Abstract
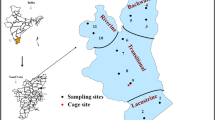
Phosphorus fractionation was employed to find the bioavailability of phosphorus and its seasonal variations in the Panangad region of Cochin estuary, the largest estuarine system in the southwest coast of India. Sequential extraction of the surficial sediments using chelating agents was taken as a tool for this. Phosphate in the water column showed seasonal variations, with high values during the monsoon months, suggesting external runoff. Sediment texture was found to be the main factor influencing the spatial distribution of the geochemical parameters in the study region. Similarly, total phosphorus also showed granulometric dependence and it ranged between 319.54 and 2,938.83 μg/g. Calcium-bound fraction was the main phosphorus pool in the estuary. Significant spatial variations were observed for all bioavailable fractions; iron-bound inorganic phosphorus (5.04–474.24 μg/g), calcium-bound inorganic phosphorus (11.16–826.09 μg/g), and acid-soluble organic phosphorus (22.22–365.86 μg/g). Among the non-bioavailable phosphorus, alkali-soluble organic fraction was the major one (51.92–1,002.45 μg/g). Residual organic phosphorus was comparatively smaller fraction (3.25–14.64% of total). The sandy and muddy stations showed distinct fractional composition and the speciation study could endorse the overall geochemical character. There could be buffering of phosphorus, suggested by the increase in the percentage of bioavailable fractions during the lean pre-monsoon period, counteracting the decreases in the external loads. Principal component analysis was employed to find the possible processes influencing the speciation of phosphorus in the study region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieux-Loyer, F., & Aminot, A. (2001). Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 52, 617–629.
Benitez-Nelson, C. R. (2000). The biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus in marine systems. Earth Science Reviews, 51, 109–135.
Caraco, N. J., Cole, J. J., & Likens, G. (1990). A comparison of phosphorus immobilization in sediments of freshwater and coastal marine systems. Biogeochemistry, 9, 277–290.
Cha, H. J., Lee, C. B., Kim, B. S., Choi, M. S., & Ruttenberg, K. C. (2005). Early diagenetic redistribution and burial of phosphorus in the sediments of the southwestern East Sea (Japan Sea). Marine Geology, 216, 127–143.
Coelho, J. P., Flindt, M. R., & Jensen, H. S. (2004). Phosphorus speciation and availability in intertidal sediments of a temperate estuary: Relation to eutrophication and annual P-fluxes. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 61, 583–590.
De Groot, C. J. (1990). Some remarks on the presence of organic phosphates in sediments. Hydrobiologia, 207, 303–309.
De Groot, C. J., & Golterman, H. L. (1993). On the importance of organic phosphate in some Camargue sediments, evidence for the importance of phytate. Hydrobiologia, 252, 117–126.
Diaz-Espejo, A., Serrano, L., & Toja, J. (1999). Changes in sediment phosphate composition of seasonal ponds during filling. Hydrobiologia, 392, 21–28.
Dvorakova, J. (1998). Phytase: Sources, preparation and exploitation. Folia Microbiologica, 43, 323–338.
Folk, R. L. (1980). Petrology of sedimentary rocks (pp. 26–27). Austin, Texas: Hemphill.
Gachter, R., & Muller, B. (2003). Why the phosphorus retention of lakes does not necessarily depend on the oxygen supply to the sediment surface. Limnology and Oceanography, 48, 929–933.
Gatcher, R., & Meyer, J. S. (1993). The role of microorganisms in mobilization and fixation of phosphorus in sediments. Hydrobiologia, 253, 103–121.
Golterman, H. L. (1996). Fractionation of sediment phosphate with chelating compounds: A simplification, and comparison with other methods. Hydrobiologia, 335, 87–95.
Golterman, H. L. (2001). Phosphate release from anoxic sediments or ‘What did Mortimer really write?’. Hydrobiologia, 450, 99–106.
Golterman, H. L., Paing, J., Serrano, L., & Gomez, E. (1998). Presence of and phosphate release from polyphosphates or phytate phosphate in lake sediments. Hydrobiologia, 364, 99–104.
Grasshoff, K., Ehrhardt, M., & Kremling, K. (1983). Methods of sea water analysis (2nd ed.). Weinhein: Verlag Chemie.
Hecky, R. E., Campbell, P., & Hendzel, L. L. (1993). The stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in particulate matter of lakes and oceans. Limnology and Oceanography, 38, 709–724.
Hedges, J. I., & Keil, R. G. (1995). Sedimentary organic matter preservation: An assessment and speculative hypothesis. Marine Chemistry, 49, 81–115.
Hou, L. J., Liu, M., Yang, Y., Ou, D. N., Lin, X., Chen, H., et al. (2009). Phosphorus speciation and availability in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 120–128.
Huanxin, W., Presley, B. J., & Armstrong, D. (1994). Distribution of sedimentary phosphorus in Gulf of Mexico estuaries. Marine Environmental Research, 37, 375–392.
Jayaprakash, A. A. (2002). Long term trends in rainfall, sea level and solar periodicity: A case study for forecast of Malabar sole and Oil sardine fishery. Journal of Marine Biological Association of India, 44, 163–175.
Jensen, H. S., Kristensen, P., Jeppesen, E., & Skytthe, A. (1992). Iron: Phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 235/236, 731–743.
Kassila, J., & Hussenot, J. (2004). Fractionation of phosphate in marine aquaculture sediments: Optimization of the ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid method and comparison with other procedures. Aquaculture Research, 35, 1339–1348.
Kautsky, L. (1998). Monitoring eutrophication and pollution in estuarine environments-focusing on the use of benthic communities. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 70, 2313–2318.
Kripa, V., Velayudhan, T. S., Shoji, J., Alloycious, P. S., Joseph, M., Radhakrishnan, P., et al. (2004). Clam fisheries of Vembanad Lake, Kerala with observations on the observations on the socio economic conditions of the clam fishers. Marine Fisheries Information Service Technical and Extension Series, 179, 14–16. http://www.casmbenvis.nic.in/sdnp/lagoon%20pdf/L152.pdf.
Krishna Prasad, M. B., & Ramanathan, A. L. (2008). Sedimentary nutrient dynamics in a tropical estuarine mangrove ecosystem. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 80, 60–66.
Lakshmilatha, P., & Appukuttan, K. K. (2002). A review of the black clam (Villorita Cyprinoides) fishery of the Vembanad Lake. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 49, 85–91.
Menon, N. N., Balchand, A. N., & Menon, N. R. (2000). Hydrobiology of the Cochin backwater system—A review. Hydrobiologia, 430, 149–183.
Millero, F., Huang, F., Zhu, X., Liu, X., & Zhang, J. (2001). Adsorption and desorption of phosphate on calcite and aragonite in seawater. Aquatic Geochemistry, 7, 33–56.
Millero, F. J., & Sohn, M. L. (1992). Chemical oceanography. Boca Raton: CRC.
Morton, S. C., & Edwards, M. (2005). Reduced phosphorus compounds in the environment. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 333–364.
Nair, C. K., Balchand, A. N., & Chacko, J. (1993). Sediment characteristics in relation to changing hydrography of Cochin estuary. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 22, 33–36.
Paludan, C., & Jensen, H. S. (1995). Sequential extraction of phosphorus in freshwater wetland and lake sediment: Significance of humic acids. Wetlands, 15, 365–373.
Paludan, C., & Morris, J. T. (1999). Distribution and speciation of phosphorus along a salinity gradient in intertidal marsh sediments. Biogeochemistry, 45, 197–221.
Perkins, R. G., & Underwood, G. J. C. (2001). The potential for phosphorus release across the sediment–water interface in a eutrophic reservoir dosed with ferric sulphate. Water Research, 35, 1399–1406.
Qasim, S. Z. (2003). Indian estuaries (p. 259). Mumbai: Allied.
Raiswell, R., Buckley, F., Berner, R. A., & Anderson, T. F. (1987). Degree of pyritization of iron as a palaeoenvironmental indicator of bottom-water oxygenation. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 58, 812–819.
Reddy, K. R., Fisher, M. M., & Ivanoff, D. (1996). Resuspension and diffusive flux of nitrogen and phosphorus in a hypereutrophic lake. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 363–371.
Renjith, K. R., & Chandramohanakumar, N. (2009). Distribution of heavy metals in the surficial sediments of a complex micro-tidal estuarine system in Southwest India. Research Journal of Chemistry and Environment, 13, 34–44.
Renjith, K. R., Varma, K. K., Haridevi, C. K., Houlath, K. H., Vijayakumar, C. T., & Joseph, P. (2004). Primary production and fishery potential of the Panangad region in the Cochin estuarine system. Journal of Marine biological Association of India, 46, 126–132.
Reynolds, C. S., & Davies, P. S. (2001). Sources and bioavailability of phosphorus fractions in freshwaters: A British perspective. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 76, 27–64.
Roden, E. E., & Edmonds, J. W. (1997). Phosphate mobilization in iron-rich anaerobic sediments: Microbial Fe (Fe (III) oxide reduction versus iron-sulfide formation. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 139, 347–378.
Rydin, E., & Brunberg, A. K. (1998). Seasonal dynamics of phosphorus in Lake Erken surface sediments. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 51, 157–167.
Short, F. T., Dennison, W. C., & Capone, D. G. (1990). Phosphorus-limited growth of the tropical seagrass Syringodium-Filiforme in carbonate sediments. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 62, 169–174.
Slomp, C. P., Van der Gaast, S. J., & Van Raaphorst, W. (1996). Phosphorus binding by poorly crystalline iron oxides in North Sea sediments. Marine Chemistry, 52, 55–73.
Srinivas, K. (1999). Seasonal and interannual variability of sea level and associated surface meteorological parameters at Cochin. Ph.D. thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India.
Stevens, R. J., & Stewart, B. M. (1982). Concentration, fractionation and characterisation of soluble organic phosphorus in river water entering Lough Neagh. Water Research, 16, 1507–1519.
Tiyapongpattana, W., Pongsakul, P., Shiowatana, J., & Nacapricha, D. (2004). Sequential extraction of phosphorus in soil and sediment using a continuous-flow system. Talanta, 62, 765–771.
Tung, J. W. T., & Tanner, P. A. (2003). Instrumental determination of organic carbon in marine sediments. Marine Chemistry, 80, 161–170.
Wen, L. S., Warnken, K. W., & Santschi, P. H. (2008). The role of organic carbon, iron, and aluminium oxyhydroxides as trace metal carriers: Comparison between the Trinity River and the Trinity River Estuary (Galveston Bay, Texas). Marine Chemistry, 112, 20–37.
Weston, D. P. (1990). Quantitative examination of macrobenthic community changes along an organic enrichment gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 61, 233–244.
Yamamuro, M. (2000). Chemical tracers of sediment organic matter origins in two coastal lagoons. Journal of Marine Systems, 26, 127–134.
Ysebaert, T., Fettweis, M., Meire, P., & Sas, M. (2005). Benthic variability in intertidal soft-sediments in the mesohaline part of the Schelde estuary. Hydrobiologia, 540, 197–216.
Zwolsman, J. J. G. (1994). Seasonal variability and biogeochemistry of phosphorus in the Scheldt Estuary, South-west Netherlands. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 39, 227–248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renjith, K.R., Chandramohanakumar, N. & Joseph, M.M. Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphorus in a tropical estuary, Southwest India. Environ Monit Assess 174, 299–312 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1458-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1458-8