Abstract
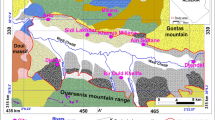
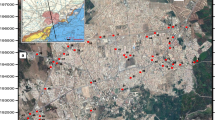
The degradation of groundwater quality, which has been noted in the recent years, is closely connected to the intensification of agriculture, the unreasonable use of chemical fertilizers and the excess consumption of large volumes of irrigation water. In the hilly region of central Thessaly in Greece, which suffers the consequences of intense agricultural use, a hydrogeological study is carried out, taking groundwater samples from springs and boreholes in the Neogene aquifers. The aim of this study is the investigation of irrigation management, water quality and suitability for various uses (water supply, irrigation), the degradation degree and the spatial distribution of pollutants using GIS. The following hydrochemical types prevail in the groundwater of the study area: Ca–Mg–HCO3, Mg–Ca–Na–HCO3 and Na–HCO3. In the above shallow aquifers, especially high values of NO3 − (31.7–299.0), NH4 + (0.12–1.11), NO2 − (0.018–0.109), PO4 3− (0.07–0.55), SO4 2− (47.5–146.5) and Cl− (24.8–146.5) are found, particularly near inhabited areas (values are in mg L−1). The water of shallow aquifers is considered unsuitable for human use due to their high polluting load, while the water of the deeper aquifers is suitable for human consumption. Regarding water suitability for irrigation, the evaluation of SAR (0.153–7.397) and EC (481–1,680 μS cm−1) resulted in classification category ‘C3S1’, indicating high salinity and low sodium water which can be used for irrigation in most soils and crops with little to medium danger of development of exchangeable sodium and salinity. The statistical data analysis, the factor analysis and the GIS application have brought out the vulnerable-problematic zones in chemical compounds of nitrogen and phosphates. The groundwater quality degradation is localized and related exclusively to human activities. Based on 2005 and 2008 estimates, the annual safe yield of the region’s aquifers were nearly 41.95 MCM. However, the existing situation is that 6.37 MCM of water is over extracted from these aquifers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo C, Postma D (1994) Geochemistry. Groundwater and pollution, Balkema
Ayers SR, Westcot DW (1985) Water quality for agriculture, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29-Rev.1. FAO Publications Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Bellos D, Sawidis T, Tsekos I (2004) Nutrient chemistry of River Pinios (Thessalia, Greece). Environ Int 30:105–115
Bornovas I, Filippakis N, Bizon JJG (1969) Geological map of Greece 1:50.000, Farsala Sheet. Publication IGME Athens
Bornovas I, Rontogianni-Tsiambaou TH (1983) Geological map of Greece 1:500.000, Publication IGME Athens
Coutagne A (1954a) Quelques considérations sur le pouvoir évaporant de l’atmosphère, le déficit d’écoulement effectif et le déficit d’écoulement maximum. La Houille Blanche 6:360–369
Coutagne A (1954b) Étude de quelques correlations hydrométéorologiques régionales et leur interpretation algebrique: La Houille blanche, 3 journées de l’Hydraulique de la Societé. Hydrotech. de France, Paris, pp 220–226
Daskalaki P, Voudouris K (2008) Groundwater quality of porous aquifers in Greece: a synoptic review. Env Geol 54(3):505–513
Davis JC (1986) Statistics and data analysis in geology. Wiley, New York
Delgado JA, Shaffer MJ (2002) Essentials of a national nitrate leaching index assessment tool. J Soil Water Conserv 57:327–335
Dimopoulos M, Chalkiadaki M, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2003) Quality of groundwater in Western Thessaly, the problem of nitrate pollution. Glob Nest Int J 5(3):185–191
Dioudis P, Filintas A, Koutseris Ε (2009) GPS and GIS based N-mapping of agricultural fields’ spatial variability as a tool for non-polluting fertilization by drip irrigation. Int J Sus Dev Plann 4(3):210–225
EΕC 91/676 (1991) Directive 91/676/EEC on nitrates from agricultural sources, European Commission Report COM(97) 473
EΕC 98/83 (1998) Council Directive 98/83/EC (Drinking Water Directive), European Commission, Brussels
Filintas A (2005) Land use systems with emphasis on agricultural machinery, irrigation and nitrates pollution, with the use of satellite remote sensing, geographic information systems and models, in watershed level in Central Greece. M.Sc. thesis, Dept. of Environment, University of Aegean, Mitilini, Greece
Filintas TΑG (2008) Study and mapping of biomass yield with the use of spatial statistics and geoinformation. M.Sc. thesis, Dept. of Natural Resources and Agriculture Engineering, Agricultural University of Athens, Athens, Greece
Filintas TΑG, Dioudis PI, Pateras DT, Hatzopoulos JN, Toulios LG (2006) Drip irrigation effects in movement, concentration and allocation of nitrates and mapping of nitrates with gis in an experimental agricultural field. In: Proc. of 3rd international conference haicta 2006 on: information systems in sustainable agriculture, agroenvironment and food technology, HAICTA, Volos, Greece, 20–23 September. ISBN 960-8029-43-0, pp 253–262
Filintas ΑG, Dioudis P, Pateras D, Κoutseris E, Hatzopoulos J, Toulios L (2007a) Irrigation water and applied nitrogens fertilizer effects in soils nitrogen depletion and nitrates GIS mapping. Proc. of 1st international conference on environmental management, engineering, planning and economics (CEMEPE/SECOTOX), June 24–28, vol III. Skiathos Island, Greece, pp 2201–2207
Filintas Α, Dioudis P, Koutseris Ε, Papadopoulos Α (2007b) Soils nitrates GIS mapping, irrigation water and applied N-fertilizer effects in soils nitrogen depletion in a drip irrigated experimental field in Thessaly basin. In: Proc. of 3rd IASME/WSEAS international conference on energy, environment, ecosystems and sustainable development (EEESD’07), July 24–26, Agios Nikolaos, Crete, Greece, WSEAS, ISBN: 978-960-8457-94-2, pp 487–492
Filintas A, Polyzos S, Stamatis G (2008a) Planning, construction and operation of dams and water reservoirs, in interelation with environmental impacts. In: Proc. of 8th international hydrogeological congress of Greece, 8–10 October, Athens, Greece, ISDN 978-960-88816-5-5, pp767–782
Filintas Α, Dioudis P, Stamatis G, Hatzopoulos J, Karyotis Th (2008b) Environmental assessment of groundwater nitrate pollution from agricultural wastes and fertilizers in central Greece watersheds using remote sensing and GIS. In: Proc. of 3rd international conference AQUA 2008 on: water science and technology with emphasis on water & climate, 16–19 October, Athens, Greece, ID-02, p 10
Filintas A, Hatzopoulos J, Polyzos S (2008c) Assessment of surface water springs’ quality by the use of GIS and geostatistical techniques. Chapter 28. In: Arabatzis G., Polyzos S (eds) Natural resources, environment and development. Tziolas Publications, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp 695–728 (in Greek)
Filintas AG, Hatzopoulos J, Parlantzas V (2009) Agriculture spray machinery pattern testing and validation by the use of gis and the use of a dilution of active ingredient in wastewater. In: Proc. of 5th international conference on energy, environment, ecosystems and sustainable development (EEESD’09), pp 334–339
Filintas A, Dioudis P, Prochaska C (2010) GIS modeling of the impact of drip irrigation, of water quality and of soil’s available water capacity on Zea mays L, biomass yield and its biofuel potential. Desalination Water Treat 13(1–3):303–319
Follett RF, Delgado JA (2002) Nitrogen fate and transport in agricultural systems. J Soil Water Conserv 57:402–408
Fytikas M, Kolios N (1979) Preliminary heat flow map of greece. In: Germak V, Rybach L (eds) Terrestrial heat flow in Europe. Springer, Berlin, pp 197–205
Hatzopoulos NJ (2008) Topographic mapping, covering the wider field of geospatial information science & technology (GIS&T). ISBN-10: 1581129866, ISBN-13: 9781581129861, Universal Publishers, 740 pp
Hatzopoulos J, Filintas AG (2009) Integrated urban planning for the safe reuse of municipal wastewater and biosludge from WWT Plants in crops and soils. Research Project Delivarables IV. Dept. of Environment, University of the Aegean, Mitilini, Greece
HNMS (2010) Meteorological data of central Greece, Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS), Greece (in Greek)
Höll K (1979) Wasser: Untersuchung, Beurteilung, Aufbereitung, Chemie, Bakteriologie, Virologie, Biologie. Berlin-New York (Walter de Gruyter), pp 515
Jacobshagen V (1986) Geologie von Griechenland. Berlin-Stuttgart, Borntraeger, p 363
Kallergis G (1970) Hydrogeological investication of Kalambaka basin (Western Thessaly), vol XIV. Institute for Geology and subsurface research, Athens, Greece (in Greek)
Kalavrouziotis I, Filintas A, Koukoulakis P, Hatzopoulos J (2011) Application of multicriteria analysis in the management and planning of treated municipal wastewater and sludge reuse in agriculture and land development: The case of Sparti’s wastewater treatment plant, Greece. Fresen Environ Bull 20(2):287–295
Kallergis G, Morphis A, Papaspyropoulos Ch, Christodoulou Th (1973) Hydrogeological investigations in the Western Thessaly basin. Hydrol Hydrogeol Investig IGME Athens, No 8, pp 166
Katsikatsos G (1992) Geology of Greece. Athens, p 451
Katsikatsos G, Mylonakis E, Triantaphyllis E, Papadeas G, Psonis K, Tsaila-Monopoli S, Skourtsi-Koroneou V (1983) Geological Map of Greece 1:50.000, Velestino Sheet. Publication IGME Athens
Koutseris Ε, Filintas Α, Dioudis P (2010) Antiflooding prevention protection, strategic environmental planning of aquatic resources and water purification: the case of Thessalian basin, in Greece. Desalination 250(1):318–322
Lambrakis N (1991) Elaboration of the hydrochemical data by PC. Miner Wealth 74:53–60
Lambrakis N, Stamatis G, Giannoulopoulos P, Voivonta A (2001) Groundwater quality and estimation of rehabilitation time of the Argolid plain’s aquifers under artificial recharge conditions. Bull Geol Soc Greece XXXIV(5):1819–1826
Lazaridis L, Kalaouzis G, Koutsoyiannis D, Marinos P (1996) Basic engineering and economic characteristics regarding water resources management of Thessaly. Proc. of the Intern. Conf. on Water Resources Management, Larissa, Technical Chamber of Greece
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater. Clarendon Press, Oxford, p 296
Marinos P, Thanos B, Perleros K, Kavadas M (1995) Groundwater in Thessaly plain (origin in Greek). In: Proc. of the 3rd Hydrogeological Congress in Greece, Heraklion – Crete, pp 468–480
Mariolakos E, Lekkas S, Alexopoulos A, Fountoulis I, Spyridonos E, Badekas I, Mariolakos D, Andreadakis E (2001a) Artificial Recharge of a karstic aquifer in Fillion mountain in Farsala basin – Thessaly (Orig. in Greek). In: Proc. of the 9th Intern. Congr. Athens, September 2001, Bull Geol Greece, vol XXXIV/5, pp 1843–1850
Mariolakos E, Lekkas S, Papadopoulos T, Alexopoulos A, Fountoulis I, Alexopoulos I, Spyridonos E, Badekas I, Mariolakos D,. Andreadakis E (2001b) The subsurface tectonic structure of the Farsala basin (Thessaly) as determining factor of the Hydrogeological conditions of the region. In: Proc. of the 9th Intern. Congr. Athens, Sept. 2001, Bull Geol Greece, vol XXXIV/5, pp 1851–1858
Mpliatsos K (2009) Agricultural and irrigated land of Nikaia region in 2008. G.A Larissa, Greece (In Greek)
NSSG (2009) Agriculture statistics of Greece-Data for 2008, National statistical Service of Greece (NSSG), Pireas, Greece
Plastiras B, Karantasi S (1985) Geological Map of Greece 1:50.000, Larissa Sheet. Publication IGME Athens
Postma D, Boesen C, Kristiansen H, Larsen F (1991) Nitrate reduction in an unconfined sandy aquifer: water chemistry, reduction processes, and geochemical modeling. Water Resour Res 27(8):2027–2045
Rhoades JD (1977) Potential for using saline agricultural drainage waters for irrigation. In: Proc. water management for irrigation and drainage. ASCE, Reno, Nevada. 20–22 July, pp 85–116
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 60. US Department of Agriculture, Washington DC, p 160
Silva RG, Cameron KC, Di HJ, Hendry T (1999) A lysimeter study of the impact of cow urine, dairy shed effluent and nitrogen fertilizer on nitrate leaching. Aust J Soil Res 37:357–369
Soil Survey Staff (1975) Soil taxonomy: a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, USA
Solley WB, Pierce RR, Perlman HA (1990) Estimated use of water in the United States in 1990. US Geological Survey Circular 1081
Soulios G (1996) General hydrogeology, vol I. University Studio Press, Thessaloniki Greece, p 295
Soulios G, Toubektsi M, Tzevelekis G, Ezeigbo H (1991) Water balance of basins in central Greece: comparison with other circum-Mediterranean basins and validity of empirical methods. Environ Geol Water Sci 18(2):85–94
Stamatis G, Boudouris K (2003) Marine and human activity influences on the groundwater quality of southern Korinthos area. Int J Hydrol Process 17:2327–2345
Stamatis G, Lambrakis Ν, Alexakis D, Zagana E (2006) Groundwater quality in Neocene and quaternary deposits of Mesogea basin in Eastern Attica (Greece). Int J Hydrol Process 20:2803–2818
Stamatis G, Parpodis K, Lambrakis N, Zagana E (2007) Origin and quality of thermal groundwaters in the region of Farsala (E. Thessaly/Greece). Bull Geol Soc Greece XXXX:570–571
Tan CS, Drury CF, Reynolds WD, Groenevelt PH, Dadfar H (2002) Water and nitrate loss through tiles under a clay loam soil in Ontario after 42 years of consistent fertilization and crop rotation. Agric Ecosyst Environ 93:121–130
USDA-SCS (1970) Irrigation water requirements. Technical Release No. 21. USDA Soil Conservation Service, Washington, DC
Voudouris K (1995) Hydrogeological conditions of the NW part of Achaia (NW Peloponnesus, Greece). Phd thesis, University of Patras, Patras, Greece (in Greek), pp 237
WHO (1984) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, vol 2. Health criteria and other supporting information, Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stamatis, G., Parpodis, K., Filintas, Α. et al. Groundwater quality, nitrate pollution and irrigation environmental management in the Neogene sediments of an agricultural region in central Thessaly (Greece). Environ Earth Sci 64, 1081–1105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0926-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0926-y