Abstract
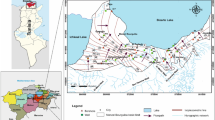
In Xynias drained Lake Basin’s area, central Greece, a hydrogeochemical research took place including groundwater sampling from 30 sampling sites, chemical analysis, and statistical analysis. Groundwaters present Ca–Mg–HCO3 as the dominant hydrochemical type, while their majority is mixed waters with non-dominant ion. They are classified as moderately hard to hard and are characterized by oxidizing conditions. They are undersaturated with respect to gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, siderite, and magnesite and oversaturated in respect to calcite, aragonite, and dolomite. Nitrate concentration ranges from 4.4 to 107.4 mg/L, meanwhile 13.3 % of the samples exceed the European Community (E.C.) drinking water permissible limit. The trace elements Fe, Ni, Cr, and Cd present values of 30, 80, 57, and 50 %, respectively, above the maximum permissible limit set by E.C. Accordingly, the majority of the groundwaters are considered unsuitable for drinking water needs. Sodium adsorption ratio values (0.04–3.98) and the electrical conductivity (227–1200 μS/cm) classify groundwaters as suitable for irrigation uses, presenting low risk and medium soil alkalization risk. Factor analysis shows that geogenic processes associated with the former lacustrine environment and anthropogenic influences with the use of fertilizers are the major factors that characterized the chemical composition of the groundwaters.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alifrangis, D., & Papamichos, N. (1995). Description-sampling laboratory analyzes of forest soils and plant tissues. Thessaloniki: Dedousi Publications.
APHA (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Method 3030 (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd ed.). Florida: CRC Press.
Aubouin, J. (1959). Contribution à létude géologique de la Grèce septentrionale: les confins de Épire et de la Thessalie. Annales Géologique des Pays Hélléniques, 10, 1–483.
Ayers, R.S., & Westcot, D.W. (1994). Water quality for agriculture. FAO irrigation and drainage water paper. http://www.fao.org/DOCReP/003/T0234e/T0234E00.htm. Accessed 1989.
Benson, V., VanLeeuwen, J. A., Stryhn, H., & Somers, G. H. (2007). Temporal analysis of groundwater nitrate concentrations from wells in Prince Edward Island, Canada: application of a linear mixed effects model. Hydrogeology Journal, 15, 1009–1019.
Bernasconi, S. M., & McKenzie, J. A. (2007). Carbonate stable isotopes/Lake sediments. Encyclopedia of Quaternary Science, 351–359.
Bottema, S. (1979). Pollen analytical investigations in Thessaly (Greece). Palaeohistoria, 21, 20–40.
César, E., Wildemeersch, S., Orban, P., Carrière, S., Brouyère, S., & Dassargues, A. (2014). Simulation of spatial and temporal trends in nitrate concentrations at the regional scale in the Upper Dyle basin, Belgium. Hydrogeology Journal, 22, 1087–1100. doi:10.1007/s10040-014-1124-2.
Charizopoulos, N. (2013). Investigation on mechanisms of quantitative and qualitative deterioration of water and soil recourses in Domokos basin by natural an anthropogenic processes. PhD Thesis, Athens: Agriculture University of Athens.
Charizopoulos, N., Stamatis, G., & Psilovikos, A. (2011). Water balance and temporal changes of the surface water quality in Xynias basin (SW Thessaly). Environment and Earth Science, 1, 275–281.
Liu, C. W., Lin, K. H., & Kuo, Y. M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313(1–3), 77–89.
Cruz, J. V., Silva, M. O., Dias, M. I., & Prudκncio, M. I. (2013). Groundwater composition and pollution due to agricultural practices at Sete Cidades volcano (Azores, Portugal). Applied Geochemistry, 29, 162–173.
Daskalaki, P., & Voudouris, K. (2008). Groundwater quality of porous aquifers in Greece: a synoptic review. Environmental Geology, 54(3), 505–513.
Demetriou, D., & Arapogiannis, E. (2001). Economic geology research lignite deposit Xyniadas Domokos. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
Digerfeldt, G., Olsson, S., & Sandgren, P. (2000). Reconstruction of lake-level changes in lake Xynias, central Greece, during the last 40 000 years. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 158, 65–82.
Digerfeldt, G., Sandgren, P., & Olsson, S. (2007). Reconstruction of Holocene lake-level changes at Lake Xinias, central Greece. The Holocene, 17(3), 361–367.
Dimopoulos, M., Chalkiadaki, M., Dassenakis, M., & Scoullos, M. (2003). Quality of groundwater in Western Thessaly, the problem of nitrate pollution. Global Nest, 5(3), 185–191.
Dokou, Z., Kourgialas, N., & Karatzas, G. (2015). Assessing groundwater quality in Greece based on spatial and temporal analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 774. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4998-0.
Dotsika, E., Poutoukis, D., Tzavidopoulos, I., Maniatis, Y., Ignatiadou, D., & Raco, B. (2009). A natron source at Pikrolimni Lake in Greece? Geochemical evidence. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 103, 133–143.
Durov, S. A. (1948). Natural waters and graphic representation of their composition. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 59, 87–90.
Eiswirth, M., Hotzl, H., & Burn, L. S. (2000). Development scenarios for sustainable urban water systems. In Sililo et al. (Eds.), Groundwater: past achievements and future challenges (pp. 917–922). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Elçi, A., & Polat, P. (2011). Assessment of the statistical significance of seasonal groundwater quality change in a karstic aquifer system near Izmir-Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 445–462. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1346-2.
ESRI (2008). ArcMap. Version 9.3 User manual, (pp 135–137). New York: ESRI.
EU Council directive 98/83 (1998). Directive of the European Parliament on the quality of water intended for human consumption. The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Official Journal, L 330.
Fantoni, D., Brozzo, G., Canepa, M., Cipolli, F., Marini, L., Ottonello, G., & Zuccolini, M. (2002). Natural hexavalent chromium in groundwaters interacting with ophiolitic rocks. Environmental Geology, 42, 871–882.
Ferriere, J. (1982). Paleogeographies et tectonigues superposees dans les Hellenides internes: les massifs de I’Othrys et du Pelion (Grece continentale). Societe de la Geologie du Nord, 8, 1–941.
Ferrière, J. (1985). Nature et de’veloppement des ophiolites Helleniques du secteur Othrys-Pelion. Ofioliti, 10, 255–278.
Fytikas, M., & Kolios, N. (1979). Preliminary heat flow map of Greece. In Germak et al. (Eds.), Terastrial heat flow in Europe (pp. 197–205). Berlin: Springer.
Gartzos, E., & Stamatis, G. (1996). Genesis of the thermal springs of the Sperchios graben, Greece. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie Mh Η2, 91–115.
Harrison, S. P., & Digerfeldt, G. (1993). European lakes as palaeohydrological and palaeoclimatic indicators. Quaternary Science Reviews, 12, 233–248.
Hellenic Military Geographical Service (1971). Τopographic maps: sheet Leontarion, 1:50000. Athens, Greece
Hellenic Military Geographical Service (1987). Τopographic maps: sheet Leontarion, 1:50000. Athens, Greece
Hynes, A. J., Nisbet, E. G., Smith, G. A., Welland, M. J. P., & Rex, D. C. (1972). Spreading and emplacement ages of some ophiolites in the Othris region (eastern Central Greece). Zeitschrift der Deutschen Geologischen Gesellschaft, 123, 455–468.
Jiang, Y., & Somers, G. (2009). Modeling effects of nitrate from non-point sources on groundwater quality in an agricultural watershed in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Hydrogeology Journal, 17, 707–724.
Jiang, Y., Wu, Y., Groves, C., Yuan, D., & Kambesis, P. (2009). Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 109(1–4), 49–61.
Ju, T. X., Kou, C. L., Zhang, S. F., & Christie, P. (2006). Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environmental Pollution, 143(1), 117–125.
Kabata-Pendias, A., Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (3nd edn.). CRC Press.
Kallergis, G. (2000). Applied-environmental hydrogeology, Volume II (2nd edn.). TEE publisher.
Karapanos, E., Katsanou, K., Karli, A., & Lambrakis, N. (2011). Evaluation of the geochemical conditions in the deep aquifer system in Vounargo area (SW Greece) based on hydrochemical data. Environment and Earth Science, 2, 201–209.
Karmis, P. (2010). Electromagnetic geophysical survey in the area of drained Lake Xyniada. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
Katsikatsos, G., Migiros, G., Triantaphyllis, M., Mettos, A. (1986). Geological structure of internal Hellenides (E. Thessaly–SW Macedonia–Euboea–Attica–Northern Cyclades islands and Lesvos). Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Geological and Geophysical Research Special Issue, 191–212.
Kattan, Z. (2002). Effects of sulphate reduction and geogenic CO2 incorporation on the determination of 14C groundwater ages—a case study of the Palaeogene groundwater system in north-eastern Syria. Hydrogeology Journal, 10, 495–508.
Lambrakis, N., Antonakos, A., & Panagopoulos, G. (2004). The use of multicomponent statistical analysis in hydrogeological environmental research. Water Research, 38(7), 1862–1872.
Lambrakis, N., Stamatis, G., Giannoulopoulos, P., Voivonta, A. (2001). Groundwater quality and estimation of rehabilitation time of the Argolid plain’s aquifers under artificial recharge conditions. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece XXXIV(5), 1819–1826.
Lambrakis, N., Zagana, E., & Katsanou, K. (2012). Geochemical patterns and origin of alkaline thermal waters in Central Greece (Platystomo and Smokovo areas). Environment and Earth Science, 69(8), 2475–2486. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2073-5.
Landon, M. K., Green, C. T., Belitz, K., Singleton, M. J., & Esser, B. K. (2011). Relations of hydrogeologic factors, groundwater reduction-oxidation conditions, and temporal and spatial distributions of nitrate, Central-Eastside San Joaquin Valley, California, USA. Hydrogeology Journal, 19, 1203–1224.
Lloyd, J., & Heathcote, J. (1985). Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater. New York: Claredon press.
Love, D., Hallbauer, D., Amos, A., & Hranova, R. (2004). Factor analysis as a tool in groundwater quality management: two southern African case studies. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 29(15–18), 1135–1143.
Mamasis, N. (2006). Precipitation and their spatial variability. Athens: National Technical University of Athens.
Marinos, G., Anastopoulos, J., Maratos, N., Melidonis, N., & Andronopoulos, B. (1957). Geological map of Greece, Sheets Anavra and Domokos, 1:50000. Athens: Institute for Geology and Subsurface Research.
Marinos, G., Anastopoulos, J., Maratos, N., Melidonis, N., & Andronopoulos, B. (1962). Geological map of Greece, sheet Leontarion, 1:50000. Athens: Institute for Geology and Subsurface Research.
Massmann, G., Pekdegera, A., & Merzb, C. (2004). Redox processes in the Oderbruch polder groundwater flow system in Germany. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 863–886.
McArthur, J. M., Banerjee, D. M., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Mishra, R., Purohit, R., Ravenscroft, P., Cronin, A., Howarth, R. J., Chatterjee, A., Talukder, T., Lowry, D., Houghton, S., & Chadha, D. K. (2004). Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 1255–1293.
Mountrakis, D. (1985). Geology of Greece. Thessaloniki: University Studio Press.
Mountrakis, D., Sapountzis, E., Kilias, A., Eleftheriadis, G., & Christofides, G. (1983). Paleogeographic conditions in the western Pelagonian margin in Greece during the initial rifting of the continental area. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 20(11), 1673–1681.
Ndung’u, K., Friedrich, S., Gonzalez, A. R., & Flegal, A. R. (2010). Chromium oxidation by manganese (hydr)oxides in a California aquifer. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 377–381.
Nematollahi, M. J., Ebrahimi, P., Razmara, M., & Ghasemi, A. (2016). Hydrogeochemical investigations and groundwater quality assessment of Torbat-Zaveh plain, Khorasan Razavi, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 2. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4968-6.
Obiefuna, G., & Orazulike, D. (2011). The hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in semiarid Yola Area, Norteast, Nigeria. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 3(4), 400–416.
Olmez, I., Beal, J., & Villaume, J. (1994). A new approach to understanding multiple-source groundwater contamination: factor analysis and chemical mass balance. Water Resources, 28(5), 1095–1101.
Pacheco, J., Marin, L., Cabrera, A., Steinich, B., & Escolero, O. (2001). Nitrate temporal and spatial patterns in 12 water-supply wells, Yucatan, Mexico. Environmental Geology, 40, 708–715.
Page, A. L., & Bingham, F. T. (1973). Cadmium residues in the environment. Residue Reviews, 48(0), 1–44.
Papadeas, G. (1996). Geological and geothermal exploration in the Sperchios basin (Greece). Energy resources investigations. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (2013). Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. United States Geological Survey. http://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/. Accessed 23 January 2013.
Philip, G. M., & Watson, D. F. (1982). A precise method for determining contoured surfaces. Australian Petroleum Exploration Association Journal, 22, 205–212.
Postma, D., Boesen, C., Kristiansen, H., & Larsen, F. (1991). Nitrate reduction in an unconfined sandy aquifer: water chemistry, reduction processes and geochemical modeling. Water Recourses Research, 27(8), 2027–2045.
Ravenscroft, P., Burgess, W. G., Ahmed, K. M., Burren, M., & Perrin, J. (2005). Arsenic in groundwater of the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh: distribution, field relations, and hydrogeological setting. Hydrogeology Journal, 13, 727–751.
Reed, M., & Marine, R. (1991). Quality control of chemical and isotopic analyses of geothermal water samples. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Washington DC: United States Department of Agriculture.
Rose, A. W., & Cravotta III, C. A. (1998). Geochemistry of coal mine drainage. In Brady et al. (Eds.), Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution prevention in Pennsylvania (pp. 1–22). Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection.
Sfetsos, K. (1988). Inventory of thermal and mineral springs of Greece, III continental Greece, hydrological and hydrogeological investigations. Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, 39, 667.
Shamsuddin, M. K. N., Sulaiman, W. N. A., Suratman, S., Zakaria, M. P., & Samuding, K. (2014). Groundwater and surface-water utilisation using a bank infiltration technique in Malaysia. Hydrogeology Journal, 22, 543–564.
Shomar, B. H., Muller, G., & Yahya, A. (2005). Geochemical features of topsoils in the Gaza Strip: natural occurrence and anthropogenic inputs. Environmental Research, 98, 372–382.
Sikora, L. G., Bent, M. G., Corey, R. B., & Keeney, D. R. (1976). Septic nitrogen and phosphorus removal test system. Groundwater, 14(5), 309–314.
Silleos, N. (1981). Relationship of physiography and soils in the Xynias basin (Fthiotida). PhD Thesis, Thessaloniki: University of Thessaloniki.
Smith, A. G., Hynes, A. J., Menzies, M., Nisbet, E. G., Price, I., Welland, M. J., & Ferrière, J. (1975). The stratigraphy of the Othris Mountains, eastern central Greece: a deformed Mesozoic continental margin sequence. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 68(3), 463–481.
Soulios, G. (1975). Hydrogeological study of the Xyniada basin (Fthiotida). PhD Thesis, Thessaloniki: University of Thessaloniki.
Stamatis, G., & Boudouris, K. (2003). Marine and human activity influences on the groundwater quality of southern Korinthos area. Hydrological Processes, 17(12), 2327–2345.
Stamatis, G., Lambrakis, M., Alexakis, D., & Zagana, E. (2006). Groundwater quality in Mesogea basin in Eastern Attica (Greece). Hydrological Processes, 20(13), 2803–2818.
Stamatis, G., Parpodis, K., Filintas, A., & Zagana, E. (2011). Groundwater quality, nitrate pollution and irrigation environmental management in the Neogene sediments of an agricultural region in central Thessaly (Greece). Environment and Earth Science, 64(4), 1081–1105.
Stamatis, G., Parpodis, K., Lambrakis, N., Zagana, E. (2007). Origin and quality of thermal groundwaters in the region of Farsala (E. Thessaly/Greece). Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece XXXX, 570–571.
Subrahmanyam, K., & Yadaiah, P. (2001). Assessment of the impact of industrial effluents on water quality in Patancheru and environs, Medak district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 9, 297–312.
Tisdale, S., & Nelsson, W. (1975). Soil fertility and fertilizers (3rd ed.). London, New York: Collier Macmillan Publication.
Tsioumas, B., Zorapas, B., Manakos, A., Stamatis, G., Gioxas, G. (2008). Charge of groundwater in nitrate ions-Xyniada Basin (Central Greece). In: Proceedings of the 8th International hydrogeological congress of Greece, (pp. 743–750), Athens, Greece.
Tsipoura-Vlachou, M., & Stamatakis, M. (2005). Mineralogy and geochemistry of evaporitic clay formations of the alkaline lake pikrolimni, Macedonia, Greece. In: Proceedings of the 7th International hydrogeological congress of Greece, (pp. 319–334), Athens, Greece.
Tziritis, E., Kelepertzis, A., Stamatakis, M. (2008). Hydrogeochemical and environmental conditions of the karst aquifer system of the Eastern region, E. Kopais-Ylikis. In: Proceedings of the 8th International hydrogeological congress of Greece, (pp.733–742), Athens, Greece.
Voudouris, K. S., Lambrakis, N. J., Papatheodorou, G., & Daskalaki, P. (1997). An application of factor analysis for the study of the hydrogeological conditions in Plio-Pleistocene aquifers of NW Achaia (NW Peloponnesus, Greece). Mathematical Geosciences, 29(1), 43–59.
Watson, D. F., & Philip, G. M. (1985). A refinement of inverse distance weighted interpolation. Geoprocessing, 2, 315–327.
Webb, J. A., & Sasowsky, I. D. (1994). The interaction of acid mine drainage with a carbonate terrane: evidence from the Obey River, north-central Tennessee. Journal of Hydrology, 161, 327–346.
Yu, G. (1996). Lake-level records and palaeoclimates of northern Eurasia. PhD Thesis, Lund: University of Lund.
Yu, G., & Harrison, S. (1995). Lake status records from Europe: database documentation. USA: World Data Center.
Zaidi, F. K., Nazzal, Y., Jafri, M. K., Naeem, M., & Izrar, A. I. (2015). Reverse ion exchange as a major process controlling the groundwater chemistry in an arid environment: a case study from northwestern Saudi Arabia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 607. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4828-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5538-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charizopoulos, N., Zagana, E. & Stamatis, G. Hydrogeochemical investigations in a drained lake area: the case of Xynias basin (Central Greece). Environ Monit Assess 188, 480 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5484-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5484-z