Abstract
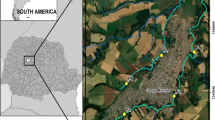
The Campos de Palmas Wildlife Refuge (RVS-CP) is a full protection conservation unit (CU) formed by private properties. The present study aimed to use the bioindicators Allium cepa L. (cytotoxicity and mutagenicity tests) and Eisenia fetida (avoidance test) to assess the quality of surface water of the Chopim River within the RVS-CP area and its surroundings during the four seasons of the year. To do so, water samples were collected at five points, four inside the RVS-CP area and a fifth point outside thereof. Samples from all sampling points had cytotoxic effect on A. cepa in at least one season of the year. Such a finding may be related to inadequate management practices (without land-use control) in the areas surrounding the sampling points such as forestry, native fields, pastures, agriculture, and housing areas. As for the animal bioindicator (E. fetida), only points 1 (in the winter) and 5 (in the autumn) were toxic. Concerning mutagenicity, points 1 and 4 (in the spring), 1 and 2 (in the summer), and 3 (in the autumn) showed mutagenic effect on A. cepa meristematic cells, therefore only within the RVS-CP area. Overall, these results show that biomonitoring can be an ally of the residents of the RVS-CP area in controlling management practices, aiming to bring together economic support and conservation of resources, especially water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABNT – Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. (2007). NBR 15537: ecotoxicologia terrestre. Ecotoxicologia aguda. Método de ensaio para minhocas.
ABNT – Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. (2011). NBR ISO 17512–1: qualidade do solo - ensaio de fuga para avaliar a qualidade de solos e efeitos de substâncias químicas no comportamento - Parte 1: Ensaio com minhocas (Eisenia fetida e Eisenia andrei).
Agritempo. (2021). Sistema de Monitoramento Agrometeorológico. Available at: https://doi.org/https://www.agritempo.gov.br/zoneamento/tabelas/PR/PALMAS_G.HTML. Accessed on July 28, 2021.
APHA - American Public Health Association. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 22nd ed. Washington: American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Pollution Control Federation.
Arias, A. R. L., Buss, D. F., Alburquerque, C., Inácio, A. F., Freire, M. M., Egler, M., Mugnai, R., & Baptista, D. F. (2007). Utilização de bioindicadores na avaliação de impacto e no monitoramento da contaminação de rios e córregos por agrotóxicos. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva, 12(1), 61–72.
Azevedo, A. R., & Coronas, M. V. (2018). Uso de testes de fuga com minhocas Eisenia andrei e Eisenia fetida para identificação da toxidade de agrotóxicos no Brasil: Uma breve revisão da literatura. Ciência e Natura, 40, 18–26.
Braga, J. R. M., & Lopes, D. M. (2015). Citotoxicidade e genotoxicidade da água do Rio Subaé (Humildes, Bahia, Brasil) usando Allium cepa L. como bioindicador. Revista Ambiente & Água, 10(1), 130–140.
BRASIL (2000). Lei nº 9.985, de 18 de julho de 2000. Regulamenta o art. 225, § 1°, incisos I, II, III e VII da Constituição Federal, institui o Sistema Nacional de Unidades de Conservação da Natureza e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União, Poder Executivo, Brasília, DF, 19 jul. 2000. Seção 1, p. 1.
BRASIL (2009). Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Programa Nacional do Meio Ambiente II – PNMA II, Fase 2, 2009–2014. p. 4.
BRASIL (2012). Resolução no. 454, de 01 de novembro de 2012. Estabelece as diretrizes gerais e os procedimentos referenciais para o gerenciamento do material a ser dragado em águas sob jurisdição nacional. Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. From https://iema.es.gov.br/Media/iema/CQAI/FIGURAS/CRSS/CONAMA/CONAMA_454_2012.pdf
BRASIL (2016). Instituto Chico Mendes de Conservação da Biodiversidade. Plano de Manejo Refúgio de Vida Silvestre dos Campos de Palmas. From https://rvscamposdepalmas.blogspot.com/p/historico.html
Buss, D. F., Oliveira, R. B., & Baptista, D. F. (2008). Monitoramento biológico de ecossistemas aquáticos continentais. Oecologia Brasiliensis, 12(3), 339–345.
Candello, F. P. (2014). Comportamento de fuga de minhocas na presença do antimicrobiano sulfadiazina em solo. Dissertation (Mestrado em Engenharia Civil) – Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas-São Paulo, 78 f.
Carvalho, K. Q., Lima, S. B., Passig, F. H., Gusmão, L. K., Souza, D. C., Kreutz, C., Belini, A. D., & Arantes, E. J. (2015). Influence of urban area on the water quality of the Campo River basin, Paraná State, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 75, 96–106.
Castella, P. R., & Britez, R. M. (2004). A floresta com araucária no Paraná: Conservação e diagnóstico dos remanescentes florestais. Ministério do Meio Ambiente.
Cortes-Eslava, J., Gomez-Arroyo, S., Risueno, M. C., & Testillano, P. S. (2018). The effects of organophosphorus insecticides and heavy metals on DNA damage and programmed cell death in two plant models. Environmental Pollution, 240, 77–86.
Danzei, A. P., & Vercellino, I. S. (2018). Uso de Bioindicadores no monitoramento da qualidade da água. Revinter, 11(1), 100–115.
Datta, D., Singh, J., Singh, J., Singh, S., & Singh, S. (2018). Assessment of genotoxic effects of pesticide and vermicompost treated soil with Allium cepa test. Sustainable Environment Research, 28, 171–178.
Düsman, E., Luzza, M., Savegnago, L., Lauxen, D., Vicentini, V. E. P., Tonial, I. B., & Sauer, T. P. (2014). Allium cepa L. as a bioindicator to measure cytotoxicity of surface water of the Quatorze River, located in Francisco Beltrão, Paraná. Brazil Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 1793–1800.
Faria, M. L. C., Costa, F. M., Silva, F. C., & Bosso, R. M. V. (2017). Potencial de citotoxicidade e mutagenicidade das águas do Rio Jaru, Estado de Rondônia, em células de Allium cepa. Gaia Scientia, 11, 104–114.
Fatma, F., Verma, S., Kamal, A., & Srivastava, A. (2018). Monitoring of morphotoxic, cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of mancozeb using Allium assay. Chemosphere, 195, 864–870.
Fieira, C., Batistella, E. P., Vincoski, J. V. A., Rosa, M. P. S., Pokrywiecki, J. C., Gomes, E. M. V., Oliveira, A. P., Pokrywiecki, T. S., & Düsman, E. (2019). Treatment of effluent containing thiamethoxam and efficiency evaluation of toxicity reduction. Environmental Technology, 42. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1703827
Fiskesjö, G. (1985). The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas, 102(1), 99–112.
Freitas, L. A., Rambo, C. L., Franscescon, F., Barros, A. F. P., De Lucca, G. S., Siebel, A. M., et al. (2017). A extração de carvão causa toxicidade de sedimentos em ambientes aquáticos em Santa Catarina. Brasil Revista Ambiente e Água, 12(4), 591–604.
Gallego, S., Nos, D., Montemurro, N., Sanchez-Hernandez, J. C., Pérez, S., Solé, M., & Martin-Laurent, F. (2021). Ecotoxicological impact of the antihypertensive valsartan on earthworms, extracellular enzymes and soil bacterial communities. Environmental Pollution, 275, 116647.
Garcia, J. M., Mantovani, P., Gomes, R. C., Longo, R. M., Demanboro, A. C., & Bettin, S. C. (2018). Degradação ambiental e qualidade da água em nascentes de rios urbanos. Sociedade Natureza, 30(1), 228–254.
Geras´kin, S., Oudalova, A., Michalik, B., Dikareva, N., & Dikarev, V. (2011). Geno-toxicity assay of sediment and water samples from the Upper Silesia post-mining areas. Polandby Means of Allium-Test. Chemosphere, 83(8), 1133–1146.
Gomes, R. P., Silva, J. A. P., Junior, M. C. C., Alburquerque, W. C. A., Scalize, P. S., Filho, A. R. G., Pires, D. J., Vieira, J. D. G., & Carneiro, L. C. (2019). Evaluation of the raw water quality: Physicochemical and toxicological approaches. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41, 2425–2442.
Hybská, H., Lobotková, M., Vanek, M., Slava, J., Knapcova, I., & Veverková, D. (2020). Biomonitoring and its in the assessment of the quality of wastewater treatment process. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 13, 8.
IBGE (2012). Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Manual Técnico da Vegetação Brasileira. IBGE, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil.
ISO (2008). International Organization For Standardization – ISO 17512–1: Qualidade do solo - Teste de prevenção para determinar a qualidade dos solos e os efeitos dos produtos químicos no comportamento - Parte 1: Teste com minhocas (Eisenia fetida e Eisenia andrei).
Iqbal, M., & Nisar, J. (2015). Cytotoxicity and mutagenicity evaluation of gamma radiation and hydrogen peroxide treated textile effluents using bioassays. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3, 1912–1917.
Iqbal, M., Abbas, M., Nisar, J., Nazir, A., & Qamar, A. Z. (2019). Bioassays based on higher plants as excellent dosimeters for ecotoxicity monitoring: A review. Chemistry International, 5(1), 1–80.
Kaur, M., Sharma, A., Soodan, R. K., Chahal, V., Kumar, V., Katnoria, J. K., & Nagpal, A. K. (2019). Allium cepa root chromosomal aberration assay: A tool to assess genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. Environmental Contaminants and Natural Products, 5, 65–93.
Lacerda, A. E. B. (2016). Conservation strategies for Araucaria Forests in southern Brazil: Assessing current and alternative approaches. Biotropica, 48(4), 537–544.
Li, P., Qian, H., Howard, K. W., Wu, J., & Lyu, X. (2014). Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 1385–1398.
Li, M., Qin, R., Jiang, W., & Liu, D. (2015). Cytogenetical effects of aluminum on root meristem cells of Helianthus annuus L. Botanical Sciences, 93, 15–22.
Luíz, A. M. E., Pinto, M. L. C., & Scheffer, E. W. O. (2012). Parâmetros de cor e turbidez relacionados aos usos do solo e à morfometria da bacia hidrográfica do rio Taquaral, São Mateus do Sul-PR. Revista Caminhos Da Geografia, 24, 290–310.
Machado, H. M. (2012). Efeitos da aplicação de resíduos de perfuração de poço de petróleo no solo, no desenvolvimento de plantas de arroz e no comportamento de Eusenia andrei. Dissertation (Mestrado em Agronomia – Ciência do Solo) - Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro, 258 f.
Marmontel, C. V. F., & Rodrigues, V. A. (2015). Parâmetros Indicativos para Qualidade da Água em Nascentes com Diferentes Coberturas de Terra e Conservação da Vegetação Ciliar. Floresta e Ambiente, 22(2), 171–181.
Matsumoto, S. T., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2004). Mutagenic potential evaluation of the water of a river that receives tannery effluent using the Allium cepa test system. Cytologia, 69(4), 399–408.
Melo, L. C. A., Silva, E. B. D., & Alleoni, L. R. F. (2014). Transfer of cadmium and barium from soil to crops grown in tropical soils. Revista Brasileira De Ciência Do Solo, 38(6), 1939–1949.
Mercado, A. S., & Caleno, J. D. Q. (2020). Cytotoxic evaluation of glyphosate, using Allium cepa L. as bioindicator. Science of The Total Environment, 700, 134452.
Merga, L. B., Mengistie, A. A., Alemu, M. T., & Van den Brink, P. J. (2021). Biological and chemical monitoring of the ecological risks of pesticides in Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. Chemosphere, 266, 129214.
Mkhinini, M., Boughattas, I., Alphonse, V., Livet, A., Bousserrhine, N., & Banni, M. (2019). Effect of treated wastewater irrigation in East Central region of Tunisia (Monastir governorate) on the biochemical and transcriptomic response of earthworms Eisenia andrei. Science of the Total Environment, 647, 1245–1255.
Oliveira, J. P. V., Santos, R. N., Pibernat, C. C., & Boeira, J. M. (2012). Genotoxicity and physical chemistry analysis of waters from Sinos River (RS) using Allium cepa and Eichhornia crassipes as bioindicators. Biochemistry and Biotechnology Reports, 1(1), 15–22.
OECD (1984). Organisation for Economic Co-Operation And Development. Guideline for testing of chemicals n. 207: earthworm acute toxicity test, Paris. From https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/9789264070042-en.pdf?expires=1634307789&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=718BBDA5CE0A7C80C1AC93E892AD1628
Pamplona-Silva, M. T., Gonçalvez, L. C., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2018). Genetic toxicity of water contaminated by microcystins collected during a cyanobacteria bloom. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 166, 223–230.
Postigo, C., Ginebreda, A., Barbieri, M. V., Barceló, D., Martín-Alonso, J., Cal, A., Boleda, M. R., Otero, N., Carrey, R., Solà, V., Queralt, E., Isla, E., Casanovas, A., Frances, G., & López, A. M. (2021). Investigative monitoring of pesticide and nitrogen pollution sources in a complex multi-stressed catchment: The lower Llobregat River basin case study (Barcelona, Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 755, 142377.
Qin, R., Jlao, Y., Zhang, S., Jiang, W., & Liu, D. (2010). Effects of aluminum on nucleoli in root tip cells and selected physiological and biochemical characters in Allium cepa var. agrogarum L. BMC Plant Biology, 10, 225–235.
Qin, R., Jiang, W., & Liu, D. (2013). Aluminum can induce alterations in the cellular localization and expression of three major nucleolar proteins in root tip cells of Allium cepa var. agrogarum L. Chemosphere, 90, 827–834.
Rodrigues, Z. P. G., Dalzochio, T., & Gehlen, G. (2016). Uso do bioensaio com Allium cepa L. e análises físico-químicas e microbiológicas para avaliação da qualidade do Rio da Ilha, RS. Brasil Acta Toxicológica Argentina, 24, 97–104.
Salles, F. J., Toledo, M. C. B., César, A. C. G., Ferreira, G. M., & Barbério, A. (2016). Cytotoxic and genotoxic assessment of surface water from São Paulo State, Brazil, during the rainy and dry seasons. Ecotoxicology, 25, 633–645.
Sales Junior, S.F., Mannarino, C. F., Bila, D. M., Parente, C. E. T., Correia, F. V., & Saggioro, E. M. (2021). Lethal and long-term effects of landfill leachate on Eisenia andrei earthworms: Behavior, reproduction and risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 285, 112029.
Schoninger, F. C. C. (2020). Diagnóstico da qualidade da água e sedimento no refúgio de vida silvestre dos campos de palmas. Dissertation (Mestrado em Engenharia Ambiental) – Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Francisco Beltrão.
Santos, G. C. G., Rodella, A. A. (2007). Poluição do solo e qualidade ambiental. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, v. 31, p.793-804.
Sieklicki, J., Bione, N. C. P., Oliveira-Filho, P. C., Souza, V. F., & Martins, K. G. (2019). Relações pontuais entre o uso e ocupação da terra e a qualidade da água obtida pela avaliação dos efeitos genotóxicos em bioindicadores vegetais. Revista Ambiente e Água, 14(2).
Silva, G. O. (2021). Agência Embrapa de Informação Tecnológica. Árvore do Conhecimento Batata. Available at: https://www.agencia.cnptia.embrapa.br/gestor/batata/arvore/CONT000gnc4knh602wx5ok0edacxlkquiqoq.html. Accessed on July 28, 2021.
Silva, J., Heuser, V., & Andrade, V. (2003). Biomonitoramento ambiental. In: J. Silva, B. Erdtmann, & J. A. P. Henriques (Eds.), Genética Toxicológica (166–180). Porto Alegre, Alcance.
Sivakumar, S. (2015). Effects of metals on earthworm life cycles: A review. Environmental and Monitoring Assessment, 187(530), 4742.
Sonda, C. (1996). A cobertura florestal nas explorações agrícolas: Quem tem e quem não tem floresta. Análise Conjuntural, 18(11–12), 25–27.
Sousa, J. M. C., Peron, A. P., Sousa, L. S., Holanda, M. M., Lima, A. M. V., Oliveira, V. A., Silva, F. C. C., Lima, L. H. G. M., Matos, L. A., Dantas, S. M. M. M., Aguiar, R. P. S., Islam, M. T., Melo-Cavalcante, A. M. C., Bonecker, C. C., & Junior, H. F. J. (2017). Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of Guaribas river water (Piauí, Brazil), influenced by anthropogenic action. Environmental and Monitoring Assessment, 189(6), 301.
Strapazzon, M. C. (2015). Reflexões acerca das racionalidades em Unidades de Conservação: o caso do Refúgio de Vida Silvestre dos Campos de Palmas. Dissertation (Mestrado em Desenvolvimento Regional) - Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Pato Branco-Paraná, 157 f.
Taniwaki, R. H., Rosa, A. H., Lima, R., Maruyama, C. R., Secchin, L. F., Calijuri, M. C., & Moschini-Carlos, V. (2013). A influência do uso e ocupação do solo na qualidade e genotoxicidade da água no reservatório de Itupararanga, São Paulo. Brasil Interciência, 38(3), 164–170.
Vibrans, A. C., McRoberts, R. E., Lingner, D. V., Nicoletti, A. L., & Moser, P. (2012). Extensão original e atual da cobertura florestal de Santa Catarina. Diversidade e conservação dos remanescentes florestais. In A. C. Vibrans, L. Sevegnani, A. L. D. Gasper, & D. V. Lingner (Eds.), Inventário Florístico Florestal de Santa Catarina (Vol. I, pp. 65–78). Blumenau, Brazil.
Vujošević, M., Andelković, S., Savić, G., & Blagojević, J. (2008). Genotoxicity screening of the river Rasina in Serbia using the Allium anaphase-telophase test. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 147, 75–81.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná (UTFPR), Campus Francisco Beltrão, Paraná State (Brazil), and the Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schutz, D.L., de Marco, I.G., Alves, G.L. et al. Biomonitoring of surface water quality in the Chopim River within the Conservation Unit Campos de Palmas Wildlife Refuge, southern Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 193, 738 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09464-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09464-6