Abstract
Utilizing the theory of change, this study analyzes the extent to which the participation in cross-national learning assessments by Kenya, Tanzania and South Africa has contributed to educational policy and curriculum reforms. Data collection involved in-depth interviews with key informants and summative content analysis of policy/strategic documents. The findings reflect that overall, at least 11 policy/strategic documents formulated between the years 2000 and 2015 in the three countries respond well to recommendations or findings emanating from the cross-national learning assessments. Two curriculum reviews/reforms attributable to cross-national learning assessments are also recorded. The inferences are drawn based on the testament by the research participants and or whether the documents contain strong references to cross-national learning assessments.

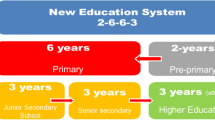
(Source: Stathers et al. 2013)

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Addey, C. (2014). Why do countries join international literacy assessments? An actor-network theory analysis with case studies from Lao PDR and Mongolia. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis. United Kingdom: University of East Anglia.
Almquist, A. (2011). Attribution versus contribution. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/pubs/docs/april_2011_cb.pdf. Accessed 4 Apr 2017
Anil, K., Mwaipopo, K., & Mugiumu, C. (2014). Has Uwezo influenced key actors in 2013? Evidence from Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda. East Africa: Twaweza.
Baird, J., Talia, I., Johnson, S., Stobart, G., Yu, G., Sprague, T., et al. (2011). Policy effects of PISA. Oxford: Oxford University Centre for Educational Assessment.
Barnett, C., & Gregorowski, R. (2013). Learning about theories of change for the monitoring and evaluation of research uptake. Institute for Development Studies. Retrieved May 9, 2018 from http://www.managingforimpact.org/sites/default/files/resource/ids_brief_theory_of_change.pdf.
Barret, A. (2009). The education millenium development goal beyond 2015: Prospects for quality and learners. London: Department for International Development.
Barrett, A., & Sørensen, T. B. (2015). Indicators for all? Monitoring quality and equity for a broad and bold post-2015 global education agenda. Open Society Foundations. Retrieved May 3, 2018 from https://www.opensocietyfoundations.org/sites/default/files/barrett-indicators-for-all-20150520.pdf.
Benavot, A., & Tanner, E. (2007). The growth of national learning assessments in the world, 1995–2006. Background paper for the EFA global monitoring report: Education For All by 2015: Will We Make It? Paris: UNESCO
Best, M., Knight, P., Lietz, P., Lockwood, C., & Nugroho, D. (2013). The impact of national and international assessment programmes on education policy, particularly policies regarding resource allocation and teaching and learning practices in developing countries. Final report. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London. Retrieved April 22, 2018 from http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Portals/0/PDF%20reviews%20and%20summaries/Education%20assessment%202013Best%20report.pdf?ver=2013-09-03-141900-363.
Breakspear, S. (2012). The policy impact of PISA: An exploration of the normative effects of international benchmarking in school system performance. Paris: OECD.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3(2), 77–101
Curtis, W., Murphy, M., & Shields, S. (2014). Research and education. London: Routledge.
Department for International Development. (2012). Broadening the range of designs and methods for impact evaluation. London: DFID.
Elks, P. (2016). The impact of assessment results on education policy and practice in East Africa. Retrieved October 21, 2018 from http://www.heart-resources.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/Think-Piece-the-impact-of-assessment-results-on-education-policy-and-practice-in-East-Africa.pdf.
Figazzolo, L. (2009). Testing, Ranking, Reforming: Impact of PISA 2006 on the education policy debate.. Brussels: Educational International. Available at: http://pages.eiie.org/quadrennialreport/2009/s3.amazonaws.com/educationinternational/2009/assets/50/Impact_of_PISA_2006_EN.pdf. Accessed 21 Oct 2016.
Goldstein, H. (2004). Education for all: The globalization of learning targets. Comparative Education, 40(1), 7–14.
Goverment of Kenya. (2005). The session paper no. 1 of 2005 on policy framework for education, training and research; Meeting the challenges of education, training and research in Kenya in the 21st Century. Nairobi: Mnistry of Education, Goverment Press.
Greaney, V., & Kellaghan, T. (2008). National assessments of educational achievement; national assessment of education achievement Series. Washington: World Bank.
Hanushek, E., & Kimko, D. (2000). Schooling, labor-force quality, and the growth of nations. American Economic Review, 90(5), 1184–1208
Hanushek, E., & Woessmann, L. (2012). Do better schools lead to more growth? Cognitive skills, economic outcomes, and causation. Journal of Economic Growth, 17, 267–321.
Hanushek, E., & Wossmann, L. (2007). The role of education quality in economic growth. In W. B. 4122. World Bank.
Ion, G., & Iucu, R. (2014). Professionals’ perceptions about the use of research in educational practice. European Journal of Higher Education, 4, 334–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2014.899154.
Kanjee, A. (2013). Large-scale assessment studies in South Africa: Trends in reporting results to schools. In S. Laher & K. Cockcroft (Eds.), Psychological assessment in South Africa: Research and applications (pp. 2000–2010). Johannesburg: WITS University Press.
Kellaghan, T., Greaney, V., & Murray, T. (2009). Using the results of a national assessment of educational achievement. National assessments of educational achievement (Vol. 5). Washington, DC: World Bank
Knight, P., Lietz, P., Nugroho, D., & Tobin, M. (2012). The impact of national and international assessment programmes on educational policy, particularly policies regarding resource allocation and teaching and learning practices in developing countries. London: EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Unit, Institute of Education, University of London. Retrieved November 2, 2017 from http://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Portals/0/PDF%20reviews%20and%20summaries/Education%20assessment%202012Knight%20protocol.pdf?ver=2012-04-10-113832-317.
Leeuw, F. L. (in press). Theory-based evaluation. online article available at: http://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/information/evaluations/pdf/impact/theory_impact_guidance.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2013.
Leeuw, F., & Vaessen, J. (2009). Impact evaluations and development: Nonie guidance on impact evaluation. Washington, DC: Worldbank.
Mayne, J. (1999). Addressing attribution through contribution analysis: Using performance measures sensibly. A joint paper by the Office of Auditor General and the Treasury Board Secretariat, Canada. Retrieved October 22, 2017 from http://kessa.org/yahoo_site_admin/assets/docs/5TH_ANNUAL_CONFERENCE_PAPER_keynoteaddress.25190110.pdf.
Mbabu, A., Peixoto, Z., Mulongo, G., Munyu, H., Ojwang, F., & Low, J. (2014). Engendered orange-fleshed project planning, implementation, monitoring and evaluation: Reaching agents of change learning kit. Nairobi: The International Potato Center.
Mulongo, G. (2014). Debating international learner assessments as a proxy measure of quality of education in the context of EFA: A review essay. World Journal of Education, 4(1), 35–47.
Mulongo, G., & Amod, Z. (2017). Participation in cross-national learning assessments and impact on capacity development: Programmes, practice, structures and teacher competency. Case study of Kenya, Tanzania and South Africa. Evaluation and Program Planning, 65, 94–105.
O ́Flynn, M. (2015). Theory of change. Oxford: INTRAC. Retrieved May 4, 2018 from https://www.intrac.org/wpcms/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Monitoring-and-Evaluation-Series-Theory-of-Change-16.pdf.
OECD. (2004). Education at a Glance 2004. Paris: OECD.
OECD (2013). Overview of progress and policy challenges in Tanzania. In OECD Investment Policy Reviews: Tanzania. OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264204348-6-en. Accessed 4 Dec 2016
Postlethwaite, N. (2004). Monitoring educational achievement. Paris: The International Institute for Educational Planning, UNESCO.
Republic of South Africa. (2010). South Africa. National development plan 2030: Our future-make it work. Pretoria: Sherino Publishers.
Republic of South Africa. (2011). Action plan to 2014: Towards the realisation of schooling 2025. Pretoria: Department of Basic Education.
Retolaza, E. I. (2011). Theory of change; A thinking and action approach to navigate in the complexity of social change processes. Guatemala: Humanistic Institute for Development Cooperation (HIVOS) and the United Nations Development Programme.
Ross, K., & Genevois, I. (2006). Cross-national studies of the quality of education: planning their design and managing their impact. Paris: UNESCO, International Institute for Education Planning. Retrieved March 23, 2017 from http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001470/147093e.pdf.
Stathers, T., David, S., Low, J., Mulongo, G., & Mbabu, A. (2013). Everything you ever wanted to know about sweetpotato: Reaching agents of change ToT manual. 6: Gender and diversity aspects. Monitoring of OFSP dissemination and uptake. Nairobi: The International Potato Center.
UNESCO. (2005). Aspects of literacy assessment; Topics and issues from the UNESCO expert meeting. Paris: UNESCO.
UNESCO. (2006). Cross-national studies of the quality of education; planning their design and managing their impact. Paris: The International Institute for Education Planning. Retrieved January 18, 2018 from http://www.sacmeq.org/sites/default/files/sacmeq/book/Ross-Genevois_Cross_National_Studies_Quality_of_Education.pdf.
UNESCO. (2017). Accountability in education: Meeting our Committments. Global Monitoring Report. Paris: UNESCO. Retrieved May 3, 2018 from http://www.right-to-education.org/sites/right-to-education.org/files/resource-attachments/GEM_Report_201718_Accountability_in_education_2017_En.pdf.
United Republic of Tanzania. (2013). The national key result area roadmap for education (2013/14–2015/16). Dar es Salaam: Ministry of Education.
Uwezo. (2011). Are our children learning? Annual assessment report. Dar-es-salaam: Uwezo, TENMET & Hivos: Available at: http://www.twaweza.org/uploads/files/ALA_UWEZO.pdf. Accessed 11 Apr 2014.
Wagner, D., Lockheed, M., Mullis, L., Martin, M., Kanjee, A., Gove, A., et al. (2012). Debate on learning assessments in developing countries. Journal of Comparative and International Education, 42, 509–545.
Wasanga, P., & Kyalo, F. (2007). National assessment initiatives in Kenya and their impact on quality of education. Nairobi: The Kenya National Examinations Council. Retrieved March 3, 2016 from http://www.iaea.info/documents/paper_1162d1dbd5.pdf.
Westhuizen, V. D., & Abrahams, M. (2002). Theory of change evaluation. Education as Change, 6(1), 98–108.
Witty, G. (2006). Education(al) research and education policy making: is conflict inevitable? British Educational Research Journal, 32(2), 159–176
World Bank. (2004). Assessing student learning in Africa. Washington, DC: The World Bank.
World BanK. (2007). Needs assessment knowledge base: Document review. Washington, DC: World Bank.
World Bank. (2014). International development association program appraisal document on a proposed IDA credit. Washington, DC: World Bank.
Zainal, Z. (2007). Case study as a research method. Jurnal Kemanusiaan, 9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulongo, G., Amod, Z. Nexus between participating in cross-national learning assessments and educational policy reforms: case study of Kenya, Tanzania and South Africa. Educ Res Policy Prac 18, 203–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10671-019-09250-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10671-019-09250-9