Abstract
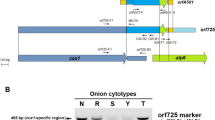
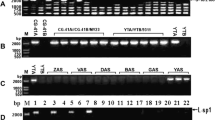
Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is a maternally inherited trait that fails to produce functional pollen grains. The CMS system is widely employed to facilitate the utilization of heterosis in major crops. However, little is known about the CMS associated genes in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). The objective of this study was to compare CMS cotton (CMS-D2) with the cytoplasm from G. harknessii and its isogenic maintainer line with the normal fertile Upland cotton cytoplasm to identify CMS-D2 specific gene(s) and to develop CMS-specific sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers. Based on Southern blot analysis using 10 mitochondrial gene-specific probes (cob, cox2, atp6, atp9, nad3, cox3, atpA, cox1, nad6 and nad9), three probes (cox3, atpA, and nad6) revealed restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) between the CMS-D2 and its isogenic maintainer line. RT-PCR confirmed that the three genes were differentially expressed between the two lines. These results indicated that there existed structural and expression variations in the three genes when the mitochondrial D2 genome was transferred into Upland cotton. Genome walking and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) were further performed to analyze the sequences of these genes and their flanking regions. For cox3 and nad6, there was only one different nucleotide each in the gene regions between the two lines. Also some nucleotides upstream of the ATG codon were different. For atpA, the sequences downstream the atpA were significantly different between the two cytoplasmic lines. Furthermore, two nucleotides at the -4 and -5 position from ATG codon were also changed between the two cytoplasms (i.e., CG→AA), and this mutation also exists in RNA sequences. Interestingly, nine nucleotides (ATGCAACTA) were also inserted at the location of 899 bp upstream of ATG codon in the CMS line. The results suggest that the abnormal sequence and expression of atpA gene is associated with CMS expression in Upland cotton. According to the significant different sequences downstream the atpA gene, a CMS-D2 specific SCAR marker was developed. The CMS-specific PCR bands were verified for 10 cultivars containing either normal- or CMS-D2cytoplasm. This will allow quick and reliable identification of the cytoplasmic types of individual plants at the seedling stage, and assessment of the purity of F1 seed lots.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Sakamoto M, Shinjyo C, Shimada H, Fujimura T (1994) A unique sequence located downstream from the rice mitochondrial atp6 may cause male sterility. Curr Genet 25:52–58
Bergman P, Edqvist J, Farbos I, Glimelius K (2000) Male-sterile tobacco displays abnormal mitochondrial atp1 transcript accumulation and reduced floral ATP/ADP ratio. Plant Mol Bio 42:531–544
Bonhomme S, Budar F, Lancelin D, Small I, Defrance MC, Pelletier G (1992) Sequence and transcript analysis of the Nco2.5 Ogura-specific fragment correlated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica cybrids. Mol Gen Genet 235:340–348
Dewey RE, Levings CS, Timothy DH (1986) Novel recombinations in the maize mitochondrial genome produce a unique transcriptional unit in the Texas male-sterile cytoplasm. Cell 44:439–449
Feng C, Guo J et al. (2000) Cytoplasmic-nuclear male sterility in cotton: comparative RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA. Proceedings of Beltwide Cotton Research Conference: 551–552
Grelon M, Budar F, Bonhomme S, Pelletier G (1994) Ogura cytoplasmic male-sterility (CMS)-associated orf138 is translated into a mitochondrial membrane polypeptide in male-sterile Brassica cybrids. Mol Gen Genet 243:540–547
Hu GH, Yu SX (2007) Extraction of high-quality total RNA in cotton leaf with improved CTAB method. Cotton Sci 19:69–70
Johns C, Lu M, Lyznik A, Mackenzie S (1992) A mitochondrial DNA sequence is associated with abnormal pollen development in cytoplasmic male sterile bean plants. Plant Cell 4:435–449
Kanzaki H, Takeda M, Kameya T (1991) Sequence analysis of a mitochondrial DNA fragment isolated from cultured cells of carrot cytoplasmic male-sterile strain. Jpn J Genet 66:719–724
Kim D, Kang J, Kim B-D (2007) Isolation and characterization of the cytoplasmic male sterility-associated orf456 gene of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Mol Bio 63:519–532
Kohler RH, Horn R, Lossl A, Zetsche K (1991) Cytoplasmic male sterility in sunflower is correlated with the co-transcription of a new open reading frame with the atpA gene. Mol Gen Genet 227:369–376
Kozak M (1999) Initiation of translation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Gene 234:187–208
Kubo T, Newton KJ (2008) Angiosperm mitochondrial genomes and mutations. Mitochondrion 8:5–14
Lee Y-P, Kim S, Lim H, Ahn Y, Sung S-K (2008) Identification of mitochondrial genome rearrangements unique to novel cytoplasmic male sterility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:719–728
Makaroff CA, Apel IJ, Palmer JD (1990) Characterization of radish mitochondrial atpA: influence of nuclear background on transcription of atpA-associated sequences and relationship with male sterility. Plant Mol Biol 15:735–746
Meyer VG (1975) Male sterility from Gossypium harknessii. J Hered 66:23–27
Moneger F, Smart CJ, Leaver CJ (1994) Nuclear restoration of cytoplasmic male sterility in sunflower is associated with the tissue-specific regulation of a novel mitochondrial gene. EMBO J 13:8–17
Paterson A, Brubaker C, Wendel J (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Bio Rep 11:122–127
Pesole G, Gissi C, Grillo G, Licciulli F, Liuni S, Saccone C (2000) Analysis of oligonucleotide AUG start codon context in eukariotic mRNAs. Gene 261:85–91
Sabar M, Gagliardi D, Balk J, Leaver CJ (2003) ORFB is a subunit of F1F(O)-ATP synthase: insight into the basis of cytoplasmic male sterility in sunflower. EMBO Rep 4:381–386
Sakai T, Imamura J (1992) Alteration of mitochondrial genomes containing atpA genes in the sexual progeny of cybrids between Raphanus sativus cms line and Brassica napus cv. Westar. Theor Appl Genet 84:923–929
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Schnable PS, Wise RP (1998) The molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration. Trend Plant Sci 3:175–180
Small ID, Isaac PG, Leaver CJ (1987) Stoichiometric differences in DNA molecules containing the atpA gene suggest mechanisms for the generation of mitochondrial genome diversity in maize. EMBO J 6:865–869
Stewart JM (1992) A new cytoplasmic male sterility and restorer for cotton. Proceedings of Beltwide Cotton Research Conference, National Cotton Council, Memphis: 610
Tang HV, Pring DR, Shaw LC, Salazar RA, Muza FR, Yan B, Schertz KF (1996) Transcript processing internal to a mitochondrial open reading frame is correlated with fertility restoration in male-sterile sorghum. Plant J 10:123–133
Wang F, Feng C, O’Connell M, Stewart J, Zhang J (2010) RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA in two cytoplasmic male sterility systems (CMS-D2 and CMS-D8) of cotton. Euphytica 172:93–99
Xue Y, Collin S, Davies DR, Thomas CM (1994) Differential screening of mitochondrial cDNA libraries from male-fertile and cytoplasmic male-sterile sugar-beet reveals genome rearrangements at atp6 and atpA loci. Plant Mol Biol 25:91–103
Yang JH, Huai Y, Zhang MF (2009) Mitochondrial atpA gene is altered in a new orf220-type cytoplasmic male-sterile line of stem mustard (Brassica juncea). Mol Biol Rep 36:273–280
Young E, Hanson M (1987) A fused mitochondrial gene associated with cytoplasmic male sterility is developmentally regulated. Cell 50:41–49
Zhang JF, Stewart JM (2001a) CMS-D8 restoration in cotton is conditioned by one dominant gene. Crop Sci 41:283–288
Zhang JF, Stewart JM (2001b) Inheritance and genetic relationships of the D8 and D2-2 restorer genes for cotton cytoplasmic male sterility. Crop Sci 41:289–294
Zhang J.F., Mara-koosham G., et al. (2004) Molecular analysis of mitochondrial genome in two cytoplasmic male sterile system of cotton. Proceedings of Beltwide Cotton Research Conference, San Antonio: 1178–1182
Acknowledgment
This research was financed by funds from the National Transgenic Major Program (2008ZX08005-001) and Special Fund for Basic Research in the Central Public Research Institutes (SJA0903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jianyong Wu and Yangcang Gong contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Gong, Y., Cui, M. et al. Molecular characterization of cytoplasmic male sterility conditioned by Gossypium harknessii cytoplasm (CMS-D2) in upland cotton. Euphytica 181, 17–29 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0357-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0357-6