Abstract
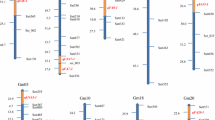
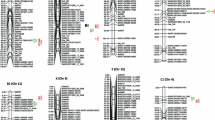
The seed oil content in soybean is an important trait that drives successful soybean quality. A recombination of inbred lines derived from a cross between the ‘Charleston’ and ‘Dongnong594’ cultivars was planted in one location (HRB) across 13 years and two locations (HXL and JMS) across 6 years in China (25 environments in total), and the genetic effects were partitioned into additive main effects, epistatic main effects and their environmental interaction effects using composite interval mapping and inclusive composite interval mapping models based on a high-density genetic map. Twelve main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were identified on chromosomes Ch3, Ch4, Ch6, Ch13, Ch15, Ch17, Ch18,Ch19 and Ch20 and detected in more than two environments. Among the intervals of the main-effect QTLs, eleven candidate genes were screened for their involvement in seed oil content and/or fatty acid biosynthesis and metabolism processes based on gene ontology and annotation information, moreover, the main effect QTL were identified in a wild soybean chromosome segment substitution lines population, the phenotype and the QTL fragment showed the identity relationship significantly. Furthermore, an analysis of epistatic interactions showed that four epistatic QTL pairs were detected, and they could explain approximately 70% of the phenotypic variation interaction with environments in total. The additive main-effect QTLs and epistatic QTL pairs contributed to high phenotypic variation under multiple environments, and the results were also validated and corroborated with previous research, indicating that marker-assisted selection can be used to improve soybean oil content and that the candidate genes can also be used as a foundation data set for research on gene functions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW (1996) Genetic basis of the evolution of adaptedness in plants. Euphytica 92:1–11. doi:10.1007/BF00022822
Bajaj D, Upadhyaya HD, Khan Y, Das S, Badoni S, Shree T, Kumar V, Tripathi S, Gowda CL, Singh S, Sharma S, Tyagi AK, Chattopdhyay D, Parida SK (2015) A combinatorial approach of comprehensive QTL-based comparative genome mapping and transcript profiling identified a seed weight-regulating candidate gene in chickpea. Sci Rep 5:9264. doi:10.1038/srep09264
Bilyeu KD, Palavalli L, Sleper DA, Beuselinck PR (2003) Three microsomal omega-3-fatty acid desaturase genes contribute to soybean linolenic acid levels. Crop Sci 43(5):1833–1838
Bolon YT, Joseph B, Cannon SB, Graham MA, Diers BW, Farmer AD, May GD, Muehlbauer GJ, Specht JE, Tu ZJ, Weeks N, Xu WW, Shoemaker RC, Vance CP (2010) Complementary genetic and genomic approaches help characterize the linkage group I seed protein QTL in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 10:41
Brim CA, Burton JW (1979) Recurrent selection in soybeans: II: selection for increased percent protein in seeds. Crop Sci 19:494–498
Brummer EC, Graef GL, Orf J, Wilcox JR, Shoemaker RC (1997) Mapping QTL for seed protein and oil content in eight soybean populations. Crop Sci 37(2):370–378
Carlborg Ö, Haley CS (2004) Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat Rev Genet 5:618–625
Chapman NH, Bonnet J, Grivet L, Lynn J, Graham N, Smith R, Sun GP, Walley PG, Poole M, Causse M, King GJ, Baxter C, Seymour GB (2012) High-resolution mapping of a fruit firmness-related quantitative trait locus in tomato reveals epistatic interaction associated with a complex combination locus. Plant Physiol 159:1644–1657
Chen QS, Zhang ZC, Liu CY, Wang WQ, Li WB (2005) Construction and analysis of soybean genetic map using recombinant inbred line of Charleston × dongnong 594. Sci Agric Sin 38:1312–1316
Choi IY, Hyten DL, Matukumalli LK, Song Q, Chaky JM, Quigley CV, Chase K, Lark KG, Reiter RS, Yoon MS, Hwang EY, Yi SI, Young ND, Shoemaker RC, van Tassell CP, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Genetics 176:685–696
Cober ER, Voldeng HD (2000) Developing high-protein, high-yield soybean populations and lines. Crop Sci 40:39–42
Cooper RL, Martin RJ, St Martin SK, Calip-DuBois A, Fioritto RJ, Schmitthenner AF (1995) Registration of ‘Charleston’ soybean. Crop Sci 35(2):593–593
Cregan PB, Jarvik T, Bush AL, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Kahler AL, Kaya N, VanToai TT, Lohnes DG, Chung J, Specht JE (1999) An integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean genome. Crop Sci 39:1464–1490. doi:10.2135/cropsci1999.3951464x
Deng Z, Hu S, Chen F, Li W, Chen J, Sun C, Zhang Y, Wang S, Song X, Tian J (2015) Genetic dissection of interaction between wheat protein and starch using three mapping populations. Mol Breed 35:1–9. doi:10.1007/s11032-015-0216-6
Diers BW, Keim P, Fehr WR, Shoemaker RC (1992) RFLP analysis of soybean seed protein and oil content. Theor Appl Genet 83:608–612
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1996) Less-than-additive epistatic interactions of quantitative trait loci in tomato. Genetics 143:1807–1817
Eskandari M, Cober ER, Rajcan I (2013) Genetic control of soybean seed oil: II. QTL and genes that increase oil concentration without decreasing protein or with increased seed yield. Theor Appl Genet 126:1677–1687
Garwin JL, Klages AL, Cronan JE (1980) Beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase II of Escherichia coli. Evidence for function in the thermal regulation of fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem 255(8):3263–3265
González AM, Yuste-Lisbona FJ, Rodiño AP, De Ron AM, Capel C, García-Alcázar M, Lozano R, Santalla M (2015) Uncovering the genetic architecture of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum resistance through QTL mapping and epistatic interaction analysis in common bean. Front Plant Sci 6:141. doi:10.3389/fpls.2015.00141
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324. doi:10.1038/hdy.1992.131
Heath RJ, Jackowski S, Rock CO (1994) Guanosine tetraphosphate inhibition of fatty acid and phospholipid synthesis in Escherichia coli is relieved by overexpression of glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (plsB). J Biol Chem 269(42):26584–26590
Hwang EY, Song Q, Jia G, Specht JE, Hyten DL, Costa J, Cregan PB (2014) A genome-wide association study of seed protein and oil content in soybean. BMC Genom 15(1):1
Hyten DL, Pantalone VR, Sams CE, Saxton AM, Landau-Ellis D, StefaniakM TR, Schmidt E (2004) Seed quality QTL in a prominent soybean population. Theor Appl Genet 109:552–561
Hyten DL, Choi I, Song Q, Specht JE, Carter TE, Shoemaker RC, Hwang E, Matukumalli LK, Cregan PB (2010) A high density integrated genetic linkage map of soybean and the development of a 1536 universal soy linkage panel for quantitative trait locus mapping. Crop Sci 50:960–968
Jansen RC (1993) Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics 135:205–211
Jansen RC, Van Ooijen JW, Stam P, Lister C, Dean C (1995) Genotype-by-environment interaction in genetic mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 91:33–37. doi:10.1007/BF00220855
Jia Y, Sun X, Sun J, Pan Z, Wang X, He S, Xiao S, Shi W, Zhou Z, Pang B, Wang L, Liu J, Ma J, Du X, Zhu J (2014) Association mapping for epistasis and environmental interaction of yield traits in 323 cotton cultivars under 9 different environments. PLoS ONE 9:e95882. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0095882
Kao CH, Zeng ZB, Teasdale RD (1999) Multiple interval mapping for quantitative trait loci. Genetics 152:1203–1216
Keim P, Diers BW, Olson TC, Shoemaker RC (1990) RFLP mapping in soybean: association between marker loci and variation in quantitative traits. Genetics 126:735–742
Korir PC, Qi B, Wang Y, Zhao T, Yu D, Chen S, Gai J (2011) A study on relative importance of additive, epistasis and unmapped QTL for aluminium tolerance at seedling stage in soybean. Plant Breed 130:551–562. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2011.01862.x
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3
Lark KG, Weisemann JM, Matthews BF, Palmer R, Chase K, Macalma T (1993) A genetic map of soybean (Glycine max L.) using an intraspecific cross of two cultivars: ‘Minsoy’ and ‘Noir 1’. Theor Appl Genet 86:901–906. doi:10.1007/BF00211039
Lee S, Freewalt KR, McHale LK, Song QJ, Jun TH, Michel AP, Dorrance AE, Rouf MA (2015) A high-resolution genetic linkage map of soybean based on 357 recombinant inbred lines genotyped with BARCSoySNP6K. Mol Breed 35(2):1–7
Lenfant N, Hotelier T, Velluet E, Bourne Y, Marchot P, Chatonnet A (2013) ESTHER, the database of the α/β-hydrolase fold superfamily of proteins: tools to explore diversity of functions. Nucl Acids Res 41(D1):D423–D429
Li H, Zhao T, Wang Y, Yu D, Chen S, Zhou R, Gai J (2011) Genetic structure composed of additive QTL, epistatic QTL pairs and collective unmapped minor QTL conferring oil content and fatty acid components of soybeans. Euphytica 182(1):117–132
Liu G, Yang J, Xu H, Zhu J (2007) Influence of epistasis and QTL x environment interaction on heading date of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet Genom 34:608–615. doi:10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60069-1
Liu YT, Li CY, Shi XX, Feng H, Wang YG (2016) Identification of QTLs with additive, epistatic, and QTL × environment interaction effects for the bolting trait in Brassica rapa L. Euphytica. doi:10.1007/s10681-016-1710-6
Luo YX, Luo CY, Du DZ, Fu Z, Yao YM, Xu CC, Zhang HS (2014) Quantitative trait analysis of flowering time in spring rapeseed (B. napus L.). Euphytica 200(3):321–335
Ma XQ, Tang JH, Teng WT, Yan JB, Meng YJ, Li JS (2007) Epistatic interaction is an important genetic basis of grain yield and its components in maize. Mol Breed 20(1):41–51
Mao T, Jiang Z, Han Y, Teng W, Zhao X, Li W (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci underlying seed protein and oil contents of soybean across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Plant Breed 132(6):630–641
Mackay TF (2014) Epistasis and quantitative traits: using model organisms to study gene-gene interactions. Nat Rev Genet 15:22–33. doi:10.1038/nrg3627
Mackay TF, Stone EA, Ayroles JF (2009) The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects. Nat Rev Genet 10:565–577. doi:10.1038/nrg2612
Mansur LM, Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Cregan PB, Lark KG (1996) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits using recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Crop Sci 36(5):1327–1336
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13
Merah O, Langlade N, Alignan M, Roche J, Pouilly N, Lippi Y, Vear F, Cerny M, Bouniols A, Mouloungui Z, Vincourt P (2012) Genetic analysis of phytosterol content in sunflower seeds. Theor Appl Genet 125:1589–1601
Mohan A, Kulwal P, Singh R, Kumar V, Mir RR, Kumar J, Prasad M, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2009) Genome-wide QTL analysis for pre-harvest sprouting tolerance in bread wheat. Euphytica 168:319–329. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-9935-2
Muerhoff AS, Griffin KJ, Johnson EF (1992) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor mediates the induction of CYP4A6, a cytochrome P450 fatty acid omega-hydroxylase, by clofibric acid. J Biol Chem 267(27):19051–19053
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Mansur LM, Cregan PB, Adler FR, Lark KG (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39(6):1642–1651
Palomeque L, Liu LJ, Li W, Hedges B, Cober ER, Rajcan I (2009) QTL in mega-environments: I. Universal and specific seed yield QTL detected in a population derived from a cross of high-yielding adapted × high-yielding exotic soybean lines. Theor Appl Genet 119:417–427. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1049-7
Palomeque L, Liu LJ, Li W, Hedges BR, Cober ER, Smid MP, Lukens L, Rajcan I (2010) Validation of mega-environment universal and specific QTL associated with seed yield and agronomic traits in soybeans. Theor Appl Genet 120:997–1003. doi:10.1007/s00122-009-1227-7
Qi Z, Wu Q, Han X, Sun Y, Du X, Liu C, Jiang H, Hu G, Chen Q (2011) Soybean oil content QTL mapping and integrating with meta-analysis method for mining genes. Euphytica 179(3):499–514
Qi ZM, Huang L, Zhu RS, Xin DW, Liu CY, Han X, Jiang HW, Hong WG, Hu GH, Zheng HK, Chen QS (2014a) A high-density genetic map for soybean based on specific length amplified fragment sequencing. PLoS ONE 9(8):e104871. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.010487
Qi ZM, Han X, Hou M, Xin DW, Wang ZY, Zhu RS, Hu ZB, Jiang HW, Li CD, Liu CY, Hu GH, Chen QS (2014b) QTL analysis of soybean oil content under 17 environments. Can J Plant Sci 94:245–261
Qi ZM, Pan JB, Han X, Qi HD, Xin DW, Wei Li, Mao XR, Wang ZY, Jiang HW, Liu CY, Hu ZB, Hu GH, Zhu RS, Chen QS (2016) Identification of major QTLs and epistatic ineractions for seed protein concentration in soybean under multiple environments based on a high-density map. Mol Breed 36:55. doi:10.1007/s11032-016-0475-x
Rakotomanga M, Saint-Pierre-Chazalet M, Loiseau PM (2005) Alteration of fatty acid and sterol metabolism in miltefosine-resistant Leishmania donovani promastigotes and consequences for drug-membrane interactions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(7):2677–2686
Ravi K, Vadez V, Isobe S, Mir R, Guo Y, Nigam S, Gowda M, Radhakrishnan T, Bertioli D, Knapp S, Varshney R (2011) Identification of several small main-effect QTLs and a large number of epistatic QTLs for drought tolerance related traits in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 122:1119–1132
Rodolphe F, Lefort M (1993) A multi-marker model for detecting chromosomal segments displaying QTL activity. Genetics 134:1277–1288
Rossi ME, Orf JH, Liu LJ, Dong Z, Rajcan I (2013) Genetic basis of soybean adaptation to North American vs. Asian mega-environments in two independent populations from Canadian × Chinese crosses. Theor Appl Genet 126:1809–1823
Salas JJ, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Characterization of substrate specificity of plant FatA and FatB acyl-ACP thioesterases. Arch Biochem Biophys 403(1):25–34
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL, Song Q, Thelen JJ, Cheng J, Xu D, Hellsten U, May GD, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya MK, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J, Tian Z, Zhu L, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang XC, Shinozaki K, Nguyen HT, Wing RA, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar D, Stacey G, Shoemaker RC, Jackson SA (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Sebolt AM, Shoemaker RC, Diers BW (2000) Analysis of a quantitative trait locus allele from wild soybean that increases seed protein concentration in soybean. Crop Sci 40(5):1438–1444
Shi J, Gonzales RA, Bhattacharyya MK (1996) Identification and Characterization of an S-Adenosyl-l-methionine:-Sterol-C-methyltransferase cDNA from Soybean. J Biol Chem 271(16):9384–9389
Shibata M, Takayama K, Ujiie A, Yamada T, Abe J, Kitamura K (2008) Genetic relationship between lipid content and linolenic acid concentration in soybean seeds. Breed Sci 58(4):361–366
Shoemaker RC, Olson TC (1993) Molecular linkage map of soybean [(Glycine max L.) Merr]. In: Genetic maps: locus maps of complex genomes. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Publisher, New York, pp 131–138
Song WC, Funk CD, Brash AR (1993) Molecular cloning of an allene oxide synthase: a cytochrome P450 specialized for the metabolism of fatty acid hydroperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90(18):8519–8523
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
Song QJ, Jenkins J, Jia GF, Hyten DL, Pantalone V, Jackson SA, Schmutz J, Cregan PB (2016) Construction of high resolution genetic linkage maps to improve the soybean genome sequence assembly Glyma1.01. BMC Genom 17(1):1
Specht JE, Chase K, Macrander M, Graef GL, Chung J, Markwell JP, Germann M, Orf JH, Lark KG (2001) Soybean response to water: a QTL analysis of drought tolerance. Crop Sci 41:493–509
Tajuddin T, Satoshi W, Naoki Y, Kyuya H (2003) Analysis of quantitative trait loci for protein and lipid contents in soybean seeds using recombinant inbred lines. Breed Sci 53:133–140
Todd J, Post-Beittenmiller D, Jaworski JG (1999) KCS1encodes a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase affecting wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 17(2):119–130
Wang F, Guo CY (2010) Molecular mapping and identification of quantitative trait loci for yield components in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Hereditas (Beijing) 32(3):271–277
Wang CS, Rutledge JJ, Gianola D (1994) Bayesian analysis of mixed linear models via Gibbs sampling with an application to litter size in Iberian pigs. Genet Sel Evol 26:91–115
Wang SC, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012a) Windows QTL cartographer 2.5 department of statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh.N.C. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm. Accessed 01 Aug 2012
Wang Z, Chen Z, Cheng J, Lai Y, Wang J et al (2012b) QTL analysis of Na + and K +concentrations in roots and shoots under different levels of NaCl stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). PLoS ONE 7:e51202
Wang L, Cheng JP, Lai YY, Du WL, Huang X, Wang ZF, Zhang HS (2014a) Identification of QTLs with additive, epistatic and QTL × development interaction effects for seed dormancy in rice. Planta 239:411–420
Wang X, Jiang GL, Green M, Scott RA, Song Q, Hyten DL, Cregan PB (2014b) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for seed yield, oil and protein contents in two recombinant inbred line populations of soybean. Mol Genet Genom 289(5):935–949
Wang ML, Khera P, Pandey MK, Wang H, Qiao L, Feng S, Tonnis B, Barkley NA, Pinnow D, Holbrook CC, Culbreath AK, Varshney RK, Guo B (2015) Genetic mapping of QTLs controlling fatty acids provided insights into the genetic control of fatty acid synthesis pathway in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PLoS ONE 10(4):e0119454
Wilcox JR (1985) Breeding soybeans for improved oil quantity and quality. R. Shibles, ed. In: Proc 3rd World Soybean Res. Con. Westview Press, Boulder, CO. pp 380–386
Wilcox JR (1998) Increasing seed protein in soybean with eight cycles of recurrent selection. Crop Sci 38(6):1536–1540
Wilson RF (2004) Seed composition. In: Boerma HR, Specht JE (eds) Soybeans: improvement, production and uses, 3rd edn. ASA, CSSA, SSA, Madison, pp 621–677
Wilson RF (2008) Soybean: market driven research needs. In: Stacey G (ed) Genetics and genomics of soybean. Springer, New York, pp 3–15
Wu X, Chang X, Jing R (2012) Genetic insight into yield-associated traits of wheat grown in multiple rain-fed environments. PLoS ONE 7:e31249
Würschum T, Maurer HP, Dreyer F, Reif JC (2013) Effect of inter-and-intragenic epistasis on the heritability of oil content in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 126(2):435–441
Xie W, Feng Q, Yu H, Huang X, Zhao Q, Xing Y, Yu S, Han B, Zhang Q (2010) Parent-independent genotyping for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:10578–10583
Xin DW, Qi ZM, Jiang HW, Hu ZB, Zhu RS, Hu JH, Han HY, Hu GH, Liu CY, Chen QS (2016) QTL location and epistatic effect analysis of 100-Seed weight using wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. & Zucc.) chromosome segment substitution lines. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0149380
Xing GN, Zhou B, Wang YF, Zhao TJ, Yu DY, Chen SY, Gai JY (2012) Genetic components and major QTL confer resistance to bean pyralid (Lamprosema indicata Fabricius) under multiple environments in four RIL populations of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 125:859–875
Xu YB, Crouch JH (2008) Marker-assisted selection in plant breeding: from pulication to practice. Crop Sci 48:391–407
Xu P, Wu XH, Wang BG, Hu TT, Lu ZF, Liu YH, Qin DH, Wang S, Li GJ (2013) QTL mapping and epistatic interaction analysis in asparagus bean for several characterized and novel horticulturally important trais. BMC Genet 14:4
Xu JF, Long Y, Wu JG, Xu HM, Zhao ZG, Wen J, Meng JL, Shi CH (2015) QTL identification on two genetic systems for rapeseed glucosinolate and erucic acid contents over two seasons. Euphytica. 205(3):647
Yang J, Zhu J (2005) Methods for predicting superior genotypes under multiple environments based on QTL effects. Theor Appl Genet 110:1268–1274
Yang J, Zhu J, Williams RW (2007) Mapping the genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 23:1527–1536
Yang J, Hu C, Hu H, Yu R, Xia Z, Ye X, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24:721–723
Yang C, Tang D, Zhang L, Liu J, Rong T (2015) Identification of QTL for ear row number and two-ranked versus many-ranked ear in maize across four environments. Euphytica 5:1–15
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Zhang YH, Liu MF, He JB, Wang YF, Xing GN, Li Y, Yang SP, Zhao TJ, Gai JY (2015) Marker-assisted breeding for transgressive seed protein content in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Theor Appl Genet 128:1061–1072
Zhao G, Wang J, Han Y, Teng W, Sun G, Li W (2008) Identification of QTL underlying the resistance of soybean to pod bore Leguminivora glycinivorella (Mats.) obraztsov, and correlation with plant, pod and seed traits. Euphytica 164:275–282
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted in the Key Laboratory of Soybean Biology in Chinese Ministry of Education in Heilongjiang Province and financially supported by National Key R & D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2016YFD0100500, 2016YFD0100300, 2016YFD0100201-21), the Research Fund for the national natural science foundation of China (31471516, 31401465, 31400074, 31501332), the China Post Doctoral Project (2015M581419), “Dongnongxuezhe project (To Chen QS)” “Young Talent project (To Qi ZM, 518062)” of Northeast agriculture university, SIPT Project of Northeast Agricultural University (201610224146), Heilongjiang Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists (JC2016004) and the outstanding academic leaders projects of Harbin (2015RQXXJ018).
Author’s contribution
Qi ZM, Qi HD and Zhang JZ contributed equally to this research. Che DD and Chen QS designed and conducted field tests and drafted the manuscript. Qi HD, Zhang XY, Xin DW and Yin ZG provided field management and protein test data. Qi ZM, Jiang HW, Zhang ZG, Zhu RS, Liu CY, Han X, Zhang JZ and Hu ZB provided the data mapping analysis, Qi ZM, Chen QS and Che DD designed the experiment, organized manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Authors state that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhaoming, Q., Xiaoying, Z., Huidong, Q. et al. Identification and validation of major QTLs and epistatic interactions for seed oil content in soybeans under multiple environments based on a high-density map. Euphytica 213, 162 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1952-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1952-y