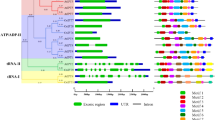
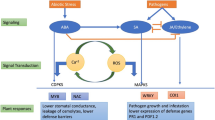
Abstract
Salt stress is an important abiotic stress, which has seriously affected the reproductive development of rice in many parts of the world. Therefore, it is particularly important to understand the genetic mechanism of salt tolerance in rice. In this study, we preliminarily located some quantitative trait loci (QTL) for root length, bud length, and survival percent under different salinity conditions (0, 100, 200 and 400 mM NaCl), using a population of chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) constructed by Nipponbare and 9311. A total of 18 QTLs were identified, which explained the phenotypic variation of 4.76–37.59%, among which 13 QTLs were detected under salt stress condition. These salt tolerance related QTLs were divided into two categories, QTL expressed both under control and salt stress conditions (qSP3, qBL8), and QTL expressed just under salt stress condition (qBL3, qRL3, qSP4, qRL5, qSP7, qSP9, qRL10, qBL11-1, qRL11-1, qRL11, qSP12). qSP3, qSP4, qRL5, qSP7, qRL10, qRL10-1, qRL11, qRL11-1, qBL11, qBL11-1 and qSP12 were reported to be related with salt stress for the first time. These QTLs identified under salt stress may be valuable genetic factors for improving salt tolerance of rice by molecular markers technology, which will help to further understand the genetic mechanism of salt tolerance of rice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammar MHM, Pandit A, Singh RK, Sameena S, Singh NK (2009) Mapping of QTLs controlling Na+, K+ and Cl− ion concentrations in salt tolerant indica rice variety CSR27. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 18(2):139–150
Asano T, Hakata M, Nakamura H, Aoki N, Komatsu S, Ichikawa H, Hirochika H, Ohsugi R (2011) Functional characterisation of OsCPK21, a calcium-dependent protein kinase that confers salt tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 75(1–2):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9717-1
Basu S, Giri RK, Benazir I, Kumar S, Rajwanshi R, Dwivedi SK, Kumar G (2017) Comprehensive physiological analyses and reactive oxygen species profiling in drought tolerant rice genotypes under salinity stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:837–850
Bian JM, Jiang L, Liu LL, Wei XJ, Xiao YH, Zhang LJ, Zhao ZG, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2010) Construction of a new set of rice chromosome segment substitution lines and identification of grain weight and related traits QTLs. Breed Sci 60(4):305–313. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.60.305
Ganie SA, Molla KA, Henry RJ, Bhat KV, Mondal TK (2019) Advances in understanding salt tolerance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 132:851–870
He X, Li L, Xu H, Xi J, Xu Z (2017) A rice Jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin gene, OsJRL, enhances Escherichia coli viability under high salinity stress and improves salinity tolerance of rice. Plant Biol 19(2):257
He Y, Yang B, He Y, Zhan C, Cheng Y, Zhang J, Zhang H, Cheng J, Wang Z (2019) A quantitative trait locus, qSE3, promotes seed germination and seedling establishment under salinity stress in rice. Wiley-Blackwell Online Open 97(6):1089–1104
Huang J, Wang MM, Bao YM, Sun SJ, Pan LJ, Zhang HS (2008) SRWD: a novel WD40 protein subfamily regulated by salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Gene 424(1–2):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2008.07.027
Huang XY, Chao DY, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Shi M, Lin HX (2009) A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control. Genes Dev 23(15):1805–1817. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1812409
Jahan N, Zhang Y, Lv Y, Song M, Guo L (2020) QTL analysis for rice salinity tolerance and fine mapping of a candidate locus qSL7 for shoot length under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul 90(1):307–319
Kumari R, Kumar P, Sharma VK, Kumar H (2018) Seedling stage salt stress response specific characterization of genetic polymorphism and validation of SSR markers in rice. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25(2):1–13
Lai Y, Cheng J, Wang Z, Zhang H, He Y (2016) Identification of QTLs with additive, epistatic, and QTL x seed maturity interaction effects for seed vigor in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 34:160–171
Lekklar C, Pongpanich M, Suriya-arunroj D, Chinpongpanich A, Tsai H, Comai L, Chadchawan S, Buaboocha T (2019) Genome-wide association study for salinity tolerance at the flowering stage in a panel of rice accessions from Thailand. BMC Genom. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5317-2
Li N, Sun J, Wang J, Liu H, Zheng H, Yang L, Liang Y, Li X, Zou D, Virk P (2017) QTL analysis for alkaline tolerance of rice and verification of a major QTL. Plant Breed 136:881–891
Li N, Zheng H, Cui J, Wang J, Zou D (2019) Genome-wide association study and candidate gene analysis of alkalinity tolerance in japonica rice germplasm at the seedling stage. Rice 12(1):24
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108(2):253–260
Luo X, Deng H, Wang P, Zhang X, Li C, Li C, Tan J, Wu G, Wang Y, Cheng Q, He H, Bian J (2020) Genetic analysis of germinating ability under alkaline and neutral salt stress by a high-density bin genetic map in rice. Euphytica 216(7):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02623-9
Mardani Z, Rabiei B, Sabouri H, Sabouri A (2014) Identification of molecular markers linked to salt-tolerant genes at germination stage of rice. Plant Breed 133(2):196–202
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3(3):269–283
Pandit A, Rai V, Bal S, Sinha S, Kumar V, Chauhan M, Gautam RK, Singh R, Sharma PC, Singh AK (2010) Combining QTL mapping and transcriptome profiling of bulked RILs for identification of functional polymorphism for salt tolerance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet Genom 284(2):121–136
Piao HL, Xuan YH, Park SH, Je BI, Park SJ, Kim CM (2010) OsCIPK31, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is involved in germination and seedling growth under abiotic stress conditions in rice plants. Mol Cells 30(1):19–27
Pires IS, Negrao S, Oliveira MM, Purugganan MD (2015) Comprehensive phenotypic analysis of rice (Oryza sativa) response to salinity stress. Physiol Plant 155(1):43–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12356
Punyawaew K, Suriya-Arunroj D, Siangliw M, Thida M, Lanceras-Siangliw J, Fukai S, Toojinda T (2016) Thai jasmine rice cultivar KDML105 carrying Saltol QTL exhibiting salinity tolerance at seedling stage. Mol Breed 36(11):150
Rao PVR, John O, Kumar SP (2018) Identification of QTLs for salt tolerance traits and prebreeding lines with enhanced salt tolerance in an introgression line population of rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 36:695–709
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146
Shi Y, Gao L, Wu Z, Zhang X, Wang M, Zhang C, Zhang F, Zhou Y, Li Z (2017) Genome-wide association study of salt tolerance at the seed germination stage in rice. BMC Plant Biol 17(1):92
Siahpoosh MR, Sanchez DH, Schlereth A, Scofield GN, Furbank RT, van Dongen JT, Kopka J (2012) Modification of OsSUT1 gene expression modulates the salt response of rice Oryza sativa cv. Taipei 309. Plant Sci 182:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.01.001
Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Yoshida K, Uemura A, Yaegashi H, Obara T, Oikawa K, Utsushi H, Kanzaki E, Mitsuoka C, Natsume S, Kosugi S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Urasaki N, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2015) MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar. Nat Biotechnol 33(5):445–449. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3188
Toda Y, Tanaka M, Ogawa D, Kurata K, Kurotani K, Habu Y, Ando T, Sugimoto K, Mitsuda N, Katoh E, Abe K, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Hattori T, Takeda S (2013) RICE SALT SENSITIVE3 forms a ternary complex with JAZ and class-C bHLH factors and regulates jasmonate-induced gene expression and root cell elongation. Plant Cell 25(5):1709–1725. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.112052
Wadekar HB, Sahi VP, Morita EH, Abe S (2013) MKRN expression pattern during embryonic and post-embryonic organogenesis in rice (Oryza sativa L. var. Nipponbare). Planta 237(4):1083–1095. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1828-2
Wang Z, Wang J, Bao Y, Wu Y, Zhang H (2011) Quantitative trait loci controlling rice seed germination under salt stress. Euphytica 178(3):297–307
Wang H, Zhang M, Guo R, Shi D, Liu B, Lin X, Yang C (2012a) Effects of salt stress on ion balance and nitrogen metabolism of old and young leaves in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 12(1):194–194
Wang Z, Cheng J, Chen Z, Huang J, Bao Y, Wang J, Zhang H (2012b) Identification of QTLs with main, epistatic and QTL × environment interaction effects for salt tolerance in rice seedlings under different salinity conditions. Theor Appl Genet 125(4):807–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1873-z
Wu H, Ye H, Yao R, Zhang T, Xiong L (2015) OsJAZ9 acts as a transcriptional regulator in jasmonate signaling and modulates salt stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 232:1–12
Wu G, Deng H, Yu M, Cai Y, Zhou D, Tan J, Yu J, Luo X, Tong S, Wang P, Zhang X, Li C, Li C, Wang Y, Cheng Q, He H, Bian J (2020) Genetic analysis of rice seed recovery under low-temperature conditions using a new CSSL population with a high-density genetic map in rice. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01189-7
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60(09):58–66
Zheng J, Wang Y, He Y, Zhou J, Li Y, Liu Q, Xie X (2014) Overexpression of an S-like ribonuclease gene, OsRNS4, confers enhanced tolerance to high salinity and hyposensitivity to phytochrome-mediated light signals in rice. Plant Sci 214:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.10.003
Zheng H, Zhao H, Liu H, Wang J, Zou D (2015) QTL analysis of Na+ and K+ concentrations in shoots and roots under NaCl stress based on linkage and association analysis in japonica rice. Euphytica 201(1):109–121
Zhou J, Wang F, Deng P, Jing W, Zhang W (2013) Characterization and mapping of a salt-sensitive mutant in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Integr Plant Biol 55(6):504–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12048
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous referees for their critical comments on this manuscript. This research was supported grants (20192ACBL20017; 20192BCB23010) from Project of Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi Province, grant (GJJ170241) from Project of Science and Technology Department of Department of Education of Jiangxi Province and grant (201910410003) from National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
Funding
This research was supported grants (20192ACBL20017; 20192BCB23010) from Project of Science and Technology Department of Jiangxi Province, grant (GJJ170241) from Project of Science and Technology Department of Department of Education of Jiangxi Province and grant (201910410003) from National Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Chen, L., Song, G. et al. Localization of salt-tolerant QTL in rice germination stage under different salinity concentrations. Euphytica 218, 78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03037-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03037-5