Abstract
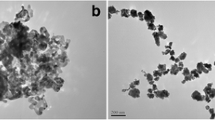
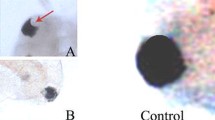
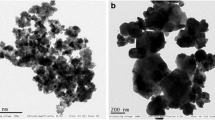
Aquatic stability and impact of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs, 10–30 nm) were investigated using Artemia salina. Acute exposure was conducted on nauplii (larvae) and adults in seawater in a concentration range from 10 to 100 mg/L TiO2 NPs for 24 and 96 h. Rapid aggregation occurred in all suspensions of TiO2 NPs to form micrometer size particles. Yet, both nauplii and adults accumulated the aggregates significantly. Average TiO2 content in nauplii ranged from 0.47 to 3.19 and from 1.29 to 4.43 mg/g in 24 and 96 h, respectively. Accumulation in adults was higher ranging from 2.30 to 4.19 and from 4.38 to 6.20 mg/g in 24 and 96 h, respectively. Phase contrast microscopy images revealed that Artemia were unable to excrete the particles. Thus, the TiO2 aggregates filled inside the guts. No significant mortality or toxicity occurred within 24 h at any dose. Lipid peroxidation levels characterized with malondialdehyde concentrations were not statistically different from those of the controls (p > 0.05). These results suggested that suspensions of the TiO2 NPs were nontoxic to Artemia, most likely due to the formation of benign TiO2 aggregates in water. In contrast, both mortality and lipid peroxidation increased in extended exposure to 96 h. Highest mortality occurred in 100 mg/L TiO2 NP suspensions; 18 % for nauplii and 14 % for adults (LC50 > 100 mg/L). These effects were attributed to the particle loading inside the guts leading to oxidative stress as a result of impaired food uptake for a long period of time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, L. K., Lyon, D. Y., & Alvarez, P. J. J. (2006). Comparative ecotoxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Research, 40, 3527–3532.
Arslan, Z., Ertas, N., Tyson, J. F., Uden, P. C., & Denoyer, E. R. (2000). Determination of trace elements in marine plankton by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 366, 273–282.
Arslan, Z., Ates, M., McDuffy, W., Agachan, M. S., Farah, I. O., Yu, W. W., & Bednar, A. J. (2011). Probing metabolic stability of CdSe nanoparticles: alkaline extraction of free cadmium from liver and kidney samples of rats exposed to CdSe nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 192–199.
Bahnemann, D. W., Kholuiskaya, S. N., Dillert, R., Kulak, A. I., & Kokorin, A. I. (2002). Photodestruction of dichloroacetic acid catalyzed by nano-sized TiO2 particles. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 36, 161–169.
Benn, T. M., & Westerhoff, P. (2008). Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 4133–4139.
Chatterjee, R. (2008). The challenge of regulating nanomaterials. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 339–343.
Choi, H., Stathatos, E., & Dionysiou, D. D. (2006). Sol–gel preparation of mesoporous photocatalytic TiO2 films and TiO2/Al2O3 composite membranes for environmental applications. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 63, 60–67.
Choi, J. Y., Ramachandran, G., & Kandlikar, M. (2009). The impact of toxicity testing costs on nanomaterial regulation. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 3030–3034.
Farkas, J., Christian, P., Urrea, J. A., Roos, N., Hassellöv, M., Tollefsen, K. E., & Thomas, K. V. (2010). Effects of silver and gold nanoparticles on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquatic Toxicology, 96, 44–52.
Farre, M., Gajda-Schrantz, K., Kantiani, L., & Barcelo, D. (2009). Ecotoxicity and analysis of nanomaterials in the aquatic environment. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 393, 81–95.
Geranio, L., Heuberger, M., & Nowack, B. (2009). The behavior of silver nanotextiles during ecotoxicty and analysis of washing. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 8113–8118.
Handy, R. D., Henry, T. B., Scown, T. M., Johnson, B. D., & Tyler, C. R. (2008). Manufactured nanoparticles: their uptake and effects on fish-a mechanistic analysis. Ecotoxicology, 17, 396–409.
Heinlaan, M., Ivask, A., Blinova, I., Dubourguier, H.-C., & Kahru, A. (2008). Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus. Chemosphere, 71, 1308–1316.
Hund-Rinke, K., & Simon, M. (2006). Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 13, 225–232.
Kanwar, A. (2007). Brine shrimp (Artemia salina) a marine animal for simple and rapid biological assays. Journal of Chinese Clinical Medicine, 2, 236–240.
Kim, K. T., Klaine, S. J., Cho, J., Kim, S. H., & Kim, S. D. (2010). Oxidative stress responses of Daphnia magna exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles according to size fraction. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 2268–2272.
Lovern, S. B., & Klaper, R. (2006). Daphnia magna mortality when exposed to titanium dioxide and fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 1132–1137.
Mills, A., Lepre, A., Elliott, N., Bhopal, S., Parkin, I. P., & O’Neill, S. (2004). Characterization of the photocatalyst Pilkington Activ™: a reference film photocatalyst? Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 160, 213–224.
Moore, M. N. (2006). Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environment International, 32, 967–976.
Nunes, B. S., Carvalho, F. D., Guilhermino, L. M., & Van Stappen, G. (2006). Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environmental Pollution, 144, 453–462.
OECD. (2004). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals (Part 202).
Pascual, P., Pedradas, J. R., Toribio, F., Lopez-Barea, J., & Peinado, J. (2003). Effect of food deprivation on oxidative stress biomarkers in fish (Sparus aurata). Chemico-Biological Interactions, 145, 191–199.
Persoone, G., Van de Vell, A., Van Steertegem, M., & Nayer, B. (1989). Predictive value for laboratory tests with aquatic invertebrates: influence of experimental conditions. Aquatic Toxicology, 14, 149–166.
Sanchez, F., Sanz, F., Santa-Maria, A., Ros, J., De Vicente, M., Encinas, M., Vinagre, E., & Barahona, M. (1997). Acute sensitivity of three age classes of Artemia salina larvae to seven chlorinated solvents. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 59, 445–451.
Sayeed, I., Parvez, S., Pandey, S., Bin-Hafeez, B., & Raisuddin, S. (2003). Oxidative stress biomarkers of exposure to deltamethrin in freshwater fish, Channa punctatus Bloch. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 295–301.
Schmidt, C. W. (2009). Nanotechnology-related environmental, health, and safety research examining the national strategy. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, A158–A161.
Schulz, J., Hohenberg, H., Pflücker, F., Gärtner, E., Will, T., & Pfeiffer, S. (2002). Distribution of sunscreens on skin. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 54, 157–163.
Sorgeloos, P. (1980). Availability of reference Artemia cysts. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 3, 363–364.
Van Ye, T. M., Roza, A. M., & Pieper, G. M. (1993). Inhibition of intestine lipid peroxidation does not minimize morphologic damage. Journal of Surgical Research, 55, 553–558.
Vanhaecke, P., Persoone, G., Claus, C., & Sorgeloos, P. (1981). Proposal for a short-term toxicity test with Artemia nauplii. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 5, 382–387.
Warheit, D. B., Hoke, R. A., Finlay, C., Donner, E. M., Reed, K. L., & Sayes, C. M. (2007). Development of a base set of toxicity tests using ultrafine TiO2 particles as a component of nanoparticle risk management. Toxicology Letters, 171, 99–110.
Wiench, K., Wohlleben, W., Hisgen, V., Radke, K., Salinas, E., Zok, S., & Landsiedel, R. (2009). Acute and chronic effects of nano- and non-nano-scale TiO2 and ZnO particles on mobility and reproduction of the freshwater invertebrate Daphnia magna. Chemosphere, 76, 1356–1365.
Xiong, D., Fang, T., Yu, L., Sima, X., & Zhu, W. (2011). Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 1444–1452.
Zeynalov, E. B., & Allen, N. S. (2006). Effect of micron and nano-grade titanium dioxides on the efficiency of hindered piperidine stabilizers in a model oxidative reaction. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 91, 931–939.
Zhao, J., Wang, Z., Liu, X., Xie, X., Zhang, K., & Xing, B. (2011). Distribution of CuO nanoparticles in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio) and their potential toxicity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 197, 304–310.
Zhu, X., Zhu, L., Li, Y., Qi, R., Duan, Z., & Lang, Y. P. (2008). Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nano-particle aqueous suspensions to zebrafish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 43, 278–284.
Zhu, X., Chang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2010). Toxicity and bioaccumulation of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere, 78, 209–215.
Zhu, X., Zhou, J., & Cai, Z. (2011). The toxicity and oxidative stress of TiO2 nanoparticles in marine abalone (Haliotis diversicolor supertexta). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 63, 334–338.
Acknowledgments
This project is funded in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI) Program (Grant No: G12RR013459) and the US Department of Defense (DOD) through the Engineer, Research and Development Center (Vicksburg, MS, USA); (contract #W912HZ-10-2-0045). The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies, and any of their sub-agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ates, M., Daniels, J., Arslan, Z. et al. Effects of aqueous suspensions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on Artemia salina: assessment of nanoparticle aggregation, accumulation, and toxicity. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3339–3348 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2794-7