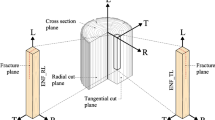
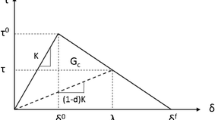
Abstract
The characterization and modeling of Ceiba plywood delamination requires extensive experimental and numerical study. A data reduction scheme, based on the compliance method and the concept of equivalent crack, is utilized. This method has two main advantages over conventional methodologies: it does not require crack monitoring during propagation and takes into account the effect of the fracture process zone at the crack tip. The characterization of delamination and the mechanical behavior of adhesive joint are influenced not only by the adhesive properties but also by the characteristics of the interface. Various modeling methods have been proposed to characterize the delamination of laminated materials. Among the most widely used methods is the cohesive zone model, which is based on fracture mechanics and damage theory and allows for an adequate prediction of the onset and propagation of the delamination simultaneously. This method consists of introducing a cohesion law in finite element modeling. Often, the determination of these parameters is obtained iteratively by matching the numerical results with the experimental results. In this study, the cohesive parameters of the bilinear traction–separation laws in each pure mode were determined. This identification was achieved through the design of experiments method and the Kriging metamodel. A finite element modeling of the Ceiba plywood delamination was then performed. The experimental tests carried out make it possible to assess the delamination resistance under mode I, mode II and mixed mode I + II loading. Following the description of the experimental procedure, the experimental and numerical results are presented and compared. Finally, the response to the delamination was represented by a semi-empirical criterion and an analysis of fracture surfaces was performed and interpreted.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfano G, Crisfield MA (2001) Finite element interface models for the delamination analysis of laminated composites: mechanical and computational issues. Int J Num Methods Eng 50:1701–1736. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.93
Andrew S, Don K, Liyong T (1998) A damage zone model for the failure analysis of adhesively bonded joints. Int J Adhes Adhes 18(6):385–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7496(98)00024-4
Bažant ZP (1985) Mechanics of fracture and progressive cracking in concrete structures. In: Sih GC, DiTommaso A (eds) Fracture mechanics of concrete: structural application and numerical calculation. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 1–94
Benzeggagh ML, Kenane M (1996) Measurement of mixed-mode delamination fracture toughness of unidirectional glass/epoxy composites with mixed-mode bending apparatus. Compos Sci Technol 56:439–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-3538(96)00005-X
Campilho RDSG, de Moura MFSF, Domingues JJMS (2005) Modelling single and double-lap repairs on composite materials. Compos Sci Technol 65:1948–1958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.04.007
Carlsson LA, Gillespie JW, Pipes RB (1986) On the analysis and design of the end notched flexure (ENF) specimen for mode II testing. J Compos Mater 20:594–604. https://doi.org/10.1177/002199838602000606
De Moura MFSF, Morais JJL, Dourado N (2008) A new data reduction scheme for mode I wood fracture characterization using the double cantilever beam test. Eng Fract Mech 75(13):3852–3865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2008.02.006
Dourado N, Morel S, de Moura MFSF, Valentin G, Morais J (2008) Comparison of fracture properties of two wood species through cohesive crack simulations. Composite A 39:415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.08.025
EL Mustaphaoui A, Chouaf A, Chergui M, Kimakh K (2019) Modeling of macroscopic delamination of plywood using design of experiments method. J Indian Acad Wood Sci 16:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13196-019-00240-1
Hashemi S, Kinloch AJ, Williams JG (1990) Mechanics and mechanisms of delamination in a poly(ether sulphone)—fibre composite. Compos Sci Technol 37(4):429–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-3538(90)90013-u
Höwer D, Lerch BA, Bednarcyk BA, Pineda EJ, Reese S, Simon J-W (2018) Cohesive zone modeling for mode I facesheet to core delamination of sandwich panels accounting for fiber bridging. Compos Struct 183:568–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.07.005
Irwin GR (1957) Analysis of stresses and strains near the end of a crack traversing a plate. J Appl Mech Trans ASME 24:351–369
Griffith AA (1921) VI. The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A 221:163–198. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1921.0006
Kinloch AJ, Wang Y, Williams JG, Yayla P (1993) The mixed-mode delamination of fibre composite materials. Compos Sci Technol 47:225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-3538(93)90031-B
Lee MJ, Cho TM, Kim WS, Lee BC, Lee JJ (2010) Determination of cohesive parameters for a mixed-mode cohesive zone model. Int J Adhes Adhes 30:322–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2009.10.005
Leguillon D (2002) Strength or toughness? A criterion for crack onset at a notch. Eur J Mech A 21:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0997-7538(01)01184-6
Li S, Thouless MD, Waas AM, Schroeder JA, Zavattieri PD (2005) Use of mode-I cohesive-zone models to describe the fracture of an adhesively-bonded polymer-matrix composite. Compos Sci Technol 65(2):281–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.07.009
Manshadi BD, Vassilopoulos AP, Botsis J (2013) A combined experimental/numerical study of the scaling effects on mode I delamination of GFRP. Compos Sci Technol 83:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.04.016
Morel S, Bouchaud E, Schmittbuhl J, Valentin G (2002) R-curve behavior and roughness development of fracture surfaces. Int J Fract 114(4):307–325. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015727911242
Morel S, Lespine C, Coureau JL, Planas J, Dourado N (2010) Bilinear softening parameters and equivalent LEFM R-curve in quasibrittle failure. Int J Solids Struct 47:837–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.11.022
Orifici AC, Herszberg I, Thomson RS (2008) Review of methodologies for composite material modelling incorporating failure. Compos Struct 86:194–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2008.03.007
Pereira FAM, Morais JJL, Dourado N, de Moura MFSF, Dias MIR (2011) Fracture characterization of bone under mode II loading using the end loaded split test. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4:1764–1773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1586-6
Pipes RB, Pagano NJ (1970) Interlaminar stresses in composite laminates under uniform axial extension. J Compos Mater 4(4):538–548. https://doi.org/10.1177/002199837000400409
Sacks J, Welch WJ, Mitchel TJ (1989) Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat Sci 4(4):409–35
Seeger M (2004) Gaussian processes for machine learning. Int J Neural Syst 14(2):69–106
Shanmugam V, Penmetsa R, Tuegel E, Clay S (2013) Stochastic modeling of delamination growth in unidirectional composite DCB specimens using cohesive zone models. Compos Struct 102:38–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.01.020
Silva MAL, Morais JJL, de Moura MFSF, Lousada JL (2007) Mode II wood fracture characterization using the ELS test. Eng Fract Mech 74(14):2133–2147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2006.10.012
Stanzl-Tschegg SE, Tan DM, Tschegg EK (1995) New splitting method for wood fracture characterization. Wood Sci. Technol. 29:31–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00196930
Tran V-D, Oudjene M, Méausoone P-J (2015) Experimental and numerical analyses of the structural response of adhesively reconstituted beech timber beams. Compos Struct 119:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.08.013
Triboulot P, Jodin P, Pluvinage G (1982) Mesure des facteurs d’intensité de contrainte critiques et des taux de restitution d’énergie dans le bois sur éprouvettes entaillées. Ann Sci for 39(1):63–76. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:19820104
Trinca AJ, Gonçalves R (2011) Comparison of elastic constants of wood determined by ultrasonic wave propagation and static compression testing. Wood Fiber Sci 43:64–75
Wang H, Vu-Khanh T (1996) Use of end-loaded-split (ELS) test to study stable fracture behaviour of composites under mode II loading. Compos Struct 36:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(96)00066-9
Wang Y, Williams JG (1992) Corrections for mode II fracture toughness specimens of composite materials. Compos Sci Technol 43:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-3538(92)90096-L
Williams M (1956) On the stress distribution at the base of a stationary crack. J Appl Mech 24(1):109–114
Yao L, Alderliesten RC, Benedictus R (2016) The effect of fibre bridging on the Paris relation for mode I fatigue delamination growth in composites. Compos Struct 140:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.12.027
Yoshihara H, Kawamura T (2006) Mode I fracture toughness estimation of wood by DCB test. Composites A 37:2105–2113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.12.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Equation 3 can be expressed as,
where the coefficients \(\alpha\), \(\beta\) and \(\gamma\) are respectively
Using the Matlab®software and only keeping the real solution it gives,
With
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Moustaphaoui, A., Chouaf, A. & Kimakh, K. Experimental and numerical study of the delamination of Ceiba plywood under mode I, mode II and mixed-mode (I + II) loading using the DCB, ELS and MMF tests. Int J Fract 231, 1–20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-021-00557-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-021-00557-4