Abstract
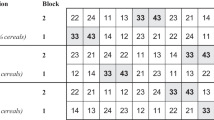
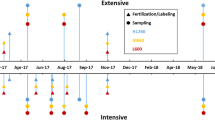
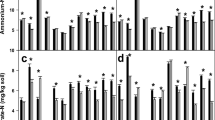
This paper describes the dynamics of soil N mineralization in the experimental intensive dairy farming system ‘De Marke’ on a dry sandy soil in the Netherlands. We hypothesized that knowledge of the effects of crop rotation on soil N mineralization and of the spatial and temporal variability of soil N mineralization in a farming system can be used to better synchronize N application with crop N requirements, and hence to increase the recovery of applied N and to reduce N losses. Soil N mineralization was recorded continuously in the soil layer 0–0.30 m, from 1992 to 2005, using a sequential in situ coring technique on six observation plots, of which two were located in permanent grassland and four in crop rotations with a 3 year grassland phase and an arable phase of 3 or 5 years, dominated by maize. Average annual soil N mineralization was highest under permanent grassland: 381 kg ha−1 and lowest under ≥3rd years arable crops: 184 kg ha−1. In temporary grassland, soil N mineralization increased in the order: 1st year, 2nd year, 3rd year grassland and in arable crops after grassland mineralization decreased in the order: 1st year, 2nd year, ≥3rd years. Total mineral N input, i.e. the sum of N mineralization and mineral N supply to soil, exceeded crop N requirements in 1st year maize and was lower than the requirements in 1st year temporary grassland. N mineralization in winter, outside the growing season, was 77 kg ha−1 in maize and 60 kg ha−1 in grassland. This points at the importance of a suitable catch crop to reduce the susceptibility to N leaching. Temporal and spatial variability of soil N mineralization was high and could not be related to known field conditions. This limits the extent to which N fertilization can be adjusted to soil N mineralization. Variability increased with the magnitude of soil N mineralization. Hence, situations with high soil N mineralization may be associated with high risks for N losses and to reduce these risks a strong build-up of soil organic N should be avoided. This might be achieved, for instance, by fermenting slurry before application on farmland to enhance the fraction mineral N in slurry at the expense of organic N.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts HFM (2000) Resource management in a ‘De Marke’ dairy farming system. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Aarts HFM, Biewinga EE, Van Keulen H (1992) Dairy farming systems based on efficient nutrient management. Neth J Agr Sci 40:285–299
Aarts HFM, Hack M, Hilhorst GJ, Mandersloot F, Meijer A, Middelkoop N, De Vries C, Zaalmink W (1994) Intermediate balance, De Marke 1992–1993. De Marke Report nr. 10, Hengelo, The Netherlands (in Dutch)
Aarts HFM, Habekotté B, Van Keulen H (2000) Groundwater recharge through optimized Intensive dairy farms. J Environ Qual 29:738–743
Abril A, Caucas V, Bucher EH (2001) Reliability of the in situ incubation methods used to assess nitrogen mineralization: a microbiological perspective. Appl Soil Ecol 17:125–130
Binkley D, Hart SC (1989) The components of nitrogen availability assessments in forest soils. Adv Soil Sci 10:57–112
Bolinder MA, Angers DA, Giroux M, Laverdiere MR (1999) Estimating C inputs retained as soil organic matter from corn (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 215:85–91
Boumans LJM, Fraters D, Van Drecht G (2005) Nitrate leaching in agriculture to upper groundwater in the sandy regions of the Netherlands during the 1992–1995 period. Environ Monit Assess 102:225–241
Bushong JT, Norman RJ, Ross WJ (2007) Evaluation of several indices of potentially mineralizable soil nitrogen. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 38:2799–2813
Carton OT, Jarvis SC (2001) N and P cycles in agriculture. In: De Clercq P, Gertsis A, Hofman G, Jarvis SC, Neeteson JJ, Sinabell F (eds) Nutrient management legislation in European countries. Department of Soil Management and Soil Care, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, pp 4–13
Conant RT, Ryan MG, Ågren GI, Birge HE, Davidson EA, Eliasson PE, Evans SE, Frey SD, Giardina GP, Hopkins FM, Hyvönen R, Kirschbaum MUF, Lavallee JM, Leifeld J, Parton WJ, Steinweg JM, Wallenstein MD, Wetterstedt JÁM, Bradford AM (2011) Temperature and soil organic matter decomposition rates: synthesis of current knowledge and a way forward. Global Change Biol 17:3392–3404
Corré WJ, Conijn JG (2004) Turnover of nitrogen in crop residues in grassland. Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Centre, Report 89. 10 pp (in Dutch)
Crohn DM (2006) Optimizing Organic Fertilizer Applications under Steady-State Conditions. J Environ Qual 35:658–669
Cusick PR, Powell JM, Kelling KA (2006) Dairy manure N mineralization estimates from incubations and litterbags. Biol Fert Soils 43:145–152
Elgersma A, Hassink J (1997) Effects of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) on plant and soil nitrogen and soil organic matter in mixtures with perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Plant Soil 197:177–186
Gill K, Jarvis SC, Hatch DJ (1995) Mineralization of nitrogen in long-term pasture soils: effects of management. Plant Soil 172:153–162
Hanselman TA, Graetz DA, Obreza TA (2004) A comparison of In Situ Methods for Measuring Net Nitrogen Mineralization Rates of Organic Soil Amendments. J Environ Qual 33:1098–1105
Hassink J (1992) Effects of soil texture and structure on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in grassland soils. Biol Fert Soils 14:126–134
Hassink J (1996) Voorspellen van het stikstofleverend vermogen van graslandgronden. In: Loonen JWG, Bach-de Wit WEM (eds) Stikstof in beeld. Naar een nieuw bemestingsadvies op grasland. Onderzoek in de mest- en ammoniakproblematiek in de veehouderij 20. DLO, Wageningen, the Netherlands. pp 15–35
Hatch DJ, Jarvis SC, Reynolds SE (1991) An assessment of the contribution of net mineralization to N cycling in grass swards using a field incubation method. Plant Soil 138:23–32
Hatch DJ, Jarvis SC, Parkinson RJ (1998) Concurrent measurements of net mineralization, nitrification, denitrification and leaching from field incubated soil cores. Biol Fert Soils 26:323–330
Hatch DJ, Bhogal A, Lovell RD, Shepherd MA, Jarvis SC (2000) Comparison of different methodologies for field measurement of net nitrogen mineralization in pasture soils under different soil conditions. Biol Fert Soils 32:287–293
Hook PB, Burke IC (1995) Evaluation of Methods for Estimating Net Nitrogen Mineralization in a Semiarid Grassland. Soil Sci Soc Am J 59:831–837
Hosper H (1997) Clearing lakes: an ecosystem approach to the restoration and management of shallow lakes in the Netherlands. Ph.D. thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, the Netherlands. 168 pp
Isaac ME, Timmer VR (2007) Comparing in situ methods for measuring nitrogen mineralization under mock precipitation regimes. Can J Soil Sci 87:39–42
Jarvis SC, Hatch DJ, Lovell RD (2001) An improved soil core incubation method for the field measurement of denitrification and net mineralization using acetylene inhibition. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 59:219–225
Johnston AE (1986) Soil organic matter, effects on soils and crops. Soil Use Manage 2:97–105
Kayser M, Benke M, Isselstein J (2011) Little fertilizer response but high N loss risk of maize growing on a productive organic-sandy soil. Agron Sustain Dev 31:709–718
Nevens F, Reheul D (2002) The nitrogen and non-nitrogen contribution effect of ploughed grass leys on the following arable forage crops: determination and optimum use. Eur J Agron 16:57–74
Pollmer WG, Eberhard D, Klein D, Dhillon BS (1979) Genetic control of nitrogen uptake and translocation in maize. Crop Sci 19:83–86
Raison RJ, Connell MJ, Khanna PK (1987) Methodology for studying dynamics of soil mineral N in situ. Soil Biol Biochem 19:521–530
Ros GH, Temminghoff EJM, Hoffland E (2011) Nitrogen mineralization: a review and meta-analysis of the predictive value of soil tests. Eur J Soil Sci 62:162–173
Schipper LA, Percival HJ, Sparling GP (2004) An approach for estimating when soils will reach maximum nitrogen storage. Soil Use Manage 20:281–286
Schröder JJ, Van Keulen H (1997) Modelling the residual N effect of slurry applied to maize land on dairy farms in The Netherlands. Neth J Agr Sci 45:477–494
Schröder JJ, Van Dijk W, De Groot WJM (1996) Effects of cover crops on the nitrogen fluxes in a silage maize production system. Neth J Agr Sci 44:293–315
Schröder JJ, Aarts HFM, Van Middelkoop JC, De Haan MHA, Schils RLM, Velthof GL, Fraters B, Willems WJ (2005) Limits to the use of manure and mineral fertilizer in grass and silage maize production, with special reference to the EU Nitrates Directive. Report 93, Plant Research International, Wageningen, the Netherlands. 48 pp
Schröder JJ, Aarts HFM, Van Middelkoop JC, Velthof GL, Reijs JW, Fraters B (2009) Nitrates Directive requires limited inputs of manure and mineral fertilizer in dairy farming systems. Report 222, Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Centre. 38 pp
Shepherd MA (1999) The effectiveness of cover crops during eight years of a UK sandland rotation. Soil Use Manage 15:41–48
Steffens G, Vetter H (1984) Stickstoffverlagerung nach Güllendüngung mit und ohne Zwischenfruchtanbau. Landw Forschung Sonderheft 40:355–362
Subler S, Parmelee RW, Allen MF (1995) Comparison of buried bag and PVC core methods for in situ measurement of nitrogen mineralization rates in an agricultural soil. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 26:2369–2381
Tyson KC, Roberts DH, Clement CR, Garwood EA (1990) Comparison of crop yields and soil conditions during 30 years under annual tillage or grazed pasture. J Agric Sci Camb 115:29–40
Van der Meer HG, Baan Hofman T (1989) Contribution of legumes to yield and nitrogen economy of leys on a biodynamic farm. In: Plancquaert P, Hagger R (eds) Legumes farming systems. EEC, Brussels, pp 25–36
Velders GJM, Aben JMM, Van Jaarsveld JA, Van Pul WAJ, De Vries WJ, Van Zanten MC (2010) Grootschalige stikstofdepositie in Nederland. Analyse bronbijdragen op provinciaal niveau. Report 500088007. RIVM, Bilthoven, p 63
Velthof GL (2003) Relaties tussen mineralisatie, denitrificatie en indicatoren voor bodemkwaliteit in landbouwgronden. Alterra Report 769, Wageningen, the Netherlands. 38 pp
Verloop J, Boumans LJM, Van Keulen H, Oenema J, Hilhorst GJ, Aarts HFM, Sebek LBJ (2006) Reducing nitrate leaching to groundwater in an intensive dairy farming system. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 74:59–74
Vertès F, Mary B (2007) Modelling the long term SOM dynamics in fodder rotations with a variable part of grassland. In: Chabbi A (ed) Organic matter dynamics in agro-ecosystems, pp 549–550 17–19 July 2007, INRA, Poitiers, France
Vinther FP (1994) Nitrogen fluxes in a cropped sandy and a loamy soil measured by sequential coring. In: Neeteson JJ, Hassink J (eds) Nitrogen mineralization in agricultural soils. AB-DLO Thema’s 1, AB-DLO, Wageningen/Haren, The Netherlands, pp 111–119
VSN International Ltd. (2012) GenStat, 14th edn. Hemel Hempstead, UK
Whitehead DC (1986) Sources and transformations of organic nitrogen in intensively managed grassland soils. In: Van der Meer HG, Ryden JC, Ennik GC (eds) Nitrogen fluxes in intensive grassland systems. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, the Netherlands. pp 47–58
Whitehead DC (1995) Grassland Nitrogen. CAB International, Wallingford 397 pp
Whitmore AP, Bradburry NJ, Johnson PA (1992) The potential contribution of ploughed grassland to nitrate leaching. Agr Ecosyst Environ 39:221–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Van Keulen: Deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verloop, J., Hilhorst, G.J., Oenema, J. et al. Soil N mineralization in a dairy production system with grass and forage crops. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 98, 267–280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9610-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9610-4