Abstract
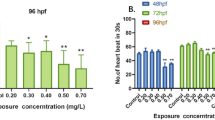
Fenpropathrin has been a commonly used insecticide to control agricultural and household insects over a few decades. Up to now, fenpropathrin residue in soil and water has been often determined due to its widespread use, which poses serious threat to environment and aquatic organisms. The potential of fenpropathrin to affect aquatic lives is still poorly understood. In this study, we used zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo as an experimental model system to evaluate the toxicity of fenpropathrin to the development of zebrafish nervous system. Zebrafish embryos were separately exposed to fenpropathrin at the dose of 0.016 mg/L, 0.032 mg/L, 0.064 mg/L, starting at 6 h post-fertilizationhpf (hpf) up to 96 hpf. The results showed that fenpropathrin exposure gives rise to physiological, behavioral, and neurodevelopmental impairments in zebrafish embryos, including enhanced acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, abnormal swimming behavior, karyopyknosis in brain cells, increased intercellular space, and uneven migration of neuron in brain area. In addition, the expressions of genes concerning neurodevelopment and neurotransmitter system were inhibited following fenpropathrin exposure. We also found that fenpropathrin exposure distinctly induced oxidative stress by increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and inhibiting the production of antioxidant enzymes catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Expectedly, some apoptosis-associated genes were induced and the apoptosis appeared in the brain and heart cells of zebrafish embryos. Moreover, fenpropathrin exposure also inhibited the expressions of genes in Nrf2 signaling pathway, such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and SOD. In summary, the results of this study indicate that oxidative stress-triggered apoptosis may be an underlying fundamental of fenpropathrin-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish embryos.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article.
References
Alm H, Kultima K, Scholz B, Nilsson A, Andrén PE, Fex-Svenningsen A, Dencker L, Stigson M (2008) Exposure to brominated flame retardant PBDE-99 affects cytoskeletal protein expression in the neonatal mouse cerebral cortex. Neurotoxicol 29(4):628–637
Amoh Y, Li L, Katsuoka K, Penman S, Hoffman RM (2005) Multipotent nestin-positive, keratin-negative hair-follicle bulge stem cells can form neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(15):5530–5534
Azizullah A, Richter P, Häder DP (2011) Comparative toxicity of the pesticides carbofuran and malathion to the freshwater flagellate Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicol 20(6):1442–1454
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98:641–653
Behra M, Cousin X, Bertrand C, Vonesch JL, Biellmann D, Chatonnet A, Strähle U (2002) Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat Neurosci 5:111–118
Berg DA, Su Y, Jimenez-Cyrus D, Patel A, Huang N, Morizet D, Lee S, Shah R, Ringeling FR, Jain R, Epstein JA, Wu QF, Canzar S, Ming GL, Song H, Bond AM (2019) A common embryonic origin of stem cells drives developmental and adult neurogenesis. Cell 177(3):654–668
Besse A, Wu P, Bruni F, Donti T, Graham BH, Craigen WJ, McFarland R, Moretti P, Lalani S, Scott KL, Taylor RW, Bonnen PE (2015) The GABA transaminase, ABAT, is essential for mitochondrial nucleoside metabolism. Cell Metab 21:417–427
Blader P, Plessy C, Strähle U (2003) Multiple regulatory elements with spatially and temporally distinct activities control neurogenin1 expression in primary neurons of the zebrafish embryo. Mech Dev 120:211–218
Bond CE, Patel P, Crouch L, Tetlow N, Day T, Abu-Hayyeh S, Williamson C, Greenfield SA (2006) Astroglia up-regulate transcription and secretion of ‘readthrough’ acetylcholinesterase following oxidative stress. Eur J Neurosci 24(2):381–386
Cheng B, Jiang F, Su M, Zhou L, Zhang H, Cao Z, Liao X, Xiong G, Xiao J, Liu F, Lu H (2020) Effects of lincomycin hydrochloride on the neurotoxicity of zebrafish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110725
Deng R, Li W, Guan Z, Zhou JM, Wang Y, Mei YP, Li MT, Feng GK, Huang W, Liu ZC, Han Y, Zeng YX, Zhu XF (2006) Acetylcholinesterase expression mediated by c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase pathway during anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 25(53):7070–7077
Deng X, Gao F, Flagg T, Anderson J, May WS (2020) Bcl2’s flexible loop domain regulates p53 binding and survival. Mol Cell Biol 40:e00457-e520
Denholm I, Devine GJ, Horsberg TE, Sevatdal S, Fallang A, Nolan DV, Powell R (2002) Analysis and management of resistance to chemotherapeutants in salmon lice, lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae). Pest Manag Sci 58(6):528–36
Fang H, Wu Y, Guo J, Rong J, Ma L, Zhao Z, Zuo D, Peng S (2012) T-2 toxin induces apoptosis in differentiated murine embryonic stem cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Apoptosis 17:895–907
Gaweł S, Wardas M, Niedworok E, Wardas P (2004) Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad Lek 57(9–10):453–455
González EA, Carty DR, Tran FD, Cole AM, Lein PJ (2018) Developmental exposure to silver nanoparticles at environmentally relevant concentrations alters swimming behavior in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol Chem 37:3018–3024
Grassi E, Santoro R, Umbach A, Grosso A, Oliviero S, Neri F, Conti L, Ala U, Provero P, DiCunto F, Merlo GR (2019) Choice of alternative polyadenylation sites, mediated by the RNA-binding protein Elavl3, plays a role in differentiation of inhibitory neuronal progenitors. Front Cell Neurosci 12:518
Hwang J, Jin J, Jeon S, Moon SH, Park MY, Yum DY, Kim JH, Kang JE, Park MH, Kim EJ, Pan JG, Kwon O, Oh GT (2020) SOD1 suppresses pro-inflammatory immune responses by protecting against oxidative stress in colitis. Redox Biol 37:101760
Jaremek M, Nieradko-Iwanicka B (2020) The effect of subacute poisoning with fenpropathrin on mice kidney function and the level of interleukin 1β and tumor necrosis factor α. Mol Biol Rep 47:4861–4865
Kanawi E, Budd R, Tjeerdema RS (2013) Environmental fate and ecotoxicology of fenpropathrin. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 225:77–93
Kim J, Oh H, Ryu B, Kim U, Lee JM, Jung CR, Kim CY, Park JH (2018) Triclosan affects axon formation in the neural development stages of zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 236:304–312
Kouzayha A, Al Ashi A, Al Akoum R, Al Iskandarani M, Budzinski H, Jaber F (2013) Occurrence of pesticide residues in Lebanon’s water resources. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:503–509
Krishnan M, Kim DK, Gie Kim S, Kang SC (2019) Thymol exposure mediates pro-oxidant shift by regulating Nrf2 and apoptotic events in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 65:1–8
Langheinrich U (2003) Zebrafish: a new model on the pharmaceutical catwalk. BioEssays 25(9):904–912
Li H, Cheng F, Wei Y, Lydy MJ, You J (2017) Global occurrence of pyrethroid insecticides in sediment and the associated toxicological effects on benthic invertebrates: An overview. J Hazard Mater 324:258–271
Li H, Zhao F, Cao F, Teng M, Yang Y, Qiu L (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction-based cardiotoxicity and neurotoxicity induced by pyraclostrobin in zebrafish larvae. Environ Pollut 251:203–211
Li VW, Tsui MP, Chen X, Hui MN, Jin L, Lam RH, Yu RM, Murphy MB, Cheng J, Lam PK, Cheng SH (2016) Effects of 4-methylbenzylidene camphor (4-MBC) on neuronal and muscular development in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:8275–8285
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lu DL, Ma Q, Sun SX, Zhang H, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) Reduced oxidative stress increases acute cold stress tolerance in zebrafish. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 235:166–173
Manjunatha B, Park SH, Kim K, Kundapur RR, Lee SJ (2018) Pristine graphene induces cardiovascular defects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryogenesis. Environ Pollut 243:246–254
McIntyre JK, Davis JW, Incardona JP, Stark JD, Anulacion BF, Scholz NL (2014) Zebrafish and clean water technology: assessing soil bioretention as a protective treatment for toxic urban runoff. Sci Total Environ 500–501:173–180
Mohamed AA, Abdellatief SA, Khater SI, Ali H, Al-Gabri NA (2019) Fenpropathrin induces testicular damage, apoptosis, and genomic DNA damage in adult rats: protective role of camel milk. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:548–558
Novoa B, Figueras A (2012) Zebrafish: model for the study of inflammation and the innate immune response to infectious diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 946:253–275
Qian H, Liu G, Lu T, Sun L (2018) Developmental neurotoxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa in the early life stages of zebrafish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:35–41
Scholz S, Fischer S, Gündel U, Küster E, Luckenbach T, Voelker D (2008) The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment–applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 15:394–404
Shang CF, Mu Y, Du JL (2015) Zebrafish swimming into neuroscience research: a visible mind in a transparent brain. SCIENTIA SINICA Vitae 45:223–236
Shen XM, Liao CY, Lu XP, Wang Z, Wang JJ, Dou W (2016) Involvement of Three Esterase Genes from Panonychus citri (McGregor) in Fenpropathrin Resistance. Int J Mol Sci 17(8):1361
Stadnicka-Michalak J, Bramaz N, Schönenberger R, Schirmer K (2021) Predicting exposure concentrations of chemicals with a wide range of volatility and hydrophobicity in different multi-well plate set-ups. Sci Rep 11(1):4680
Tang W, Wang D, Wang J, Wu Z, Li L, Huang M, Xu S, Yan D (2018) Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 191:990–1007
Wang H, Meng Z, Liu F, Zhou L, Su M, Meng Y, Zhang S, Liao X, Cao Z, Lu H (2020a) Characterization of boscalid-induced oxidative stress and neurodevelopmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Chemosphere 238:124753
Wang J, Zhang H, Zheng X, Liu R, Zong W (2020b) In vitro toxicity and molecular interacting mechanisms of chloroacetic acid to catalase. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109981
Weston DP, Holmes RW, You J, Lydy MJ (2005) Aquatic toxicity due to residential use of pyrethroid insecticides. Environ Sci Technol 39(24):9778–9784
Xia M, Wang X, Xu J, Qian Q, Gao M, Wang H (2021) Tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate exposure to zebrafish causes neurodevelopmental toxicity and abnormal locomotor behavior. Sci Total Environ 758:143694
Xu M, Cui Z, Zhao L, Hu S, Zong W, Liu R (2018) Characterizing the binding interactions of PFOA and PFOS with catalase at the molecular level. Chemosphere 203:360–367
Zhang Z, Yang L, Wang B, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Li D, Zhang S, Gao H, Wang X (2017) Protective role of liriodendrin in mice with dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 52:203–210
Zhu XY, Wu YY, Xia B, Dai MZ, Huang YF, Yang H, Li CQ, Li P (2020) Fenobucarb-induced developmental neurotoxicity and mechanisms in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol 79:11–19
Funding
This work is supported by the earmarked fund for the Project Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31960735, 32160871, and 32160872), Jiangxi Agriculture Research System (JXARS-06), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M662279), and Jiangxi Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019KY43, 2020RC22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TY conducted and designed experiment. XX, HM, XH, YL, HZ, JL, JG, and MX analyzed the results; CH wrote the manuscript; DL revised the manuscript and supervised this study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that all experiments involving zebrafish were ethical. All of our experiments were conducted in compliance with the standard ethical guidelines and under control of Nanchang University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, T., Xu, X., Mao, H. et al. Fenpropathrin exposure induces neurotoxicity in zebrafish embryos. Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 1539–1554 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01134-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01134-9