Abstract
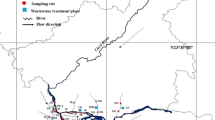
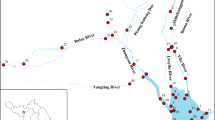
Bisphenol A (BPA), one of the endocrine-disrupting chemicals, was detected in water collected from Kao-Pin River and its tributaries. Results indicated that 59% of the water samples contained BPA. Concentrations ranged from less than the limit of detection (LOD, 0.037) to 4.23 μg/L. The mean concentrations were 0.16, 0.20, 1.02, 1.30, and 0.30 μg/L for sampling sites S1, S2, S3, S4, and S5, respectively. Concentrations were not significantly different between high and low-flow periods in sites S2, S3, and S4. In site S1, concentrations in the high-flow period were significantly greater than during the lower flow period, and in site S5, BPA concentration in the low-flow period was significantly greater than in the high-flow period. The BPA mass flow rate in site S5 was greater in the high-flow period than in the low-flow period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakura, H., Matsuto, T., & Tanaka, N. (2004). Behavior of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in leachate from MSW landfill sites in Japan. Waste Management (New York, N.Y.), 24, 613–622. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2004.02.004.
Belfroid, A., van Velzen, M., van der Horst, B., & Vethaak, D. (2002). Occurrence of bisphenol A in surface water and uptake in fish: Evaluation of field measurements. Chemosphere, 49, 97–103. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00157-1.
Bolz, U., Hagenmaier, H., & Körner, W. (2001). Phenolic xenoestrogens in surface water, sediments, and sewage sludge from Baden-Wurttemberg, south-west Germany. Environmental Pollution, 115, 291–301. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00100-2.
Boyd, G. R., Palmeri, J. M., Zhang, S., & Grimm, D. A. (2004). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in stromwater canals and Bayou St. John in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. The Science of the Total Environment, 333, 137–148. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.018.
Fromme, H., Küchler, T., Otto, T., Pilz, K., Müller, J., & Wenzel, A. (2002). Occurrence of phthalates and bisphenol A and F in the environment. Water Research, 36, 1429–1438. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00367-0.
Goodman, J. E., McConnell, E. E., Sipes, I. G., Witorsch, R. J., Slayton, T. M., Yu, C. J., et al. (2006). An updated weight of the evidence evaluation of reproductive and developmental effects of low doses of bisphenol A. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 36, 387–457. doi:10.1080/10408440600758317.
Heemken, O. P., Reincke, H., Stachel, B., & Theobald, N. (2001). The occurrence of xenoestrogens in the Elbe rive and the North Sea. Chemosphere, 45, 245–259. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00570-1.
Insightful (2001). S-Plus 6 for windows user’s guide. Washington USA: Insightful Corporation, Seattle.
Jobling, S., Casey, D., Rodgers-Gray, T., Oehlmann, J., Shulte-Oehlmann, U., Pawlowski, S., et al. (2003). Comparative responses of molluscs and fish to environmental estrogens and an estrogenic effluent. Aquatic Toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 66, 205–220. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(03)00134-6.
Kang, J. H., Aasi, D., & Katayama, Y. (2007). Bisphenol A in the aquatic environment and its endocrine-disruptive effects on aquatic organisms. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 37, 607–625. doi:10.1080/10408440701493103.
Kang, J. H., & Kondo, F. (2002a). Effects of bacterial counts and temperature on the biodegradation of bisphenol A in river water. Chemosphere, 49, 493–498. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00315-6.
Kang, J. H., & Kondo, F. (2002b). Bisphenol A degradation by bacteria isolated from river water. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 43, 265–269. doi:10.1007/s00244-002-1209-0.
Kang, J. H., & Kondo, F. (2005). Bisphenol A degradation in seawater is different from that in river water. Chemosphere, 60, 1288–1292. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.058.
Kang, J. H., Kondo, F., & Katayama, Y. (2006). Human exposure to bisphenol A. Toxicology, 226, 79–89. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2006.06.009.
Kang, I. J., Yokota, H., Oshima, Y., Tsuruda, Y., Oe, T., Imada, N., et al. (2002). Effects of bisphenol A on the reproduction of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 2394–2400. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2002)021<2394:EOBAOT>2.0.CO;2.
Kashiwada, S., Ishikawa, H., Miyamoto, N., Ohnishi, Y., & Magara, Y. (2002). Fish test for endocrine-disruption and estimation of water quality of Japanese rivers. Water Research, 36, 2161–2166. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00406-7.
Klecka, G. M., Gonsior, S. J., West, R. J., Goodwin, P. A., & Markham, D. A. (2001). Biodegradation of bisphenol A in aquatic environments: River die-away. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 2725–2735. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<2725:BOBAIA>2.0.CO;2.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., et al. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: A national reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 1202–1211. doi:10.1021/es011055j.
Lahnsteiner, F., Berger, B., Kletzl, M., & Weismann, T. (2005). Effect of bisphenol A on maturation and quality of semen and eggs in the brown trout, Salmo trutta f. fario. Aquatic Toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 75, 213–224. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.08.004.
Maffini, M. V., Rubin, B. S., Sonnenschein, C., & Soto, A. M. (2006). Endocrine disruptors and reproductive health: The case of bisphenol-A. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 254–255, 179–186. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2006.04.033.
Palisade (2002). Guide to using @RISK risk analysis and simulation add-in for Microsoft Excel. V 4.5. Palisade Corporation, Newfield, NY, USA.
Pastva, S. D., Villalobos, S. A., Kannan, K., & Giesy, J. P. (2001). Morphological effects of bisphenol A on the early life stages of medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere, 45, 535–541. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00018-2.
Patrolecco, L., Capri, S., De Angelis, S., Pagnotta, R., Polesello, S., & Valsecchi, S. (2006). Partition of nonylphenol and related compounds among different aquatic compartment in Tiber River (central Italy). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 172, 151–166. doi:10.1007/s11270-005-9067-9.
Pojana, G., Gomiero, A., Jonkers, N., & Marcomini, A. (2007). Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environment International, 33, 929–936. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.05.003.
Stachel, B., Ehrhorn, U., Heemken, O. P., Lepom, P., Reincke, H., Sawal, G., et al. (2003). Xenoestrogens in the River Elbe and its tributaries. Environmental Pollution, 124, 497–507. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00483-9.
Staples, C. A., Dorn, P. B., Klecka, G. M., O’Block, S. T., & Harris, L. R. (1998). A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere, 36, 2149–2173. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)10133-3.
Staples, C. A., Dorn, P. B., Klecka, G. M., O’Block, S. T., Branson, D. R., & Harris, L. R. (2000). Bisphenol A concentration in receiving waters near US manufacturing and processing facilities. Chemosphere, 40, 521–525. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00288-X.
Suzuki, T., Nakagawa, Y., Takano, I., Yaguchi, K., & Yasuda, K. (2004). Environmental fate of bisphenol A and its biological metabolites in river water and their xeno-estrogenic activity. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 2389–2396. doi:10.1021/es030576z.
Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration (TEPA) (2003). Environmental Hormones Investigation. EPA 92-E3S5-02-01, Taipei, Taiwan.
Tsuda, T., Suga, K., Kaneda, E., & Ohsuga, M. (2000). Determination of 4-nonylphenol, nonylphenol monoethoxylate, nonylphenol diethoxylate and other alkylphenols in fish and shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 746, 305–309. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00322-4.
Urase, T., & Miyashita, K. I. (2003). Factors affecting the concentration of bisphenol A in leachates from solid waste disposal sites and its fate in treatment processes. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 5, 77–82. doi:10.1007/s101630300012.
Van den Belt, K., Verheyen, R., & Witters, H. (2003). Comparison of vitellogenin responses in zebrafish and rainbow trout following exposure to environmental estrogens. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 271–281. doi:10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00004-6.
Voordeckers, J. W., Fennell, D. E., Jones, K., & Haggblom, M. M. (2002). Anaerobic biotransformation of tetrabromobisphenol A, tetrachorobisphenol A, and Bisphenol A in estuarine sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 696–701. doi:10.1021/es011081h.
Yamamoto, T., Yasuhara, A., Shiraishi, H., & Nakasugi, O. (2005). Bisphenol A in hazardous waste landfill leachates. Chemosphere, 42, 415–418. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00079-5.
Ying, G. G., & Kookana, R. S. (2005). Sorption and degradation of estrogen-like-endocrine disrupting chemicals in soil. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 2640–2645. doi:10.1897/05-074R.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TC., Shue, MF., Yeh, YL. et al. Bisphenol A occurred in Kao-Pin River and its tributaries in Taiwan. Environ Monit Assess 161, 135–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0733-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0733-4