Abstract
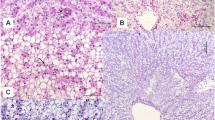
Due to the wide use of glyphosate (GLY) in soybean cultivation, their residues in the environment may affect non-target organisms such as fish, developing toxic effects. Despite GLY being widely used in Brazil, there are few studies comparing the effects of commercial formulations in native freshwater fish species. Silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) were exposed to three different commercial formulations of GLY 48 % (Orium®, Original® and Biocarb®) at 0.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mg/L for 96 h. The effects in thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and histological alterations were analysed in the liver, whereas alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were studied in the plasma. In the liver, TBARS levels increased and CAT decreased in all treatments and herbicides tested in comparison with the control group. The SOD increased at 2.5 mg/L of Orium®, Original® and 5.0 mg/L Orium® and Biocarb®, whereas GST increased at 2.5 mg/L Orium® and decreased at 2.5 mg/L Biocarb® when compared to the control group. The main histopathological alterations in hepatic tissue were vacuolisation, leucocyte infiltration, degeneration of cytoplasm and melanomacrophage in all GLY treatments. The ALT decreased after exposure to 2.5 mg/L of Biocarb® and AST increased at 2.5 mg/L of Orium®, Original® and 5.0 mg/L of Biocarb® in comparison with the control group. In summary, the oxidative damage generated by GLY may have caused the increased formation of free radicals that led to the histological alterations observed in hepatocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antón FA, Laborda E, Ariz M (1994) Acute toxicity of the herbicide glyphosate to fish. Chemosphere 28:745–753. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(94)90228-3
Antunes MIPP, Spurio RS, Godoi DA (2008) Cloridrato de benzocaína na anestesia de carpas (Cyprinus carpio). Semina Cienc Agrár 29:151–156. doi:10.5433/1679-0359.2008v29n1p151
Aparicio VC, Gerónimo ED, Marino D et al (2013) Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminimethyl-phosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 93:1866–1873. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.041
Ayoola SO (2008) Toxicity of glyphosate herbicide on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) juvenile. Afr J Agric Res 3:825–834 (Article Number: 6E4299538453)
Baldisserotto B (2009) Piscicultura continental no Rio Grande do Sul: situação atual, problemas e perspectivas para o futuro. Cienc Rural 39:291–299. doi:10.1590/S0103-84782008005000046
Barcellos LJG, Kreutz LC, Quevedo RM et al (2004) Nursey rearing of jundiá, Rhamdia quelen (Quoy and Gaimard) in cages: cage type, stocking density and stress response to confinement. Aquaculture 232:383–394. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00545-3
Bradford MMA (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brausch MJ, Smith NP (2007) Toxicity of three polyethoxylated tallowamine surfactant formulations to laboratory and field collected fairy shrimp, Thamnocephalus platyurus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:217–221. doi:10.1007/s00244-006-0151-y
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–309. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(78)52032-6
Capkin E, Terzi E, Boran H et al (2010) Effects of some pesticides on the vital organs of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Tissue Cell 42:376–382. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2010.10.001
Cattaneo R, Loro VL, Spanevello R et al (2008) Metabolic and histological parameters of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to commercial formulation of 2,4-D (dichlorophenoxiacetic acid) herbicide. Pestic Biochem Physiol 92:133–137. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2008.07.004
Cattaneo R, Clasen B, Loro VL et al (2011) Toxicological responses of Cyprinus carpio exposed to a commercial formulation containing glyphosate. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:597–602. doi:10.1007/s00128-011-0396-7
Crestani M, Menezes C, Glusczak L et al (2006) Effects of clomazone herbicide on hematological and some parameters of protein and carbohydrate metabolism of silver catfish Rhamdia quelen. Ecotoxicol Environ Toxicol 65:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.06.008
Crestani M, Menezes C, Glusczak L et al (2007) Effects of clomazone herbicide on biochemical and histological aspects of silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) and recovery pattern. Chemosphere 67:2305–2311. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.090.70
Ferreira D, Motta AC, Kreutz LC et al (2010) Assessment of oxidative stress in Rhamdia quelen exposed to agrochemicals. Chemosphere 79:914–921. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.03.024
Giesy JP, Dobson S, Solomon KR (2000) Ecotoxicological risk assessment for Roundup® herbicide. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 16:35–120. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-1156-3_2
Glusczak L, Loro VL, Pretto A et al (2011) Acute exposure to glyphosate herbicide affects oxidative parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61:624–630. doi:10.1007/s00244-011-9652-4
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jacoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferase, the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hidalgo C, Rios C, Hidalgo M et al (2004) Improved coupled-column liquid chromatographic method for the determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1035:153–157. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.02.044
Hose JE, Mcgurk MD, Marty GD et al (1996) Sublethal effects of the Exxon Valdez oil spill on herring embryos and larvae: morphological, cytogenetic, and histopathological assessment 1989–1991. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:2355–2365
Hued AC, Oberhofer S, Bistoni MA (2012) Exposure to a commercial glyphosate formulation (Roundup®) alters normal gill and liver histology and affects male sexual activity of Jenynsia multidentata (Anablepidae, Cyprinodontiformes). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62:107–117. doi:10.1007/s00244-011-9686-7
Jiraungkoorskul W, Upatham ES, Kruatrachue M et al (2003) Biochemical and histophatological effects of glyphostate herbicide on nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ Toxicol 18:260–267. doi:10.1002/tox.10123
Kreutz LC, Barcellos LJG, Silva TO et al (2008) Acute toxicity test for agricultural pesticides on silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) fingerlings. Cienc Rural 38:1050–1055. doi:10.1590/S0103-84782008000400022
Kumar N, Sharma R, Tripathi G et al (2014) Cellular metabolic, stress and histological response on exposure to acute toxicity of endosulfan in tilapia (Oreochomis mossambicus). Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.22026
Langiano VC, Martinez CBR (2008) Toxicity and effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Physiol 147:222–231. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.09.009
Mela M, Guiloski IC, Doria HB et al (2013) Effects of the herbicide atrazine in neotropical catfish (Rhamdia quelen). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 93:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.03.026
Menezes CC, Fonseca MB, Loro VL et al (2011) Roundup effects on oxidative stress parameters and recovery pattern of Rhamdia quelen. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:665–671. doi:10.1007/s00244-010-9574-6
Michalany J (1980) Técnica histológica em Anatomia Patológica, com instruções para o cirurgião, enfermeira e citotécnico. EPU, São Paulo, p 277p
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the auto-oxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Modesto KA, Martinez CBR (2010a) Effects of Roundup Transorb® on fish: hematology, antioxidant defenses and acetylcholineserase activity. Chemosphere 81:781–787. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.07.005
Modesto KA, Martinez CBR (2010b) Roundup® causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere 78:294–299. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.047
Moreno NC, Sofia SH, Martinez CBR (2014) Genotoxic effects of the herbicide Roundup Transorb® and its active ingredient glyphosate on the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:448–454. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.12.012
Nelson DP, Kiesow LA (1972) Enthalpy of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase at 25 °C (with molar extinction coefficients of H2O2 solutions in the UV). Anal Biochem 49:474–478. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(72)90451-4
Pesce S, Fajon C, Bardot C et al (2008) Longitudinal changes in microbial planktonic communities of a French river in relation to pesticide and nutrients inputs. Aquat Toxicol 86:352–360. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.11.016
Poleksic V, Mitrovic-Tutundzic V (1994) Fish gills as a monitor of sublethal and chronic effects of pollution. In: Müller R, Lloyd R (eds) Sublethal and chronic effects of pollutants on freshwater fish. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, pp 339–352
Pretto A, Loro VL, Menezes C et al (2011) Commercial formulation containing quinclorac and metsulfuron-methyl herbicides inhibit acetylcholinesterase and induce biochemical alterations in tissues of Leporinus obtusidens. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:336–341. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.10.003
Ramírez-Duarte WF, Rondón-Barrangán IS, Eslava-Mocha PR (2008) Acute toxicity and histopathological alterations of Roundup® herbicide on “cachama blanca” (Piaractus brachypomus). Pesqui Vet Bras 28:547–554. doi:10.1590/S0100-736X2008001100002
Salbego J, Pretto A, Gioda CR et al (2010) Herbicide formulation with glyphosate affects growth, acetycholinesterase activity and metabolic and hematological parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:740–745. doi:10.1007/s00244-009-9464-y
Salbego J, Pretto A, Silva VMM et al (2014) Glyphosate on digestive enzymes activity in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Cienc Rural 44:1603–1607. doi:10.1590/0103-8478cr20131399
Sarkar B, Chatterjee A, Adhikari S et al (2005) Carbofuran and cypermethrin-induced histophatological alterations in liver of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) and its recovery. J App Ichthyol 21:131–135. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0426.2004.00590.x
Sinhorin VDG, Sinhorin AP, Teixeira JMS et al (2014) Effects of the acute exposition to glyphosate-based herbicide on oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant responses in a hybrid Amazon fish surubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:181–187. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.040
Szarek A, Siwicki A, Andrzejewska E et al (2000) Effects of the herbicide Roundup® on the ultraestructural pattern of hepatocytes in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Mar Environ Res 50:253–266. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(00)00088-X
Toni C, Menezes C, Clasen B et al (2013) Oxidative stress in carp exposed to quinclorac herbicide under rice field condition. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:27–31. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.01.028
Topal A, Atamanalp M, Uçar A et al (2015) Effects of glyphosate on juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): transcriptional and enzymatic analyses of antioxidant defence system, histopathological liver damage and swimming performance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:206–214. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.09.027
Tsui MTK, Chu LM (2008) Environmental fate and non-target impact of glyphosate-based herbicide (Roundup®) in a subtropical wetland. Chemosphere 71:439–446. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.059
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149. doi:10.1016/S1382-6689(02)00126-6
WHO—World Health Organization (1994) Environmental health criteria: glyphosate. Geneva
Williams GM, Kroes R, Munro IC (2000) Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans. Regul Toxicol Pharm 31:117–165. doi:10.1006/rtph.1999.1371
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Federal University of Santa Maria for the support and facilities and the financial support and fellowships from the Brazilian agency CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murussi, C.R., Costa, M.D., Leitemperger, J.W. et al. Exposure to different glyphosate formulations on the oxidative and histological status of Rhamdia quelen . Fish Physiol Biochem 42, 445–455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0150-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0150-x