Abstract
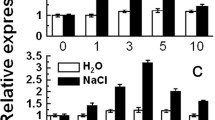
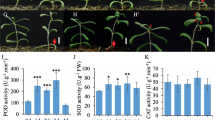
Calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) are a group of typical Ser/Thr protein kinases that mediate calcium signals. Extensive studies using Arabidopsis plants have demonstrated that many calcium signatures that activate CIPKs originate from abiotic stresses. However, there are few reports on the functional demonstration of CIPKs in other plants, especially in grasses. In this study, we used a loss-of-function mutation to characterize the function of the rice CIPK gene OsCIPK31. Exposure to high concentrations of NaCl or mannitol effected a rapid and transient enhancement of OsCIPK31 expression. These findings were observed only in the light. However, longer exposure to most stresses resulted in downregulation of OsCIPK31 expression in both the presence and absence of light. To determine the physiological roles of OsCIPK31 in rice plants, the sensitivity of oscipk31::Ds, which is a transposon Ds insertion mutant, to abiotic stresses was examined during germination and seedling stages. oscipk31::Ds mutants exhibited hypersensitive phenotypes to ABA, salt, mannitol, and glucose. Compared with wild-type rice plants, mutants exhibited retarded germination and slow seedling growth. In addition, oscipk31::Ds seedlings exhibited enhanced expression of several stress-responsive genes after exposure to these abiotic stresses. However, the expression of ABA metabolic genes and the endogenous levels of ABA were not altered significantly in the oscipk31::Ds mutant. This study demonstrated that rice plants use OsCIPK31 to modulate responses to abiotic stresses during the seed germination and seedling stages and to modulate the expression of stress-responsive genes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum, G., Long, J.C., Jenkins, G.I., and Trewavas, A.J. (1999). Stimulation of the blue light phototropic receptor NPH1 causes a transient increase in cytosolic Ca2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13554–13559.
Cheng, S.H., Willmann, M.R., Chen, H.C., and Sheen, J. (2002a). Calcium signaling through protein kinases. The Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase gene family. Plant Physiol. 129, 469–485.
Cheng, W.H., Endo, A., Zhou, L., Penney, J., Chen, H.C., Arroyo, A., Leon, P., Nambara, E., Asami, T., Seo, M., et al. (2002b). A unique short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase in Arabidopsis glucose signaling and abscisic acid biosynthesis and functions. Plant Cell 14, 2723–2743.
Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., Grant, J.J., Batistic, O., Li, L., Kim, B.G., Lee, S.C., Kudla, J., and Luan, S. (2007). Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 52, 223–239.
Cheong, Y.H., Sung, S.J., Kim, B.-Gi., Pandey, G.K., Cho, J.-S., Kim, K.-N., and Luan, S. (2010) Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 29, 159–165.
Evans, N.H., McAinsh, M.R., and Hetherington, A.M. (2001). Calcium oscillations in higher plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 415–420.
Guo, Y., Xiong, L., Song, C.P., Gong, D.M., Halfter, U., and Zhu, J.K. (2002). A calcium sensor and its interacting protein kinase are global regulators of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 3, 233–244.
Guo, Y., Qiu, Q.S., Quintero, F.J., Pardo, J.M., Ohta, M., Zhang, C., Schumaker, K.S., and Zhu, J.K. (2004). Transgenic evaluation of activated mutant alleles of SOS2 reveals a critical requirement for its kinase activity and C-terminal regulatory domain for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16, 435–449.
Halfter, U., Ishitani, M., and Zhu, J.K. (2000). The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3735–3740.
Harmon, A.C., Gribskov, M., Gubrium, E., and Harper, J.F. (2001). The CDPK superfamily of protein kinases. New Phytol. 151, 175–183.
Hu, H.H., Dai, M.Q., Yao, J.L., Xiao, B.Z., Li, X.H., Zhang, Q.F., and Xiong, L.Z. (2006). Over expressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 35, 12987–12992.
Hu, H.C., Wang, Y.Y., and Tsay, Y.F. (2009). AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J. 7, 264–278.
Kang, D.J., Seo, Y.J., Lee, J.D., Ishii, R., Kim, K.U., Shin, D.H., Park, S.K., Jang, S.W., and Lee, I.J. (2005). Jasmonic acid differentially affects growth, Ion uptake and abscisic acid concentration in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 191, 273–282.
Kim, K.N., Cheong, Y.H., Grant, J.J., Pandey, G.K., and Luan, S. (2003a). CIPK3, calcium sensor-associated protein kinase that regulates abscisic acid and cold signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15, 411–423.
Kim, K.N., Lee, J.S., Han, H., Choi, S.A., Go, S.J., and Yoon, I.S. (2003b). Isolation and characterization of a novel rice Ca2+-regulated protein kinase gene involved in responses to diverse signals including cold, light, cytokinins, sugars and salts. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 1191–1202.
Kim, C.M., Piao, H.L., Park, S.J., Chon, N.S., Je, B.I., Sun, B., Park, S.H., Park, J.Y., Lee, E.J., Kim, M.J., et al. (2004). Rapid, largescale generation of Ds transposant lines and analysis of the Ds insertion sites in rice. Plant J. 39, 252–263.
Knight, H., and Knight, M.R. (2001). Abiotic stress signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk. Trends Plant Sci. 6, 262–267.
Kolukisaoglu, U., Weinl, S., Blazevic, D., Batistic, O., and Kudla, J. (2004). Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol. 134, 43–58.
Lee, K.W., Chen, P.W., Lu, C.A., Chen, S., Ho, T.H., and Yu, S.M. (2009). Coordinated responses to oxygen and sugar deficiency allow rice seedlings to tolerate flooding. Sci. Signal. 2, ra61.
Li, L., Kim, B.G., Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., and Luan, S. (2006). A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12625–12630.
Liu, J., Ishitani, M., Halfter, U., Kim, C.S., and Zhu, J.K. (2000). The Arabidopsis thaliana SOS2 gene encodes a protein kinase that is required for salt tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3730–3734.
Luan, S., Kudla, J., Rodriguez-Concepcion, M., Yalovsky, S., and Gruissem, W. (2002). Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14, S389–S400.
MacRobbie, E.A.C. (2000). ABA activates multiple Ca2+ fluxes in stomatal guard cells, triggering vacuolar K1 (Rb1) release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12361–12368.
Mohammad, M.I., Chiharu, T., Megumi, W.S., Misugi, U., Md, S.J., Choji, M., Yoshimasa, N., Izumi, C.M., and Yoshiyuki, M. (2009). Myrosinases, TGG1 and TGG2, redundantly function in ABA and MeJA signaling in Arabidopsis guard cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 50, 1171–1175.
Nakashima, K., Tran, L.S.P., Van, Nguyen, D., Fujita, M., Maruyama, K., Todaka, D., Ito, Y., Hayashi, N., Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi, S. (2007). Functional analysis of a NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC6 involved in abiotic and biotic stressresponsive gene expression in rice. Plant J. 51, 617–630.
Oh, S.J., Song, S.I., Kim, Y.S., Jang, H.J., Kim, S.Y., Kim, M.J., Kim, Y.K., Nahm, B.H., and Kim, J.K. (2005). Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol. 138, 341–351
Ohba, H., Steward, N., Kawasaki, S., Berberich, T., Ikeda, Y., Koizumi, N., Kusano, T., and Sano, H. (2000). Diverse response of rice and maize genes encoding homologs of WPK4, an SNF1-related protein kinase from wheat, to light, nutrients, low temperature and cytokinins. Mol. Gen. Genet. 263, 359–366.
Pandey, G.K., Cheong, Y.H., Kim, K.N., Grant, J.J., Li, L., Hung, W., D’Angelo, C., Weinl, S., Kudla, J., and Luan, S. (2004). The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 1912–1924.
Pandey, G.K., Cheong, Y.H., Kim, B.G., Grant, J.J., Li, L., and Luan, S. (2007). CIPK9: a calcium sensor-interacting protein kinase required for low-potassium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 17, 411–421.
Price, J., Li, T.-C., Kang, S.G., Na, J.K., and Jang, J.-C. (2003). Mechanisms of glucose signaling during germination of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 132, 1424–1438.
Rabbani, M.S., Maruyama, K., Abe, H., Khan, M.A., Katsura, K., Ito, Y., Yoshiwara, K., Seki, M., Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2003). Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol. 133, 1755–1767.
Sanchez-Barrena, M.J., Martinez-Ripoll, M., Zhu, J.K., and Albert, A. (2005). The structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana SOS3: molecular mechanism of sensing calcium for salt stress response. J. Mol. Biol. 345, 1253–1264.
Sanders, D., Brownlee, C., and Harper, J.F. (1999). Communicating with calcium. Plant Cell 11, 691–706.
Snedden, W.A., and Fromm, H. (2001). Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytol. 151, 35–66.
Song, C.P., Agarwal, M., Ohta, M., Guo, Y., Halfter, U., Wang, P., and Zhu, J.K. (2005). Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell 17, 2384–2396.
Tripathi, V., Parasuraman, B., Laxmi, A., and Chattopadhyay, D. (2009). CIPK6, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plant. Plant J. 58, 778–790.
Xiang, Y., Huang, Y., and Xiong, L. (2007). Characterization of stressresponsive CIPK genes in rice for stress tolerance improvement. Plant Physiol. 144, 1416–1428.
Xiong, L., Lee, H., Ishitani, M., and Zhu, J.K. (2002). Regulation of osmotic stress-responsive gene expression by the LOS6/ABA1 locus in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8588–8596.
Xu, J., Li, H.D., Chen, L.Q., Wang, Y., Liu, L.L., He, L., and Wu, W.H. (2006). A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin Blike proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125, 1347–1360.
Yang, W., Kong, Z., Omo-Ikerodah, E., Xu, W., Li, Q., and Xue, Y. (2008). Calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase OsCIPK23 functions in pollination and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. Genomics 35, 531–543, S1–2.
Zielinski, R.E. (1998). Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49, 697–725.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Piao, Hl., Xuan, Yh., Park, S.H. et al. OsCIPK31, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is involved in germination and seedling growth under abiotic stress conditions in rice plants. Mol Cells 30, 19–27 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0084-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0084-1