Abstract
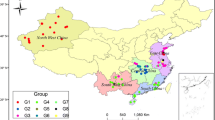
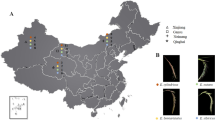
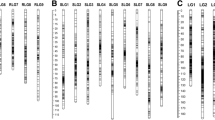
Bermudagrass is a warm season grass widely cultivated for turf and fodder. Nonetheless, the grass has poor forage quality because animals that consume it fail to assimilate its organic matter efficiently. Thus, identification of the marker-trait association between simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and forage-quality-related traits in diverse bermudagrass accessions would enable efficient selection of high forage quality bermudagrass cultivars. Association mapping of 8 forage-related-quality traits with 1474 markers was conducted in 60 diverse bermudagrass accessions from five geographical regions in China. Significant variations in eight phenotypic and physiological traits were observed among the 60 accessions. A total of 1474 alleles were amplified by 104 SSR primers. The average gene diversity and polymorphic information content for the study sample were 0.2097 and 0.1748 respectively. The clustering analysis suggested that geographic origin influenced genetic distances between accessions. A total of 76 markers significantly associated with traits at P < 0.01; 73 with a single trait and 3 with two traits each. Nevertheless, only 41 significant marker-trait associations (MTAs) were observed after Bonferroni test was separately conducted for each trait. Forty-one microsatellites had significant associations with 8 forage-quality-related traits. These markers provide a feasible means of genetically improving forage quality in bermudagrass after further authentication.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADF:
-
Acid detergent fiber
- ADL:
-
Acid detergent lignin
- AFLPs:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphisms
- B:
-
Biomass
- CA:
-
Crude ash
- CF:
-
Crude fat
- CP:
-
Crude protein
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl-trimethyl-ammonium-bromide
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- CWCs:
-
Cell-wall-associated components
- DM:
-
Dry matter
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- GLM:
-
General liner model
- H:
-
Height
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- MAF:
-
Major allele frequency
- MC:
-
Moisture content
- MTAs:
-
Marker-trait associations
- MLM:
-
Mixed linear model
- NDF:
-
Neutral detergent fiber
- PIC:
-
Polymorphic information content
- QTLs:
-
Qualitative trait loci
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- TDN:
-
Total digestible nutrients
References
Abdurakhmonov IY, Kohel RJ, Yu JZ, Pepper AE, Abdullaev AA, Kushanov FN, Salakhutdinov IB, Buriev ZT, Saha S, Scheffler BE, Jenkins JN, Abdukarimov A (2008) Molecular diversity and association mapping of fiber quality traits in exotic G. hirsutum L. germplasm. Genomics 92:478–487. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.07.013
Abdurakhmonov IY, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Buriev ZT, Shermatov SE, Scheffler BE, Pepper AE, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Abdukarimov A (2009) Linkage disequilibrium based association mapping of fiber quality traits in G. hirsutum L. variety germplasm. Genetica 136:401–417. doi:10.1007/s10709-008-9337-8
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B. doi:10.2307/2346101
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Camus-Kulandaivelu L, Veyrieras JB, Madur D, Combes V, Fourmann M, Barraud S, Dubreuil P, Gouesnard B, Manicacca D, Charcosset A (2006) Maize adaptation to temperate climate: relationship between population structure and polymorphism in the Dwarf8 Gene. Genetics 172:2449–2463. doi:10.1534/genetics.105.048603
Casler MD, Duncan RR (2003) Turfgrass biology, genetics, and breeding. Wiley, New Jersey
Chen Y, Zein I, Brenner EA, Andersen JR, Landbeck M, Ouzunova M, Lübberstedt T (2010) Polymorphisms in monolignol biosynthetic genes are associated with biomass yield and agronomic traits in European maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biol 10:12. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-12
Chen X, Min D, Yasir TA, Hu Y-G (2012) Genetic diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite Chinese winter wheat investigated with SSR markers. PLoS ONE 7:e44510. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044510
Ciofi C, Milinkovitch MC, Gibbs JP, Caccone A, Powell JR (2002) Microsatellite analysis of genetic divergence among populations of giant Galápagos tortoises. Mol Ecol 11:2265–2283. doi:10.1046/J.1365-294X.2002.01617.X
Comont D, Winters A, Gomez LD, McQueen-Mason SJ, Gwynn-Jones D (2013) Latitudinal variation in ambient UV-B radiation is an important determinant of Lolium perenne forage production, quality, and digestibility. J Exp Bot 64:2193–2204. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert077
Dang X, Liu E, Liang Y, Liu Q, Breria CM (2016) QTL detection and elite alleles mining for stigma traits in Oryza sativa by association mapping. Front Plant Sci 7:1–14. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.01188
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. doi:10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard J (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x
Flint-Garcia SA, Thuillet AC, Yu J, Pressoir G, Romero SM, Mitchell SE, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2005) Maize association population: a high-resolution platform for quantitative trait locus dissection. Plant J 44:1054–1064. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02591.x
Fulgueira CL, Amigot SL, Gaggiotti M, Romero LA, Basílico JC (2007) Forage quality: techniques for testing. Fresh Prod 1:121–131
Gharehshekhlou HR, Rasouli B, Ghotbi AA, Amiri B (2012) Forage quality analysis of Dactylic glomerata, Onobrychis sativa and Setaria galauca in North of Iran by different methods. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 4:1962–1966
Giordano A, Liu Z, Panter SN, Dimech AM, Shang Y, Wijesinghe H, Fulgueras K, Ran Y, Mouradov A, Spangenberg GC (2014) Reduced lignin content and altered lignin composition in the warm season forage grass Paspalum dilatatum by down-regulation of a Cinnamoyl CoA Reductase Gene. Transgenic Res 23:503–517. doi:10.1007/s11248-014-9784-1
Guimarães EP, Ruane J, Scherf BD, Sonnino A, Dargie JD (2007) Marker-assisted selection: current status and future perspectives in crops, livestock, forestry and fish. Food Agric Org 127:1–494
Gul S, Safdar M (2009) Proximate composition and mineral analysis of cinnamon. Pak J Nutr 8:1456–1460. doi:10.3923/pjn.2009.1456.1460
Hamblin MT, Mitchell SE, White GM, Gallego J, Kukatla R, Wing RA, Paterson AH, Kresovich S (2004) Comparative population genetics of the panicoid grasses: sequence polymorphism, linkage disequilibrium and selection in a diverse sample of Sorghum bicolor. Genetics 167:471–483
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SPAGeDI: a versatile computer program to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2:618–620. doi:10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00305.x
Heldman D (2003) Encyclopedia of agricultural, food, and biological engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York
IBM. Corp. (2014) IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24.0. Armonk, NY
Jakobsson M, Edge MD, Rosenberg NA (2013) The relationship between FST and the frequency of the most frequent allele. Genetics 193:515–528. doi:10.1534/genetics.112.144758
Jiang H, Huang L, Ren X, Chen Y, Zhou X, Xia Y, Huang J, Lei Y, Yan L, Wan L, Liao B (2014) Diversity characterization and association analysis of agronomic traits in a Chinese peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) mini-core collection. J Integr Plant Biol 56:159–169. doi:10.1111/jipb.12132
Kraakman ATW, Niks RE, Van den Berg PMMM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 446:435–446. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.026831
Li H, Liu L, Lou Y, Hu T, Fu J (2011) Genetic diversity of Chinese natural bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) germplasm using ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 127:555–561. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2010.12.001
Li X, Yan W, Agrama H, Jia L, Jackson A, Moldenhauer K, Yeater K, McClung A, Wu D (2012) Unraveling the complex trait of harvest index with association mapping in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 7:e29350. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029350
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Loiselle BA, Sork VL, Nason J, Graham C (1995) Spatial genetic structure of a tropical understory shrub, Psychotria officinalis (Rubiaceae). Am J Bot 82:1420–1425
Lou Y, Hu L, Chen L, Sun X, Yang Y, Liu H, Xu Q (2015) Association analysis of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers with agronomic traits in tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). PLoS ONE 10:e0133054. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133054
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Noli E, Tuberosa R (2005) Population structure and long-range linkage disequilibrium in a durum wheat elite collection. Mol Breed 15:271–289. doi:10.1007/s11032-004-7012-z
Mezmouk S, Dubreuil P, Bosio M, Décousset L, Charcosset A, Praud S, Mangin B (2011) Effect of population structure corrections on the results of association mapping tests in complex maize diversity panels. Theor Appl Genet 122:1149–1160. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1519-y
Mian MA, Saha MC, Hopkins AA, Wang ZY (2005) Use of tall fescue EST-SSR markers in phylogenetic analysis of cool-season forage grasses. Genome 48:637–647. doi:10.1139/g05-029
Montgomery S (2008) Linkage disequilibrium-understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat Rev Genet 9:477–485. doi:10.1038/nrg2361
Neale DB, Sewell MM, Brown GR (2002) Molecular dissection of the quantitative inheritance of wood property traits in loblolly pine. Ann For Sci 59:595–605. doi:10.1051/forest:2002045
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106:283–292. doi:10.1086/282771
Newman YC, Adesogan AT, Vendramini J, Sollenberger L (2009) Defining forage quality 1–5. The Texas A & M university system. http://publications.tamu.edu/FORAGE/PUB_forage_Defining%20Forage%20Quality.pdf. Accessed 20 Sept 2016
Porras-Hurtado L, Ruiz Y, Santos C, Phillips C, Carracedo A, Lareu MV (2013) An overview of STRUCTURE: applications, parameter settings, and supporting software. Front Genet 4:1–13. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00098
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959. doi:10.1016/0379-0738(94)90222-4
Ravi K, Vadez V, Isobe S, Mir RR, Guo Y, Nigam SN, Gowda MV, Radhakrishnan T, Bertioli DJ, Knapp SJ, Varshney RK (2011) Identification of several small main-effect QTLs and a large number of epistatic QTLs for drought tolerance related traits in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 122:1119–1132. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1517-0
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11479–11484. doi:10.1073/pnas.201394398
Saghai Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhangf Q, Allard RW (1994) Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barley: species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Popul Biol 91:5466–5470. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.12.5466
Saha MC, Mian R, Zwonitzer JC, Chekhovskiy K, Hopkins AA (2005) An SSR- and AFLP-based genetic linkage map of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.). Theor Appl Gene 110:323–336. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1843-1
Salvi S, Tuberosa R, Chiapparino E, Maccaferri M, Veillet S, van Beuningen L, Isaac P, Edwards K, Phillips RL (2002) Toward positional cloning of Vgt1, a QTL controlling the transition from the vegetative to the reproductive phase in maize. Plant Mol Biol 48:601–613. doi:10.1023/A:1014838024509
Selvaraj MG, Schubert AM, Ayers JL, Baring MR (2009) Identification of QTLs for pod and kernel traits in cultivated peanut by bulked segregant analysis. Electron J Biotechnol. doi:10.2225/vol12-issue2-fulltext-13
Sinclair TR, Seligman NG (1995) Global environment change and simulated forage quality of wheat I. Nonstressed conditions. Field Crop Res 40:19–27. doi:10.1016/0378-4290(94)00091-P
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D (2008) Determination of ash in biomass laboratory analytical procedure (LAP). Nrel/Tp-510-4262226: 18
Sun X, Du Z, Ren J, Amombo E, Hu T, Fu J (2015) Association of SSR markers with functional traits from heat stress in diverse tall fescue accessions. BMC Plant Biol 15:1–13. doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0494-5
Vernesi C, Crestanello B, Pecchioli E, Tartari D, Caramelli D, Hauffe H, Bertorelle G (2003) The genetic impact of demographic decline and reintroduction in the wild boar (Sus scrofa): a microsatellite analysis. Mol Ecol 12:585–595. doi:10.1046/J.1365-294X.2003.01763.X
Wang M, Jiang N, Jia T, Leach L, Cockram J, Waugh R, Ramsay L, Thomas B, Luo Z (2012) Genome-wide association mapping of agronomic and morphologic traits in highly structured populations of barley cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 124:233–246. doi:10.1007/s00122-011-1697-2
Wang Z, Liao L, Yuan X, Guo H, Guo A, Liu J (2013) Genetic diversity analysis of Cynodon dactylon (bermudagrass) accessions and cultivars from different countries based on ISSR and SSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 46:108–115. doi:10.1016/j.bse.2012.09.001
Weinkauf M (2012) BenjaminiHochberg.xlsx. Version 1.1
Wu Y, Taliaferro CM (2005) Bermudagrass. In: Singh RJ, Jauhar PP (eds) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering, and crop improvement. Taylor & Francis, Florida, pp 229–275
Wu YQ, Taliaferro CM, Martin DL, Goad CL, Anderson JA (2006) Genetic variability and relationships for seed yield and its components in Chinese Cynodon accessions. Field Crop Res 98:245–252. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2006.02.003
Xie HL, Ji HQ, Liu ZH, Tian GW, Wang CL, Hu YM, Tang JH (2009) Genetic basis of nutritional content of stover in maize under low nitrogen conditions. Euphytica 165:485–493. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9764-8
Xie J, Kong X, Chen J, Hu B, Wen P, Zhuang J, Bao J (2011) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for fiber and lignin contents from an interspecific cross Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 12:518–526. doi:10.1631/jzus.B1000299
Xie Y, Luo H, Hu L, Sun X, Lou Y, Fu J (2014) Classification of genetic variation for cadmium tolerance in Bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.] using physiological traits and molecular markers. Ecotoxicology 23:1030–1043. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1247-1
Xie Y, Sun X, Ren J, Fan J (2015) Genetic diversity and association mapping of cadmium tolerance in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.]. Plant Soil 390:307–321. doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2391-y
Yu J, Buckler ES (2006) Genetic association mapping and genome organization of maize. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:155–160. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2006.02.003
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S, Buckler ES (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208. doi:10.1038/ng1702
Yu X, Bai G, Luo N, Chen Z, Liu S, Liu J, Warnke SE, Jiang Y (2011) Association of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers with submergence tolerance in diverse populations of perennial ryegrass. Plant Sci 180:391–398. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.10.013
Zeisset I, Beebee TJ (2001) Determination of biogeographical range: an application of molecular phylogeography to the European pool frog Rana lessonae. Proc R Soc London B Biol Sci 268:933–938. doi:10.1098/rspb.2001.1600
Zhang P, Liu X, Tong H, Lu Y, Li J (2014) Association mapping for important agronomic traits in core collection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with SSR markers. PLoS ONE 9:e111508. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111508
Acknowledgement
This research was financially supported by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31502009) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 31672482).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY and JF conceived and designed the experiment. MMG performed the research, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. JF and XY revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gitau, M.M., Fan, J., Xie, Y. et al. Genetic diversity and association mapping of forage quality in diverse bermudagrass accessions. Euphytica 213, 234 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2024-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-2024-z