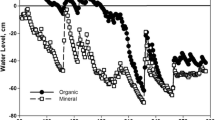
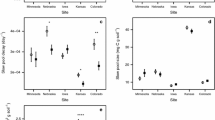
Abstract
Earlier studies by the authors on English soils under grassland strongly supported their hypothesis that soil/plant systems have naturally evolved to conserve nitrogen (N) by having a close match between the dynamics of mineral-N production in soils and the dynamics of plant N requirements. Thus, maximum mineral-N production in soils occurred in spring when plant N requirements were greatest and were very low in mid to late summer. Low temperature and a high C:N ratio of senescing material helped to conserve N in winter, but mobile N was associated with pollution inputs. We test the hypothesis that under the much more arid conditions of Pakistan, soil/plant systems naturally have evolved to conserve mineral-N, especially over the very dry and cooler months between October and February. When soils from a grassland site were incubated at ambient temperatures after removal of plant roots and exclusion of atmospheric N inputs, there was consistent evidence of immobilization of nitrate and immobilization and possibly volatilization of ammonia/ammonium. In the wetter months of July and August, the soil at 0–10 cm depth showed no evidence of significant ammonium-N production in July and only small ammonium production at 10–20 cm depth in August, but was associated with significant nitrate-N immobilization in August. Nitrate leaching only appeared likely towards the end of the rainy season in September. The results strongly suggest that, under grass, the retention of atmospheric N inputs over the long dry periods is regulating the pools of available N in the soils, rather than the N produced by mineralization of soil organic matter.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, F. (2013). Analysis of a historical (1981–2010) temperature record of the Punjab province of Pakistan. Earth Interact. 17, 1–23.
Akhtar, M. S., & Memon, M. (2009). Biomass and nutrient uptake by rice and wheat: a three-way interaction of potassium ammonium and soil type. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41, 2965–2974.
Austin, A. T., Yahdjian, l., Stark, J. M., Belnap, J., Porporato, A., Norton, U., Ravetta, D. A., & Schaeffe, S. M. (2004). Water pulses and biogeochemical cycles in arid and semiarid ecosystems. Oecologia, 141, 221–235.
Ayub, M. R., Ahmad, R., Tanveer, A., Ahmad, H. Z., & Sharar, M. S. (1999). Growth, yield and quality of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) as affected by different levels of NPK application. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2, 80–82.
Bhatti, A., McClean, C. J., & Cresser, M. S. (2013). Does plant uptake or low soil mineral-N production limit mineral-N losses to surface waters and groundwater from soils under grass in summer? Environmental Pollution, 178, 128–134.
Bijay, S., Yadvinder, S., & Sekhon, G. S. (1995). Fertilizer-N use efficiency and nitrate pollution of groundwater in developing countries. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 20, 167–184.
Bremner, J. M., & Tabatabai, M. A. (1972). Use of an ammonia electrode for determination of ammonium in Kjeldahl analysis of soils. Communications in Soil Sciences and Plant Analysis, 3, 71–80.
Buresh, R. J., Austin, E. R., & Craswell, E. T. (1982). Analytical methods in 15N research. Fertilizer Research, 3, 37–62.
Chen, C. R., Xu, Z. H., Zhang, S. L., & Keay, P. (2005). Soluble organic nitrogen pools in forest soils of subtropical Australia. Plant and Soil, 277, 285–297.
Chen, J., Xiao, G., Kuzyakov, Y., Jenerette, G. D., Ma, Y., Liu, W., Wang, Z., & Shen, W. (2017). Soil nitrogen transformation responses to seasonal precipitation changes are regulated by changes in functional microbial abundance in a subtropical forest. Biogeosciences, 14, 2513–2525.
Contosa, A. R., Frey, S. D., & Cooper, A. B. (2011). Seasonal dynamics of soil respiration and N mineralization in chronically warmed and fertilized soils. Ecosphere, 2, 1–21.
Cookson, W. R., Muller, C., O’Brien, P. A., Murphy, D. V., & Grierson, P. F. (2006). Nitrogen dynamics in an Australian semiarid grassland soil. Ecology, 87, 2047–2057.
Corre, M. D., Schnabel, R. R., & Stout, W. L. (2002). Spatial and seasonal variation of gross nitrogen transformations and microbial biomass in a northeastern US grassland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 445–457.
Cui, M., & Caldwell, M. M. (1997). A large ephemeral release of nitrogen upon wetting of dry soil and corresponding root responses in the field. Plant and Soil, 191, 291–299.
Dempsey, R. J., Slaton, N. A., Norman, R. J., & Roberts, T. L. (2017). Ammonia volatilization, rice yield, and nitrogen uptake responses to simulated rainfall and urease inhibitor. Agronomy Journal, 109, 363–377.
Dorana, J. W., Elliottb, E. T., & Paustianb, K. (1998). Soil microbial activity, nitrogen cycling, and long-term changes in organic carbon pools as related to fallow tillage management. Soil Tillage and Research, 49, 3–18.
Ehleringer, J. R. (2001). The productivity of deserts. In J. Roy, B. Saugier, & H. A. Mooney (Eds.), Terrestrial global productivity (pp. 345–362). San Diego: Academic Press.
FAO. (2007). Chapter 3. The fertilizer sector. FAO Corporate Document Repository. Available at http://www.fao.org/docrep/007/y5460e/y5460e07.htm#topofpage. Accessed 21 November 2017.
Farhat, F., Ahmad, A., Safeeq, M., Ali, S., Saleem, F., Hammad, H. M., & Farhad, W. (2014). Changes in precipitation extremes over arid to semiarid and subhumid Punjab, Pakistan. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 116, 671–680.
Fierer, N., & Schimel, J. P. (2002). Effects of drying–rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 777–787.
Follett, R. F. (1992). Fertilizer related pollution issues for managing nutrients. In M. S. Bajwa, N. S. Pasricha, P. S. Sidhu, M. R. Chaudhary, D. K. Benbi, & V. Beri (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Symposium on Nutrient Management for Sustained Productivity, vol. 1 (pp. 227–243). India: Punjab Agriculture University of Ludhiana.
Ford, D. J., Cookson, W. R., Adams, M. A., & Grierson, P. F. (2007). Role of soil drying in nitrogen mineralization and microbial community function in semi-arid grasslands of north-west Australia. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 1557–1569.
Galloway, J. N., Dentener, F. J., Capone, D. G., Boyer, E. W., Howarth, R. W., Seitzinger, S. P., Asner, G. P., Cleveland, C. C., Green, P. A., Holland, E. A., Karl, D. M., Michaels, A. F., Porter, J. H., Townsend, A. R., & Vöosmarty, C. J. (2004). Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry, 70, 153–226.
Gao, Y., & Cheng, J. (2013). Spatial and temporal variations of grassland soil organic carbon and total nitrogen following grazing exclusion in semiarid Loess Plateau, northwest China. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B Soil & Plant Science, 63, 704–711.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle-size analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 1—Physical and mineralogical methods (Vol. 2, pp. 383–411). Madison: SSSA.
Goulding, K. W. T., Bailey, N. J., Bradbury, N. J., & Hargreaves, P. (1998). Nitrogen deposition and its contribution to nitrogen cycling and associated soil processes. New Phytologist, 139, 49–58.
Guntinas, M. E., Leiros, M. C., Traser-Cepeda, C., & Gil-Sotres, F. (2012). Effects of moisture and temperature on net soil nitrogen mineralization: a laboratory study. European Journal of Soil Biology, 48, 73–80.
Homyak, P. M., Allison, S. D., Huxman, T. E., Goulden, M. L., & Treseder, K. K. (2017). Effects of drought manipulation on soil nitrogen cycling: a meta-analysis. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 122, 3260–3272.
Hooper, D. U., & Johnson, L. (1999). Nitrogen limitation in dry land ecosystems: responses to geographical and temporal variation in precipitation. Biogeochemistry, 46, 247–293.
Hussain, A., Murtaza, G., Ghafoor, A., Basra, S. M. A., Qadir, M., & Sabir, M. (2010). Cadmium contamination of soils and crops by long term use of raw effluent, ground and canal waters in agricultural lands. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 12, 851–856.
Joshi, B., Singh, S. D., Devi, B. M., Pathak, H., Sharma, D. K., & Chaudhary, A. (2017). Effect of elevated temperature on soil microbial activity and nitrogen transformations in wheat crop (Triticum aestivum). Indian Journal of Agriculture Sciences, 87, 167–172.
Keeney, D. R., & Nelson, D. W. (1982). Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In A. L. Page (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, agronomy. 9, part 2: chemical and microbiological properties (2nd ed., pp. 643–698). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Leitner, S., Minixhofer, P., Inselsbacher, E., Keiblinger, K. M., Zimmermann, M., & Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. (2017). Short-term soil mineral and organic nitrogen fluxes during moderate and severe drying–rewetting events. Applied Soil Ecology, 114, 28–33.
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Niu, L., Xu, X., & Tian, Y. (2014). Interactive effects of soil temperature and moisture on soil N mineralization in a Stipa krylovii grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Land, 6, 571–580.
Li, X., Shi, H., Xu, W., Liu, W., Wang, X., Hou, L., Feng, F., Yuan, W., Li, L., & Xu, H. (2015). Seasonal and spatial variations of bulk nitrogen deposition and the impacts on the carbon cycle in the arid/semiarid grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. PLoS One, 10, e0144689.
Lovett, G. M., & Rueth, H. (1999). Soil nitrogen transformations in beech and maple stands along a nitrogen deposition gradient. Ecological Applications, 9, 1330–1344.
Macduff, J. H., Jarvis, S. C., & Roberts, D. H. (1990a). Nitrate leaching under grazed grassland: measurements using ceramic cup soil solution samplers. In R. Merckx, H. Vereecken, & K. Vlassak (Eds.), Fertilization and the environment (pp. 72–78). Leuven: Leuven University Press.
Macduff, J. H., Steenvoorden, J. H. A. M., Scholefield, D., & Cuttle, S. P. (1990b). Nitrate leaching from grazed grassland, Proceedings of the 13th General Meeting, European Grassland Federation, 2, 18–24.
Mian, I. A., Riaz, M., & Cresser, M. S. (2008). What controls the nitrate flush when air dried soils are rewetted? Chemistry & Ecology, 24, 259–267.
Peterjohn, W. T., & Schlesinger, W. H. (1990). Nitrogen loss from deserts in the south-western United States. Biogeochemistry, 10, 67–79.
Phoenix, G. K., Hicks, W. K., Cinderby, S., Kuylenstierna, J. C. I., Stock, W. D., Dentener, F. J., Giller, K. E., Austin, A. T., Lefroy, R. D. B., Gimeno, B. S., Ashmore, M. R., & Ineson, P. (2006). Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in world biodiversity hotspots: the need for a greater global perspective in assessing n deposition impacts. Global Change Biology, 12, 470–476.
Phoenix, G. K., Emmett, B. A., Britton, A. J., Caporn, S. J. M., Dise, N. B., Helliwell, R., Jones, L., Leake, J. R., Leith, I. D., Sheppard, L. J., Sowerby, A., Pilkington, M. G., Rowe, E. C., Ashmore, M., & Power, S. A. (2012). Impacts of atmospheric nitrogen deposition: responses of multiple plant and soil parameters across contrasting ecosystems in long-term field experiments. Global Change Biology, 18, 1197–1215.
Pointing, S. B., & Belnap, J. (2012). Microbial colonization and controls in dryland systems. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 551–562.
Rayment, G. E., & Higginson, F. R. (1992). Soil pH. In Australian Laboratory Handbook of Soil and Water Chemical Methods (pp. 17–18). Melbourne: Inkata Press.
Reynolds, B., & Edwards, A. (1995). Factors influencing dissolved nitrogen concentrations and loadings in upland streams of the UK. Agricultural Water Management, 27, 181–202.
Riaz, M., Mian, I. A., & Cresser, M. S. (2008). Extent and causes of 3D spatial variations in potential N mineralization and the risk of ammonium and nitrate leaching from a N-impacted permanent grassland near York, UK. Environmental Pollution, 156, 1075–1082.
Riaz, M., Mian, I. A., & Cresser, M. S. (2009). Controls on inorganic N species transformations and potential leaching in freely drained sub-soils of heavily N-impacted acid grassland. Biogeochemistry, 92, 263–279.
Saetre, P., & Stark, J. M. (2005). Microbial dynamics and carbon and nitrogen cycling following re-wetting of soils beneath two semi-arid plant species. Oecologia, 142, 247–260.
Satti, P., Mazzarino, M. J., Gobbi, M., Funes, F., Roselli, L., & Fernandez, H. (2003). Soil N dynamics in relation to leaf litter quality and soil fertility in north-western Patagonian forests. Journal of Ecology, 91, 173–181.
Schwinning, S., Starr, B. I., Wojcik, N. J., Miller, M. E., Ehleringer, J. E., & Sanford Jr., R. L. (2005). Effects of nitrogen deposition on an arid grassland in the Colorado Plateau cold desert. Rangeland Ecology & Management, 58, 565–574.
Silver, W. L., Ryals, R., & Eviner, V. (2010). Soil carbon pools in California’s annual grassland ecosystems. Rangeland Ecology and Management, 63, 128–136.
Singh, Y., Singh, B., & Timsina, J. (2005). Crop residue management for nutrient cycling and improving soil productivity in rice-based cropping systems in the tropics. Advances in Agronomy, 85, 269–407.
Sinsabaugh, R. L., Belnap, J., Rudgers, J., Kuske, C. R., Martinez, N., & Sandquist, D. (2015). Soil microbial responses to nitrogen addition in arid ecosystems. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 819.
Stevens, C. J., Dise, N. B., Mountford, J. O., & Gowing, D. J. (2004). Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science, 303, 1876–1879.
Tahir, M. A., & Rasheed, H. (2008). Distribution of nitrate in the water resources of Pakistan. African Journal of Environmental Sciences & Technology, 11, 397–403.
Tian, Y., Quyang, H., Gao, Q., Xu, X., Song, M., & Xu, X. (2010). Responses of soil nitrogen mineralization to temperature and moisture in alpine ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 218–224.
Vitousek, P. M., Aber, J. D., Howarth, R. W., Likens, G. E., Matson, P. A., Schindler, D. W., Schlesinger, W. H., & Tilman, D. G. (1997). Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecological Applications, 7, 737–750.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 34, 29–38.
Wang, S., Nan, J., Shi, C., Fu, Q., Gao, S., Wang, D., Cui, H., Saiz-Lopez, A., & Zhou, B. (2015). Atmospheric ammonia and its impacts on regional air quality over the megacity of Shanghai, China. Scientific Reports, 5, 15842.
Whitehead, D. C., & Raistrick, N. (1991). Effects of some environmental factors on ammonia volatilization from simulated livestock urine applied to soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 11, 279–284.
Zhang, X., Wang, Q., Li, L., & Han, X. (2008). Seasonal variations in nitrogen mineralization under three land use types in a grassland landscape. Acta Geologica, 34, 322–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatti, A., Ahmad, J., Qasim, M. et al. Effects of anthropogenic nitrogen deposition on soil nitrogen mineralization and immobilization in grassland soil under semiarid climatic conditions. Environ Monit Assess 190, 490 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6865-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6865-2