Abstract
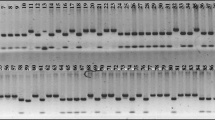
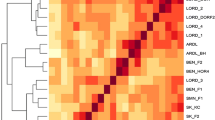
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers generated from expressed sequence tag (EST) sequences represent useful tools for genotyping and their development is relatively easy because of the public availability of EST databases. We report design and application of EST–SSRs to assess the level of genetic diversity among thirty-five asparagus cultivars and to fingerprint DePaoli, a new variety released by University of California, Riverside. DNA was isolated from bulks of pooled cladophylls coming from five plants of each variety to reduce the number of DNA extractions and PCR reactions. Allele frequencies were estimated from the intensity of the bands in two bulks and two individual plant samples for each variety. Although asparagus varieties derive from a limited germplasm pool, eight EST–SSR loci differentiated all of the analyzed cultivars. Moreover, UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) and neighbor-joining trees, as well as principal components analysis separated the cultivars into clusters corresponding to the geographical areas where they originated.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean
References
Aceto S, Sica M, Gamba G, Pontieri S, Farina A, Gaudio L (2003) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci from Asparagus acutifolius (Liliaceae). Mol Ecol Notes 3:242–243
Collins HE, Li H, Inda SE, Anderson J, Laiho K, Tuomilehto J, Seldin MF (2000) A simple and accurate method for determination of microsatellite total allele content differences between DNA pools. Hum Genet 106(2):218–226
Doré C (1977) In vitro techniques as an efficient tool in asparagus breeding. Acta Hort 78:89–94
Ellison JH, Scheer DF, Wagner JJ (1960) Asparagus yield as related to plant vigor, earliness and sex. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 75:411–415
Flory WS (1932) Genetic, cytological investigations on Asparagus officinalis L. Genetics 17:432–467
Geoffriau E, Denoue D, Rameau C (1992) Assessment of genetic variation among asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) populations and cultivars: agromorphological and isozymic data. Euphytica 61:169–179
Gonzáles-Castañón ML (1997) Isozyme gene markers in asparagus used to classify fifty asparagus cultivars. Acta Hort 479:77–84
Hollingsworth WO, Christie CB, Nichols A, Neilson HF (1998) Detection of variation among and within asparagus hybrids using random amplified DNA (RAPD) markers. New Zeal J Crop Hort 26:1–9
Khandka DK, Nejidat A, Golan-Goldhirsh A (1996) Polymorphism and DNA markers for asparagus cultivars identified by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Euphytica 887:39–44
Knaflewski M (1996) Genealogy of asparagus cultivars. Acta Hort 415:87–91
Kuhl JC, Havey MJ, Martin WJ, Cheung F, Yuan Q, Landherr L, Hu Y, Leebens-Mack J, Town CD, Sink KC (2005) Comparative genomic analyses in Asparagus. Genome 48:1052–1060
Loptien H (1979) Identification of the sex chromosome pair in asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.). Z Pflanzenzucht 82:162–173
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
O’Connell LM, Russell J, Ritland K (2004) Fine-scale estimation of outcrossing in western redcedar with microsatellite assay of bulked DNA. Heredity 93(5):443–449
Oetting WS, Lee HK, Flanders DJ, Wiesner GL et al (1995) Linkage analysis with multiplexed short tandem repeat polymorphisms using infrared fluorescence and M13 tailed primers. Genomics 30:450–458
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 365–386
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Yang H-J, Clore WJ (1974) Development of complete plantlets from moderately vigorous shoots of stock plants of asparagus in vitro. HortScience 9:138–140
Yang H-J (1977) Tissue culture technique developed for asparagus propagation. HortScience 12(2):140–141
Acknowledgements
We thank Neil Stone for assistance in collecting the samples, John Ikeda for primer design, Xinrong Ye for the DNA extraction protocol and Lisa Mu for assistance in SSR analysis. Funding was provided by the University of California and the University of Catania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caruso, M., Federici, C.T. & Roose, M.L. EST–SSR markers for asparagus genetic diversity evaluation and cultivar identification. Mol Breeding 21, 195–204 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9120-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9120-z