Abstract
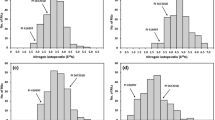
Phosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient required for many biological and metabolic plant functions. Phosphate is the form of P used by plants. Reducing the amount of P in the seed can further aide breeding efforts to reduce the amount of P released into the environment due to the indigestibility of the complexes formed with metal ions. Analysis of the variation of phosphorus concentration in soybean seed under non-stressed conditions revealed that phosphorus ranged from 3,948.1 to 5,695.8 μg/g total phosphorous (TP) in combined years. The averages for independent years were significantly different from one another. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of TP was performed to identify candidate gene(s) that is (are) involved in P accumulation in soybean seed. One putative QTL region was identified on chromosome 12 in the combined data that contained a phosphate transporter gene. Two additional suggestive QTL were identified on chromosomes 7 and 17 with chromosome 7 having both a phosphate transport gene and a ZIP transporter gene in the region of the QTL. There were additional genes in these regions that are involved in phosphate metabolism and transport.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2009) JMP ~ 8: statistical discovery software
Bilyeu KD, Zeng P, Coello P, Zhang ZJ, Krishnan HB, Bailey A, Beuselinck PR, Polacco JC (2008) Quantitative conversion of phytate to inorganic phosphorus in soybean seeds expressing a bacterial phytase. Plant Physiol 146:468–477
Blair MW, Sandoval TA, Caldas GV, Beebe SE, Páez MI (2009) Quantitative trait locus analysis of seed phosphorus and seed phytate content in a recombinant inbred line population of common bean. Crop Sci 49:237–246
Chiou TJ, Liu H, Harrison MJ (2001) The spatial expression patterns of a phosphate transporter (MtPT1) from Medicago truncatula indicate a role in phosphate transport at the root/soil interface. Plant J 25:281–293
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Cichy KA, Caldas GV, Snapp SS, Blair MW (2009) QTL analysis of seed iron, zinc, and phosphorus levels in an Andean bean population. Crop Sci 49:1742–1750
Correll DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27:261–266
de Cianzio SR, Fehr WR (1980) Genetic control of iron deficiency chlorosis in soybeans. Iowa State J Res 54:367–375
Divecha N, Irvine RF (1995) Phospholipid signaling review. Cell 80:269–278
Fehr WR (1987) Principles of cultivar development: theory and technique. Macmillan Publishing Company, New York
Fehr WR, Voss BK, Cianzio S (1984) Registration of a germplasm line of soybean, A7. Crop Sci 24:390–391
Flugge U-I (1999) Phosphate translocators in plastids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:27–45
Flügge UI, Fischer K, Gross A, Sebald W, Lottspeich F, Eckerskorn C (1989) The triose phosphate-3-phosphoglycerate-phosphate translocator from spinach chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA clone and import of the in vitro synthesized precursor protein into chloroplasts. Eur Mol Biol Organ J 8:39–46
Fu J, Peterson K, Guttieri M, Souza E, Raboy V (2008) Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) inositol monophosphatase: gene structure and enzyme characteristics. Plant Mol Biol 67:629–642
Gao Y, Shang C, Maroof MAS, Biyashev RM, Grabau EA, Kwanyuen P, Burton JW, Buss GR (2007) A modified colorimetric method for phytic acid analysis in soybean. Crop Sci 47:1797–1803
Jansen RC (1993) Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics 135:205–211
Jansen RC (1994) Controlling the Type I and Type II errors in mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics 138:871–881
King KE, Peiffer GA, Lauter N, Reddy M, Lin SF, Cianzio S, Shoemaker RC (2012) Mapping of iron and zinc quantitative trait loci in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) for association to iron deficiency chlorosis resistance. J Plant Nutr (in press)
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li Y-D, Wang Y-J, Tong Y-P, Gao J-G, Zhang J-S, Chen S-Y (2005) QTL mapping of phosphorus deficiency tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Euphytica 142(1–2):137–142
Liang Q, Cheng X, Mei M, Yan X, Liao H (2010) QTL analysis of root traits as related to phosphorus efficiency in soybean. Ann Bot 106:223–234
Lin S, Cianzio S, Shoemaker R (1997) Mapping genetic loci for iron deficiency chlorosis in soybean. Mol Breed 3:219–229
Liu B, Fujita T, Yan Z-H, Sakamoto S, Xu D, Abe J (2007) QTL mapping of domestication-related traits in soybean (Glycine max). Ann Bot 100:1027–1038
Loewus FA, Loewus MW (1983) Myo-Inositol: its biosynthesis and metabolism. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 34:137–161
Lou Yi, Gou J-Y, Xue H-W (2007) PIP5K9, an Arabidopsis phosphatidylinositol monophosphate kinase, interacts with a cytosolic invertase to negatively regulate sugar-mediated root growth. Plant Cell 19:163–181
Marschner H (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants, vol 2, Academic Press, San Diego
Maupin LM, Rosso ML, Shang C, Rainey KM (2011) Genotype × environment interaction and stability of phosphorus concentration in two soybean germplasm sources with modified phosphorus composition. Crop Sci 51:1518–1524
Oltmans SE, Fehr WR, Welke GA, Raboy V, Peterson KL (2005) Agronomic and seed traits of soybean lines with low-phytate phosphorus. Crop Sci 45:593–598
Pao SS, Paulsen IANT, Saier MH (1998) Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiology 62:1–34
Paran I, Zamir D (2003) Quantitative traits in plants: beyond the QTL. Trends Genet 19:303–306
Poirier Y, Bucher M (2002) Phosphate transport and homeostasis in Arabidopsis. The Arabidopsis Book 1:1–35
Price AH (2006) Believe it or not, QTLs are accurate! Trends Plant Sci 11:213–216
Raboy V (1997) Accumulation and storage of phosphate and minerals. In: Larkins BA, Vasil IK (eds) Cellular and molecular biology of plant seed development, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 441–477
Raboy V (2001) Seeds for a better future: “low phytate” grains help to overcome malnutrition and reduce pollution. Trends Plant Sci 6:458–462
Raboy V, Dickinson DB, Below FE (1984) Variation in seed total phosphorus, phytic acid, zinc, calcium, magnesium, and protein among lines of Glycine max and G. soja1. Crop Sci 24:431–434
Raboy V, Young KA, Dorsch JA, Cook AL (2001) Genetics and breeding of seed phosphorus and phytic acid. J Plant Physiol 158:489–497
Raghothama KG (1999) Phosphate acquisition. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:665–693
Reddy NR, Pierson MD, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1989) Phytates in cereals and legumes, CRC Press, Boca Raton
Schlemmer U, Müller H, Jany KD (1995) The degradation of phytic acid in legumes prepared by different methods. Eur J Clin Nutr 49(Suppl 3):S207–S210
Schmutz J, Cannon SB, Schlueter J, Ma J, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten DL et al (2010) Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature 463:178–183
Schulz B, Kolukisaoglu HU (2006) Genomics of plant ABC transporters: the alphabet of photosynthetic life forms or just holes in membranes? FEBS Lett 580:1010–1016
Sharpley AN, Withers PJA (1994) The environmentally-sound management of agricultural phosphorus. Fertilizer Res 39:133–146
Smith FW, Mudge SR, Rae AL, Glassop D (2003) Phosphate transport in plants. Plant Soil 248:71–83
Song Qijian, Jia G, Zhu Y, Grant D, Nelson RT, Hwang E-Y, Hyten DL, Cregan PB (2010) Abundance of SSR motifs and development of candidate polymorphic SSR markers (BARCSOYSSR_1.0) in soybean. Crop Sci 50:1950–1960
Tatusov Roman L, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Kiryutin B, Koonin EV, Krylov DM et al (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform 4:1–14
Tiwari VK, Rawat N, Chhuneja P, Neelam K, Aggarwal R, Randhawa GS, Dhaliwal HS, Keller B, Singh K (2009) Mapping of quantitative trait Loci for grain iron and zinc concentration in diploid A genome wheat. J Hered 100:771–776
Tsao GT, Zheng Y, Lu J, Gong CS (1997) Adsorption of heavy metal ions by immobilized phytic acid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 63–65:731–741
van Ooijen, JW (2009) MapQTL 6: software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations of diploid species. Wageningen, The Netherlands. http://www.kyazma.nl/docs/MQ6Manual.pdf. Accessed 30 March 2011
Vreugdenhil D, Aarts MGM, Koornneef M, Nelissen H, Ernst WHO (2004) Natural variation and QTL analysis for cationic mineral content in seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 27:828–839
Willems G, Frérot H, Gennen J, Salis P, Saumitou-Laprade P, Verbruggen N (2010) Quantitative trait loci analysis of mineral element concentrations in an Arabidopsis halleri × Arabidopsis lyrata petraea F2 progeny grown on cadmium-contaminated soil. New Phytol 187:368–379
Wu Z, Zhao J, Gao R, Hu G, Gai J, Xu G, Xing H (2011) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of two members of the Pht1 family of phosphate transporters in Glycine max. PLoS ONE 6:1–12
Zheng L, Huang F, Narsai R, Wu J, Giraud E, He F, Cheng L et al (2009) Physiological and transcriptome analysis of iron and phosphorus interaction in rice seedlings. Plant Physiol 151:262–274
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the USDA-ARS and Iowa State University. Names are necessary to report factually on the available data; however, the USDA neither guarantees nor warrants the standard of the product, and the use of the name by the USDA implies no approval of the product to the exclusion of others that may also be suitable. Additionally, The authors thank Jonathan Hobbs of the Iowa State University Agriculture Experiment Station Consulting Group for assistance with data imputation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, K.E., Lauter, N., Lin, S.F. et al. Evaluation and QTL mapping of phosphorus concentration in soybean seed. Euphytica 189, 261–269 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0797-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0797-7