) Spatiotemporal variability and key influencing factors of river fecal coliform within a typical complex watershed. Water Res 178:115835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115835
Zhao Z, Qin W, Bai Z, Ma L (2019) Agricultural nitrogen and phosphorus emissions to water and their mitigation options in the Haihe Basin, China. Agric Water Manag 212:262–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.002
Zhu M (2011) Study on Agrieultural NPS Loads of Hai he Basin and Assessment on its Environmental Impact. Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, BeiJing
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFE0103100); Sustainable Resource Management for Adequate and Safe Food Provision project (KNAW-MOST SURE: 258 5160957392-DEELPRJ_1, 2017–2021); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972517); Wageningen Institute for Environment and Climate Research (WIMEK) of Wageningen University; the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572210); President’s International Fellowship Initiative, PIFI of the Chinese Academy of Science (2015VEA025); Hebei Dairy Cattle Innovation Team of Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (HBCT2018120206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Strokal, M., Kroeze, C. et al. Nutrient and manure management to improve water quality in urbanizing Baiyangdian. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 127, 51–67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-022-10232-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-022-10232-2