Abstract
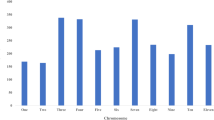
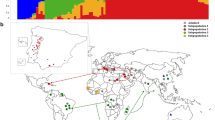
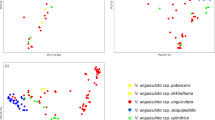
The evolution of species is complex and subtle which always associates with the genetic variation and environment adaption during active/passive spread or migration. In crops, this process is usually driven and influenced by human activities such as domestication, cultivation and immigration. One method to discover this process is to analyze the genetic diversity of those crops in different regions. This research first assessed the similarity and differentiation between genetic diversity of genotype and phenotype in 768 world-wild cowpea germplasm which were collected by USDA and US breeding programs. Totally 1048 genotyping by sequencing (GBS) derived single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 17 agronomic traits were used to analyze the genetic diversity, distance, cluster and phylogeny. The group differentiation was analyzed based on both the genotype distances from 1048 SNP markers and the phenotypic (Mahalanobis) distance D2 from 11 traits. A consistent result of diversity in genotype (polymorphism information content, PIC) and phenotype (Shannon and Simpson index) indicated that the East Africa and South Asia sub-continents were the original and secondary regions of cowpea domestication. Both dendrograms built by genetic distance present relationship among different regions, and the Mantel coefficient showed medium correlation level (r = 0.58) between genotype and phenotype. The information of both genotypic and phenotypic differentiations may help us to understand evolution and migration of cowpea more comprehensively and also will inform breeders how to use cowpea germplasm in breeding programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agah S, Kim H, Mertens-Talcott SU, Awika JM (2017) Complementary cereals and legumes for health: synergistic interaction of sorghum flavones and cowpea flavonols against LPS-induced inflammation in colonic myofibroblasts. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201600625
Arbelaez JD, Moreno LT, Singh N, Tung CW, Maron LG, Ospina Y, Martinez CP, Grenier C, Lorieux M, McCouch S (2015) Development and GBS-genotyping of introgression lines (ILs) using two wild species of rice, O. meridionalis and O. rufipogon, in a common recurrent parent, O. sativa cv. Curinga. Mol Breed. 10.1007/s11032-015-0276-7
Ariani A, Teran JCBMY, Gepts P (2016) Genome-wide identification of SNPs and copy number variation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) using genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS). Mol Breed. 10.1007/s11032-016-0512-9
Bauchet G, Grenier S, Samson N, Bonnet J, Grivet L, Causse M (2017) Use of modern tomato breeding germplasm for deciphering the genetic control of agronomical traits by Genome Wide Association study. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2857-9
Baudoin J, Maréchal R (1985) Cowpea taxonomy, origin and germplasm. Cowpea research, production and utilization. Wiley, Chichester, pp 3–9
Behura R, Kumar S, Saha B, Panda MK, Dey M, Sadhukhan A, Mishra S, Alam S, Sahoo DP, Sugla T, Sahoo L (2015) Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp]. Methods Mol Biol 1223:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1695-5_20
Bower A (2007) African American foodways: explorations of history and culture. University of Illinois Press, Champaign
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Cai CM, Van K, Kim MY, Jun TH, Shin JH, Cho SY, Lee YS, Lee SH (2008) SNP discovery, linkage analysis and microsynteny in tentative consensus sequences derived from roots cDNA in a supernodulating soybean mutant. Euphytica 164(1):189–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9702-9
Caruso M, Federici CT, Roose ML (2008) EST-SSR markers for asparagus genetic diversity evaluation and cultivar identification. Mol Breed 21(2):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9120-z
Celik I, Bodur S, Frary A, Doganlar S (2016a) Genome-wide SNP discovery and genetic linkage map construction in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) using a genotyping by sequencing (GBS) approach. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0558-8
Celik I, Camci H, Kose A, Kosar FC, Doganlar S, Frary A (2016b) Molecular genetic diversity and association mapping of morphine content and agronomic traits in Turkish opium poppy (Papaver somniferum) germplasm. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0469-8
Chen HL, Liu LP, Wang LX, Wang SH, Wang ML, Cheng XZ (2015) Development of SSR markers and assessment of genetic diversity of adzuki bean in the Chinese germplasm collection. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-015-0383-5
Ching A, Caldwell KS, Jung M, Dolan M, Smith OS, Tingey S, Morgante M, Rafalski AJ (2002) SNP frequency, haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite maize inbred lines. BMC Genet. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-3-19
Cobb JN, Declerck G, Greenberg A, Clark R, McCouch S (2013) Next-generation phenotyping: requirements and strategies for enhancing our understanding of genotype-phenotype relationships and its relevance to crop improvement. Theoret Appl Genet 126(4):867–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2066-0
Darling KF, Schweizer M, Knudsen KL, Evans KM, Bird C, Roberts A, Filipsson HL, Kim JH, Gudmundsson G, Wade CM, Sayer MDJ, Austin WEN (2016) The genetic diversity, phylogeography and morphology of Elphidiidae (Foraminifera) in the Northeast Atlantic. Mar Micropaleontol 129:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marmicro.2016.09.001
de Oliveira EJ, Ferreira CF, da Silva Santos V, de Jesus ON, Oliveira GA, da Silva MS (2014) Potential of SNP markers for the characterization of Brazilian cassava germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 127(6):1423–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2309-8
Deulvot C, Charrel H, Marty A, Jacquin F, Donnadieu C, Lejeune-Hénaut I, Burstin J, Aubert G (2010) Highly-multiplexed SNP genotyping for genetic mapping and germplasm diversity studies in pea. BMC Genom 11(1):468
Earl DA (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, Buckler ES, Mitchell SE (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14(8):2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform 1:47–50
Fang J, Chao C-CT, Roberts PA, Ehlers JD (2007a) Genetic diversity of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] in four West African and USA breeding programs as determined by AFLP analysis. Genet Resour Crop Ev 54(6):1197–1209
Fang JG, Chao CCT, Roberts PA, Ehlers JD (2007b) Genetic diversity of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] in four West African and USA breeding programs as determined by AFLP analysis. Genet Resour Crop Ev 54(6):1197–1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9101-9
Faris DG (1965) The origin and evolution of the cultivated forms of Vigna Sinensis. Can J Genet Cytol 7(3):433–452. https://doi.org/10.1139/g65-058
Fatokun C, Danesh D, Young N, Stewart E (1993) Molecular taxonomic relationships in the genus Vigna based on RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 86(1):97–104
Gizaw S, Van Arendonk JAM, Komen H, Windig JJ, Hanotte O (2007) Population structure, genetic variation and morphological diversity in indigenous sheep of Ethiopia. Anim Genet 38(6):621–628. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.2007.01659.x
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2010) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res 38(1):D843–D846. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp798
Hartl DL, Clark AG, Clark AG (1997) Principles of population genetics, vol 116. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
He G, Prakash CS, Jarret RL (1995) Analysis of genetic diversity in a sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas) germplasm collection using DNA amplification fingerprinting. Genome 38(5):938–945
Huynh B-L, Close TJ, Roberts PA, Hu Z, Wanamaker S, Lucas MR, Chiulele R, Cissé N, David A, Hearne S, Fatokun C, Diop NN, Ehlers JD (2013) Gene pools and the genetic architecture of domesticated cowpea. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.03.0005
Ichihashi H, Honda K, Wakami N (2005) Robust PCA with intra-sample outlier process based on fuzzy Mahalanobis distances and noise clustering. In: Fuzz-IEEE 2005: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp 640–645
Jaaska V, Jaaska V (1988) Isoenzyme variation in the generaPhaseolus and Vigna (Fabaceae) in relation to their systematics: aspartate aminotransferase and superoxide dismutase. Plant Syst Evol 159(3–4):145–159
Kamphuis LG, Gao L, Singh KB (2012) Identification and characterization of resistance to cowpea aphid (Aphis craccivora Koch) in Medicago truncatula. BMC Plant Biol 12:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-101
Kanchikerimath M, Singh D (2001) Soil organic matter and biological properties after 26 years of maize-wheat-cowpea cropping as affected by manure and fertilization in a Cambisol in semiarid region of India. Agr Ecosyst Environ 86(2):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(00)00280-2
Kapoor-Vijay P, White J (1992) Global biodiversity strategy. Conservation biology: a training manual for biological diversity and genetic resources. Commonwealth Science Council, pp 13–22
Krishna K (2014) Cowpea farming zones of Africa and Asia. Agroecosystems: soils, climate, crops, nutrient dynamics, and productivity. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 139–146
Li H (2011) A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27(21):2987–2993. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr509
Li X, Yan W, Agrama H, Hu B, Jia L, Jia M, Jackson A, Moldenhauer K, McClung A, Wu D (2010) Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of genetic differentiation and diversity in the USDA rice mini-core collection. Genetica 138(11–12):1221–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9521-5
Li CQ, Song L, Zhu YJ, Zhai YJ, Wang QL (2017) Genetic diversity assessment of upland cotton variety resources in china based on phenotype traits and molecular markers. Crop Sci 57(1):290–301. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2016.03.0200
Liu KJ, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21(9):2128–2129. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Lu Y, Yan J, Guimaraes CT, Taba S, Hao Z, Gao S, Chen S, Li J, Zhang S, Vivek BS, Magorokosho C, Mugo S, Makumbi D, Parentoni SN, Shah T, Rong T, Crouch JH, Xu Y (2009) Molecular characterization of global maize breeding germplasm based on genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 120(1):93–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1162-7
Mahalakshmi V, Ng Q, Lawson M, Ortiz R (2007) Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] core collection defined by geographical, agronomical and botanical descriptors. Plant Genet Resour 5(03):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1479262107837166
Mantel N (1967) Correction. Biometrics 23(4):854–1000
Muchero W, Diop NN, Bhat PR, Fenton RD, Wanamaker S, Pottorff M, Hearne S, Cisse N, Fatokun C, Ehlers JD (2009a) A consensus genetic map of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp.] and synteny based on EST-derived SNPs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(43):18159–18164
Muchero W, Matthews WC, Diop NN, Bhat PR, Wanamaker S, Ehlers JD, Close TJ, Roberts PA (2009b) Qtl mapping of root-knot nematode resistance in cowpea (Vigna Unguiculata) using est-derived Snp markers. J Nematol 41(4):361–362
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106:283–292
Neuman RJ, Saccone NL, Holmans P, Rice JP, Sun LW (2000) Clustering methods applied to allele sharing data. Genet Epidemiol 19:S57–S63
Odong TL, Jansen J, van Eeuwijk FA, van Hintum TJ (2013) Quality of core collections for effective utilisation of genetic resources review, discussion and interpretation. Theor Appl Genet 126(2):289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1971-y
Osman M, Emmingham WH, Sharrow SH (1998) Growth and yield of sorghum or cowpea in an agrisilviculture system in semiarid India. Agroforest Syst 42(1):91–105. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006147926915
Peng L, Ru M, Wang BQ, Wang Y, Li B, Yu J, Liang ZS (2014) Genetic diversity assessment of a germplasm collection of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. based on morphology, ISSR and SRAP markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.01.020
Qin J, Shi AN, Xiong HZ, Mou BQ, Motes D, Lu WG, Miller JC, Scheuring DC, Nzaramba MN, Weng YJ, Yang W (2016) Population structure analysis and association mapping of seed antioxidant content in USDA cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) core collection using SNPs. Can J Plant Sci 96(6):1026–1036. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjps-2016-0090
Qin J, Shi AN, Mou BQ, Bhattarai G, Yang W, Weng YJ, Motes D (2017) Association mapping of aphid resistance in USDA cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) core collection using SNPs. Euphytica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1830-z
Rostoks N, Mudie S, Cardle L, Russell J, Ramsay L, Booth A, Svensson JT, Wanamaker SI, Walia H, Rodriguez EM, Hedley PE, Liu H, Morris J, Close TJ, Marshall DF, Waugh R (2005) Genome-wide SNP discovery and linkage analysis in barley based on genes responsive to abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genom 274(5):515–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0046-z
Sall J, Lehman A, Stephens ML, Creighton L (2012) JMP start statistics: a guide to statistics and data analysis using JMP. SAS Institute, Cary
Santos CA, Boiteux LS (2013) Breeding biofortified cowpea lines for semi-arid tropical areas by combining higher seed protein and mineral levels. Genet Mol Res 12(4):6782–6789. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.December.16.4
Schroder S, Mamidi S, Lee R, McKain MR, McClean PE, Osorno JM (2016) Optimization of genotyping by sequencing (GBS) data in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-015-0431-1
Scott SJ (1977) Nitrogen-fixation in cowpea (Vigna-Unguiculata-(L) Walp) as influenced by available nitrate levels. HortScience 12(4):388–389
Scowcroft WR, Gibson AH (1975) Nitrogen-fixation by rhizobium associated with tobacco and cowpea cell-cultures. Nature 253(5490):351–352
Shi AN, Buckley B, Mou BQ, Motes D, Morris JB, Ma JB, Xiong HZ, Qin J, Yang W, Chitwood J, Weng YJ, Lu WG (2016) Association analysis of cowpea bacterial blight resistance in USDA cowpea germplasm. Euphytica 208(1):143–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1610-1
Shirasawa K, Maeda H, Monna L, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2007) The number of genes having different alleles between rice cultivars estimated by SNP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 115(8):1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0632-z
Simmonds NW (1976) Evolution of crop plants. Longman Group Ltd., Harlow
Singh SR, Rachie KO (1985) Cowpea research, production and utilization. Wiley, New York
Singh B, Chambliss O, Sharma B (1997) Recent advances in cowpea breeding. Adv Cowpea Res 3049
Singh P, Prasuhn D, Yeh RM, Destito G, Rae CS, Osborn K, Finn MG, Manchester M (2007) Bio-distribution, toxicity and pathology of cowpea mosaic virus nanoparticles in vivo. J Control Release 120(1–2):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.04.003
Singh SK, Kakani VG, Surabhi GK, Reddy KR (2010) Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.) genotypes response to multiple abiotic stresses. J Photochem Photobiol B 100(3):135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.05.013
Smartt J (1986) Cowpea research, production and utilization. Edited by S. R. Singh and K. O. Rachie. Chichester, New York, etc.: John Wiley and Sons (1985), pp. 460, £22.50. Exp Agric 22(04):431. https://doi.org/10.1017/s001447970001468x
Smith JM (1989) Evolutionary genetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Su W, Wang L, Lei J, Chai S, Liu Y, Yang Y, Yang X, Jiao C (2017) Genome-wide assessment of population structure and genetic diversity and development of a core germplasm set for sweet potato based on specific length amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0172066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172066
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm092
Timko MP, Ehlers JD, Roberts PA (2007) Cowpea. In: Pulses, sugar and tuber crops. Springer, New York, pp 49–67
Uncu AO, Frary A, Karlovsky P, Doganlar S (2016) High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) identification and mapping in the sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genome with genotyping by sequencing (GBS) analysis. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11032-016-0604-6
Wang QB, Zhang L, Zheng PJ (2015) Genetic diversity and evolutionary relationship analyses within and among Raphanus species using EST-SSR markers. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0261-1
Xiong HZ, Shi AN, Mou BQ, Qin J, Motes D, Lu WG, Ma JB, Weng YJ, Yang W, Wu DX (2016) Genetic diversity and population structure of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160941
Xu P, Wu X, Wang B, Luo J, Liu Y, Ehlers J, Close T, Roberts P, Lu Z, Wang S (2012) Genome wide linkage disequilibrium in Chinese asparagus bean (Vigna unguiculata ssp. sesquipedialis) germplasm: implications for domestication history and genome wide association studies. Heredity 109(1):34–40
Yanagisawa T, Kiribuchi-Otobe C, Hirano H, Suzuki Y, Fujita M (2003) Detection of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) controlling the waxy character in wheat by using a derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (dCAPS) marker. Theor Appl Genet 107(1):84–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1235-y
Zeka D, Sedlak P, Sedlakova V, Sharma K, Vejl P (2015) Phenotype and molecular diversity evaluation of some wild 2n Solanum species (super series Rotata). Chil J Agr Res 75(2):147–151. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392015000200002
Zhou H, Muehlbauer G, Steffenson B (2012) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite barley breeding germplasm from the United States. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 13(6):438–451. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, H., Qin, J., Shi, A. et al. Genetic differentiation and diversity upon genotype and phenotype in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.). Euphytica 214, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2088-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2088-9