Abstract
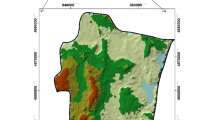
Karst ecosystems are one of the ecologically sensitive areas most affected by the dramatic harmful effects of the desertification process due to their structural, geomorphologic, and ecologic characteristics. The objective of this study was to assess and mapping ecologically sensitive areas (ESAs) for monitoring desertification and improving degraded forest areas in karst ecosystems. Sensitive ecological areas were evaluated using the Mediterranean Desertification and Land Use Methodology (MEDALUS) by considering soil quality, vegetation quality, climate quality, and management quality. Three new parameters (exposed rocky surface index, soil organic carbon index, and depression area index) were added specifically to karst ecosystem were evaluated using the Analytic Hierarchic Process (AHP) to determine ecological sensitivity. The study area is Sarimsak Karstic Mountain located in Andirin, Kahramanmaras. Soil organic carbon exposed rocky surface and depression area indices were evaluated over 110 soil samples. Values of each indices were determined according to the AHP methodology. The new SQImodified map, which was generated using new indices unique to karstic ecosystems provided a more precise spatial distribution. The results indicated that 44.49% of the study area is Critical, 51.94% is Fragile, and 3.58% is Potential in terms of desertification levels. In areas identified as Critical; agricultural fields, rangelands, and rocky surfaces cover 71.54%. Urban areas were evaluated as 100% Fragile class. Forested areas were evaluated in the Fragile and Potential class. The forest cover class affects Fragile and Potential status very closely. With the increase in forest cover rate, it has reduced fragility. The most critical ESAi classification area (C3) was detected in rangelands. Specific indices should be created to provide a realistic perspective in the combat to desertification in karst ecosystems.


(Modified from Kosmas et al., 1999)

(Modified from Saaty, 1980)
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, D., Kumar, T., & Jhariya, D. (2021). Intelligent vulnerability prediction of soil erosion hazard in semi-arid and humid region. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 2524–2551.
Akbari, M., Memarian, H., Neamatollahi, E., Shalamzari, M. J., Noughani, M. A., & Zakeri, D. (2020). Prioritizing policies and strategies for desertification risk management using MCDM–DPSIR approach in northeastern Iran. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23, 2503–25231.
Aksu, G. A., & Küçük, N. (2020). Evaluation of urban topography–biotope–population density relations for Istanbul-Beşiktaş urban landscape using AHP. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(2), 733–758.
Bai, X. Y., Wang, S. J., & Xiong, K. N. (2013). Assessing spatial temporal evolution processes of karst rocky desertification land: indications for restoration strategies. Land Degradation & Development, 24, 47–56.
Basu, T., & Pal, S. (2020). A GIS-based factor clustering and landslide susceptibility analysis using AHP for Gish River Basin, India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22, 4787–4819.
Besser, H., & Hamed, Y. (2021). Environmental impacts of land management on the sustainability of natural resources in Oriental Erg Tunisia, North Africa. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01135-9.
Blumenthal, M. (1947). Geology of Taurus Mountains at the hinterland of Seydişehir-Beyşehir: MTA Publ., ser. D, 2, Ankara.
Botoni, E., Larwanou, M., & Reij, C. (2010). La régénération naturelle assistée (RNA): une opportunité pour reverdir. de la Grande Muraille Verte, IRD Editions, pp. 151-162
Boudjemline, F., & Semar, A. (2018). Assessment and mapping of desertification sensitivity with MEDALUS model and GIS – Case study: basin of Hodna, Algeria. Journal of Water and Land Development, 36, 17–26.
Bouyoucos, G. J. (1962). Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils. Agronomy Journal, 54, 464–465.
Budak, M., Günal, H., Çelik, İ, Yıldız, H., Acir, N., & Acar, M. (2018). Environmental sensitivity to desertification in northern Mesopotamia; application of modified MEDALUS by using analytical hierarchy process. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11(17), 481.
Cabral, A. C., De Miguel, J. M., & Rescia, A. J. (2003). Shrub encroachment in Argentinean savannas. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14(2), 145–152. https://doi.org/10.1658/1100-9233(2003)014[0145:SEIAS]2.0.CO;2.
Chen, H. S., & Wang, K. L. (2008). Soil water research in karst mountain areas of southwest China. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 29(6), 734–738.
Clark, S. C. (1996). Mediterranean ecology and an ecological synthesis of the field sites. In J. Brandt & J. Thornes (Eds.), Mediterranean desertification and land use. (pp. 271–299). New York: John Willey & Sons.
D’Antonio, C. M., & Vitousek, P. M. (1992). Biological invasions by exotic grasses, the grass/fire cycle, and global change. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 23, 63–87.
Descroix, L., Viramontes, D., Vauclin, M., Barrios, J. L. G., & Esteves, M. (2001). Influence of soil surface features and vegetation on runoff anderosion in the Western Sierra Madre (Durango, Northwest Mexico). CATENA, 43, 115–135.
Dindaroglu, T. (2015). Resistance to the reclamation of environmentally sensitive areas through the establishment of a new forest ecosystem. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 24(4), 1195–1203.
Dindaroglu, T. (2020). Determination of ecological networks for vegetation connectivity using GIS & AHP technique in the Mediterranean degraded karst ecosystems. Journal of Arid Environments. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2020.104385.
Dindaroglu, T., Gundogan, R., & Karaoz, M. O. (2019). Determination of spatial distribution of topsoil organic carbon stock using geostatistical technique in a karst ecosystem. International Journal of Global Warming, 19(3), 251–266.
Dindaroğlu, T., & Vermez, Y. (2019). Classification and mapping of some site features of karst ecosystems (Sarımsak Mountain Andırın-Kahramanmaraş). Turkish Journal of Forest Science, 3(1), 60–83.
DISMED (2005). http://dismed.eionet.eu.int/ Desertification information system for the Mediterranean
Dregne H.E, Chou N.T. (1992) Global desertification dimensions and costs. In: Dregne, H.E. (Ed.). Degradation and restoration of arid lands, Texas, Tech. University, Lubbock. pp. 249–282
ESRI. (2011). Arcgis desktop: release 10. . Environmental Systems Research Institute.
Febles, G. J., Vega, C. M., Tolón, B. A., & Lastra, B. X. (2012). Assessment of soil erosion in karst regions of Havana, Cuba. Land Degradation and Development, 23, 465–474.
Feoli, E., Giacomich, P., Mignozzi, K., Ozturk, M., & Scimone, M. (2003). Monitoring desertification risk with an index integrating climatic and remotely-sensed data: An example from the coastal area of Turkey. Management of the Environmental Quality, 14, 10–21.
Ferrara, A., Salvati, L., Sateriano, A., & Nole, A. (2012). Performance evaluation and costs assessment of a key indicator system to monitor desertification vulnerability. Ecological Indicators, 23, 123–129.
Gonzalez, P. (2001). Desertification and a shift of forest species in the West African Sahel. Climate Research, 17, 217–228.
Griffiths, J. C., & Dushenko, W. T. (2011). Effectiveness of GIS suitability mapping in predicting ecological impacts of proposed wind farm development on Aristazabal Island, BC. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 13(6), 957–991.
Gulcur, F., (1974). The Book of Physical and Chemical Analysis Methods of Soil. Kutulmus Printing House, IU Publication No. 1970, Faculty of Forestry Publication No. 201, Istanbul, 225 p.
Guo, F., Jiang, G., Yuan, D., & Polk, J. (2013). Evolution of major environmental geological problems in karst areas of southwestern china. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(7), 2427–2435.
Haktanır, K., Karaca, A., & Omar, S. M. (2004). The prospects of the impact of desertification on Turkey, Lebanon, Syria and Iraq. In A. Marquina (Ed.), Environmental Challenges in the Mediterranean 2000–2050, Chapter 9. (pp. 139–154). Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Hamdouch, A., & Zuindeau, B. (2010). Sustainable development, 20 years on: methodological innovations, practices and open issues. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 53(4), 427–438.
Hornero, J., Manzano, M., Ortega, L., & Custodio, E. (2016). Integrating soil water and tracer balances, numerical modelling and GIS tools to estimate regional groundwater recharge: application to the Alcadozo Aquifer System (SE Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 568, 415–432.
Huang, Q. H., & Cai, Y. L. (2007). Spatial pattern of karst rock desertifi- cation in the middle of Guizhou Province, Southwestern China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1325–1330.
Irmak, A. (1954). Research methods of soil in the field and in the laboratory. Istanbul Univ. Publications 599/27.
Jensen, S. K., & Domingue, J. O. (1988). Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographic information system analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 54, 1593–1600.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., Dewangan, R., Pal, D., & Dewangan, P. K. (2017). Assessment of groundwater quality index for drinking purpose in the Durg district, Chhattisgarh using Geographical Information System (GIS) and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) techniques. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 89(4), 453–459.
Jiang, Z. C., Lian, Y. Q., & Qin, X. Q. (2014). Rocky desertification in Southwest China: impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth Science Reviews, 132, 1–12.
Johnston, K., Hoef, M., Krivoruchko, K., & Lucas, N. (2001). Using ArcGIS geostatistical Analyst. . ESRI.
Kosmas, C., Danalatos, N., Moustakas, N., Tsatiris, B., Kallianou, C. H., & Yassoglou, N. (1993). The impacts of parent material and landscape position on drought and biomass production of wheat under semi-arid conditions. Soil Technology, 6, 337–349.
Kosmas, C., Danalatos, N. G., & Gerontidis, S. (2000). The effect of land parameters on vegetation performance and degree of erosion under Mediterranean conditions. CATENA, 40, 3–17.
Kosmas, C., Kirkby, M. J., & Geeson, N. (Eds.). (1999). The Medalus Project: Mediterranean desertification and land use: Manual on key indicators of desertification and mapping environmentally sensitive areas to desertification. Directorate-General Science, Research and Development.
Kozlu, H. (1987). Misis-Andırın Dolaylarının Stratigrafisi ve Yapısal Evrimi. Türkiye 7. Petrol Kong., Ankara, pp. 104–116.
Langemeyer, J., Gómez-Baggethun, E., Haase, D., Scheuer, S., & Elmqvist, T. (2016). Environmental science & policy bridging the gap between ecosystem service assessments and land-use planning through multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA). Environmental Science & Policy., 62, 45–56.
Liu, J., Gao, J., Ma, S., Wang, W., & Zou, C. (2015). Comprehensive evaluation of ecoenvironmental sensitivity in Inner Mongolia China. China Environmental Science, 35(2), 591–598.
Maidment, D. R. ( 2002). Arc Hydro, GIS for Water Resources. ESRI, Redlands, California, USA. Isbn: 1-58948034-1
Maidment, D. R., Djokic, D. (2000). Hydrologic and Hydraulic Modeling Support With Geographical Information Systems. Esri, Redlands, California, USA. Isbn: 927378100
MGM. (2017). General Directorate of State Meteorology Affairs, Kahramanmaraş Meteorology Provincial Directorate, Kahramanmaras - Andirin Meteorology Station Report Book, pp. 1975-2010
Mick, D. (2010). Human interaction with Caribbean karst landscapes: past, present and future. Acta Carsologica, 39, 137–146.
Nelson, D.W., Sommers, L. E. (1996). Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3. Chemical Methods, Ed: Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, C.T., Sumner, M.E., Soil Science Society of America, 5, 961-1010
Okin, G. S., Murray, B., & Schlesinger, W. H. (2001). Degradation of sandy arid shrubland environments: observations, process modeling, and management implications. Journal of Arid Environments, 47, 123–144.
Peng, J., Xu, Y. Q., Zhang, R., Xiong, K. N., & Lan, A. J. (2013). Soil erosion monitoring and its implication in a limestone land suffering from rocky desertification in the Huajiang Canyon, Guizhou, Southwest China. Environment and Earth Science, 69, 831–841.
Poesen, J., van Wesemael, B., Bunte, K., & Benet, A. (1998). Variation of rock fragment cover and size along semiarid hillslopes: a book of case study from southern Spain. Geomorphology, 23, 323–335.
Puigdefabregas, J. (1998). Ecological impacts of global change on drylands and their implications on desertification. Land Degradation and Rehabilitation, 9, 393.
Ramanathan, R. A. (2001). Note on the use of the analytic hierarchy process for environmental impact. Journal of Environmental Management, 63, 27–35.
Rossi, R. (2020). Desertification and agriculture. European Parliamentary Research Service PE 646.171 https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2020/646171/EPRS_BRI(2020)646171_EN.pdf
Roxo, M. J., Mourao, J., Rodrigues, M. L., & Casimiro, P. C. (1999). Applicatıon of the proposed methodology for defining ESAs of the Alentejo region Metrola municipality. .
Saaty, R.W., Rokou, E., Adams, W. J. (2019). Super Decisions Software development is sponsored by the Creative Decisions Foundation. Accessed Date: 10.12.2019. https://www.superdecisions.com/about/index.php?section=devTeam
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process. . McGraw-Hill.
Saaty, T. L. (1990). How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. European Journal of Operational Research, 48(1), 9–26.
Saaty, T. L. (1991). Método de Análise Hierárquica. . São Paulo.
Saaty, T. L., & Vargas, L. G. (1994). Decision making in economic, political, social, and technological environments with the analytic hierarchy process. . RWS Publications.
Salvati, L. (2014). Toward a ‘Sustainable’land degradation? Vulnerability degree and component balance in a rapidly changing environment. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 16(1), 239–254.
Seager, R. (2007). Model projections of an imminent transition to a more arid climate in southwestern North America. Science, 16(5828), 1181–1184.
Sharma, K. D. (1998). The hydrological indicators of desertification. Journal of Arid Environments, 39(2), 121–132.
Smith, P., Calvin, K., Nkem, J., Campbell, D., Cherubini, F., Grassi, G., Korotkov, V., Hoang, A. L., Lwasa, S., McElwee, P., Nkonya, E., Saigusa, N., Soussana, J. F., Taboada, M. A., Manning, C., Nampanzira, D., Navarro, C. A., Vizzarri, M., House, J., … Rounsevell, M. (2019). Which practices co-deliver food security, climate change mitigation and adaptation, and combat land degradation and desertification? Global Change Biology, 26(3), 1532–1575.
Symeonakis, E., Karathanasi, N., Koukoulas, S., & Panagopoulos, G. (2014). Monitoring sensitivity to land degradation and desertification with the environmentally sensitive area index: the case of Lesvos Island. Land Degradation and Development, 22, 184–197.
UNCCD. (1994). United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification in Those Countries Experiencing Serious Drought and/or Desertification Particularly in Africa: United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification Text with Annexes. . UNEP.
UNEP (2007). Natural Disasters and Desertification. United Nations Environment Programme. Post-Conflict Environmental Assessment. ISBN: 978-92-807-2702-9, p: 69
USGS (1997). United States Geological Survey article “Desertification” <http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/deserts/desertification/> Maintained by Publications Service Center Last modified 10/29
Veni, G., DuChene, H., Crawford, N.C., Groves, C.G., Huppert, G.N., Kastning, E.H., Olson, R., Wheeler, B.J. (2001). Living With Karst. American Geological Institute, ISBN 0–922152–58–6
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37(1), 29–38.
Wang, D. L., Zhu, S. Q., & Huang, B. L. (2005). Internal Factors Influencing Karst Rocky Desertification (in Chinese). J. Zhej. For. Coll., 22, 266–271.
Williams, J., Prebble, R. E., Williams, W. T., & Hignett, C. T. (1983). The influence of texture, structure and clay mineralogy on the soil moisture characteristic. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 21, 15–32.
Wu, X., Liu, H., Huang, X., & Zhou, T. (2011). Human driving forces: Analysisof rocky desertification in karst region in guanling county, guizhou province. Chinese Geographical Ence, 21(5), 92–100.
Xu, E. Q., & Zhang, H. Q. (2014). Characterization and interaction of driving factors in karst rocky desertification: a case study from Changshun China. Solid Earth, 5, 1329–1340. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-5-1329-2014.
Yılmaz, Y., & Gurer, Ö. F. (1996). Andırın Kahramanmaraş dolayında Misis Andırın kuşağının jeolojisi ve evrimi. Turkish Journal Of Earth Sciences, 5, 39–55.
Zhang, D. F., & Zhou, D. Q. (2001). Intrinsic driving mechanism of land rocky desertification in karst regions of Guizhou Province. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 21, 1–5.
Zhang, P., Li, L., Pan, G., & Ren, J. (2006). Soil quality changes in land degradation as indicated by soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a karst area of southwest Guizhou China. Environmental Geology, 51(4), 609–619.
Zou, H., & Ma, X. (2021). Identifying resource and environmental carrying capacity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China: The perspectives of spatial differences and sustainable development. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01271-w.
Zuindeau, B. (2007). Territorial equity and sustainable development. Environmental Values, 16(2), 253–268.
Acknowledgement
The authors thank to Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University, Faculty of Forestry, Soil Science & Ecology laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozgul, M., Dindaroglu, T. Multi-criteria analysis for mapping of environmentally sensitive areas in a karst ecosystem. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 16529–16559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01363-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01363-7