Abstract
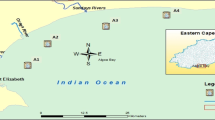
Bisphenol analogs (BPs) are widely used in industrial and commercial products and have been detected in surface water, sediment, sewage, and sludge. The presence of BPs in the natural environment poses threats to the aquatic ecosystem and human health. The concentration, distribution, seasonal variation, and risk assessment of BPA and BPA structural analogs including BPB, BPF, BPS, BPZ, BPAF, and BPAP in surface water and sediment during dry season and flood season in Luoma Lake and its inflow rivers in Jiangsu Province, China, were investigated in this study. The detection frequency of BPA and BPF was 100%. Although the use of BPA is restricted, BPA is still the dominant BPs in surface water and sediment. The concentration of BPs in surface water during flood season was higher than that in dry season. The concentrations of BPs in Fangting River, Zhongyun River, and Bulao River were higher than those in Luoma Lake. The average concentrations of BPs in surface water were in the order of BPA > BPF> BPS> BPB > BPZ > BPAF> BPAP. Compared with other studies, the concentration of BPs in Luoma Lake was moderate. There is no significant spatial distribution and difference in seasonal variation of BPs concentration in sediment (p > 0.05). Compared with other studies, the contamination of BPs in sediment of Luoma Lake was relatively low. Risk quotient (RQ) was used to evaluate the ecological risk of BPs in water environment, and the 17β estradiol equivalent (EEQ) method was used to estimate the estrogenic activity of BPs. The risk assessment showed no high ecological risk (RQ < 1.0) and estrogenic risk (EEQ < 1.0 ng/L) in dry season and flood season. The estimated RQ and EEQt indicated that the ecological and human health impacts were negligible in the short term.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Availability of data and materials will be available upon request.
References
Ali M, Jaghbir M, Salam M, Al-Kadamany G, Damsees R, Al-Rawashdeh N (2018) Testing baby bottles for the presence of residual and migrated bisphenol A. Environ Monit Assess 191:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7126-0
Barboza L, Cunha SC, Monteiro C, Fernandes JO, Guilhermino L (2020) Bisphenol A and its analogs in muscle and liver of fish from the North East Atlantic Ocean in relation to microplastic contamination. Exposure and risk to human consumers. J Hazard Mater 393:122419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122419
Catenza CJ, Farooq A, Shubear NS, Donkor KK (2021) A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues. Chemosphere 268:129273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129273
Chen D, Kannan K, Tan H, Zheng Z, Feng Y, Wu Y, Widelka M (2016) Bisphenol analogues other than BPA: environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity-a review. Environ Sci Technol 50:5438–5453. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05387
Cheng D, Liu X, Wang L, Gong W, Liu G, Fu W, Cheng M (2014) Seasonal variation and sediment-water exchange of antibiotics in a shallower large lake in North China. Sci Total Environ 476-477:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.010
Choi YJ, Lee LS (2017) Partitioning behavior of bisphenol alternatives BPS and BPAF compared to BPA. Environ Sci Technol 51:3725–3732. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b05902
Cunha SC, Fernandes JO (2010) Quantification of free and total bisphenol A and bisphenol B in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MD-GC/MS). Talanta 83:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.08.048
Dan L, Wu S, Xu H, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Shi L, Yao C, Liu Y, Cheng J (2017) Distribution and bioaccumulation of endocrine disrupting chemicals in water, sediment and fishes in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake: implications for ecological and human health risks. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 140:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.045
Dumitrascu M, Mares C, Petca RC, Sandru F, Popescu RI, Mehedintu C, Petca A (2020) Carcinogenic effects of bisphenol A in breast and ovarian cancers. Oncol Lett 20:282. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.12145
Eladak S, Grisin T, Moison D, Guerquin M-J, N'Tumba-Byn T, Pozzi-Gaudin S, Benachi A, Livera G, Rouiller-Fabre V, Habert R (2015) A new chapter in the bisphenol A story: bisphenol S and bisphenol F are not safe alternatives to this compound. Fertil Steril 103:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.11.005
European Commission (2019) Analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticide residues and analysis in food and feed. SANTE/12682/2019
Feng Y, Yin J, Jiao Z, Shi J, Li M, Shao B (2012) Bisphenol AF may cause testosterone reduction by directly affecting testis function in adult male rats. Toxicol Lett 211:201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.03.802
Feng Y, Jiao Z, Shi J, Li M, Guo Q, Shao B (2016) Effects of bisphenol analogues on steroidogenic gene expression and hormone synthesis in H295R cells. Chemosphere 147:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.081
Figueira V, Serra EA, Vaz-Moreira I, Brandao TR, Manaia CM (2012) Comparison of ubiquitous antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae populations isolated from wastewaters, surface waters and drinking waters. J Water Health 10:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2011.002
Gewurtz SB, Tardif G, Power M, Backus SM, Dove A, Dubé-Roberge K, Garron C, King M, Lalonde B, Letcher RJ, Martin PA, McDaniel TV, McGoldrick DJ, Pelletier M, Small J, Smyth SA, Teslic S, Tessier J (2021) Bisphenol A in the Canadian environment: a multimedia analysis. Sci Total Environ 755:142472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142472
González N, Cunha SC, Ferreira R, Fernandes JO, Marquès M, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2020) Concentrations of nine bisphenol analogues in food purchased from Catalonia (Spain): comparison of canned and non-canned foodstuffs. Food Chem Toxicol 136:110992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110992
Hercog K, Maisanaba S, Filipič M, Sollner-Dolenc M, Kač L, Žegura B (2019) Genotoxic activity of bisphenol A and its analogues bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF and their mixtures in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Sci Total Environ 687:267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.486
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Alba AR, Barcelo D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Herrero O, Aquilino M, Sánchez-ArgüelloP PR (2018) The BPA-substitute bisphenol S alters the transcription of genes related to endocrine, stress response and biotransformation pathways in the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). PLoS One 13:e193387. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193387
Hu Y, Yan X, Shen Y, Di M, Wang J (2019) Occurrence, behavior and risk assessment of estrogens in surface water and sediments from Hanjiang River, Central China. Ecotoxicology 28:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-2007-4
Huang GM, Tian XF, Fang XD, Ji FJ (2016) Waterborne exposure to bisphenol F causes thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 147:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.080
Huang Z, Zhao JL, Yang YY, Jia YW, Zhang QQ, Chen CE, Liu YS, Yang B, Xie L, Ying GG (2020) Occurrence, mass loads and risks of bisphenol analogues in the Pearl River Delta region, South China: urban rainfall runoff as a potential source for receiving rivers. Environ Pollut 263:114361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114361
IyIgUndoGdu I, UstUndaG A, Duydu Y (2020) Toxicological evaluation of bisphenol A and its analogues. Turk J Pharm Sci 17:457–462. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.galenos.2019.58219
Jin H, Zhu L (2016) Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 103:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.059
Kong M, Bu YQ, Zhang Q, Zhang SH, Xing LQ, Gao ZQ, Bi FZ, Hu GJ (2021) Distribution, abundance, and risk assessment of selected antibiotics in a shallow freshwater body used for drinking water, China. J Environ Manag 280:111738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111738
Kovačič A, Gys C, Kosjek T, Covaci A, Heath E (2019) Photochemical degradation of BPF, BPS and BPZ in aqueous solution: Identification of transformation products and degradation kinetics. Sci Total Environ 664:595–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.064
Krishnan AV, Stathis P, Permuth SF, Tokes L, Feldman D (1993) Bisphenol-A: an estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 132:2279–2286. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.132.6.8504731
Li Y, Yan H, Yu Y, Zou C, Tian L, Xin X, Zhang S, Li Z, Ma F, Ge RS (2021) Bisphenol B stimulates Leydig cell proliferation but inhibits maturation in late pubertal rats. Food Chem Toxicol 153:112248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112248
Liao C, Liu F, Moon HB, Yamashita N, Yun S, Kannan K (2012) Bisphenol analogues in sediments from industrialized areas in the United States, Japan, and Korea: spatial and temporal distributions. Environ Sci Technol 46:11558–11565. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303191g
Liu Y, Zhang S, Song N, Guo R, Chen M, Mai D, Yan Z, Han Z, Chen J (2017) Occurrence, distribution and sources of bisphenol analogues in a shallow Chinese freshwater lake (Taihu Lake): implications for ecological and human health risk. Sci Total Environ 599-600:1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.069
Liu Y, Su W, Zhu Y, Xiao L, Hu T (2020) Endocrine disrupting compounds in the middle and lower reaches of the Lhasa River Basin: occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 727:138694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138694
Liu D, Wu P, Zhao N, Nie S, Cui J, Zhao M, Jin H (2021a) Differences of bisphenol analogue concentrations in indoor dust between rural and urban areas. Chemosphere 276:130016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130016
Liu J, Zhang L, Lu G, Jiang R, Yan Z, Li Y (2021b) Occurrence, toxicity and ecological risk of bisphenol A analogues in aquatic environment - a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111481
Martínez-Ibarra A, Martinez-Razo LD, MacDonald-Ramos K, Morales-Pacheco M, Vázquez-Martínez ER, López-López M, Rodríguez Dorantes M, Cerbón M (2021) Multisystemic alterations in humans induced by bisphenol A and phthalates: experimental, epidemiological and clinical studies reveal the need to change health policies. Environ Pollut 271:116380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116380
Nomiri S, Hoshyar R, Ambrosino C, Tyler CR, Mansouri B (2019) A mini review of bisphenol A (BPA) effects on cancer-related cellular signaling pathways. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:8459–8467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04228-9
Pang Q, Li Y, Meng L, Li G, Luo Z, Fan R (2019) Neurotoxicity of BPA, BPS, and BPB for the hippocampal cell line (HT-22): an implication for the replacement of BPA in plastics. Chemosphere 226:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.177
Pastor-Belda M, Bastida D, Campillo N, Pérez-Cárceles MD, Motas M, Viñas P (2016) A study of the influence on diabetes of free and conjugated bisphenol A concentrations in urine: development of a simple microextraction procedure using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed 129:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.07.042
Qian Y, Jia X, Ding T, Yang M, Yang B, Li J (2021) Occurrence and removal of bisphenol analogues in wastewater treatment plants and activated sludge bioreactor. Sci Total Environ 758:143606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143606
Qiu W, Shao H, Lei P, Zheng C, Qiu C, Yang M, Zheng Y (2018) Immunotoxicity of bisphenol S and F are similar to that of bisphenol A during zebrafish early development. Chemosphere 194:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.125
Qiu W, Zhan H, Hu J, Zhang T, Xu H, Wong M, Xu B, Zheng C (2019) The occurrence, potential toxicity, and toxicity mechanism of bisphenol S, a substitute of bisphenol A: a critical review of recent progress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.114
Rochester JR, Bolden AL (2015) Bisphenol S and F: a systematic review and comparison of the hormonal activity of bisphenol A substitutes. Environ Health Perspect 123:643–650. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408989
Rosenmai AK, Dybdahl M, Pedersen M, Vugt-Lussenburg BMAV, Wedebye EB, Taxvig C, Vinggaard AM (2014) Are structural analogues to bisphenol a safe alternatives? Toxicol Sci 139:35–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfu030
Ruan T, Liang D, Song S, Song M, Wang H, Jiang G (2015) Evaluation of the in vitro estrogenicity of emerging bisphenol analogs and their respective estrogenic contributions in municipal sewage sludge in China. Chemosphere 124:150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.12.017
Si W, Cai Y, Liu J, Shen J, Chen Q, Chen C, Ning L (2019) Investigating the role of colloids on the distribution of bisphenol analogues in surface water from an ecological demonstration area, China. Sci Total Environ 673:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.142
Song S, Song M, Zeng L, Wang T, Liu R, Ruan T, Jiang G (2014) Occurrence and profiles of bisphenol analogues in municipal sewage sludge in China. Environ Pollut 186:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.023
Ullah A, Pirzada M, Jahan S, Ullah H, Turi N, Ullah W, Siddiqui MF, Zakria M, Lodhi KZ, Khan MM (2018) Impact of low-dose chronic exposure to bisphenol A and its analogue bisphenol B, bisphenol F and bisphenol S on hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular activities in adult rats: a focus on the possible hormonal mode of action. Food Chem Toxicol 121:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.08.024
van Leeuwen SP, Bovee TF, Awchi M, Klijnstra MD, Hamers AR, Hoogenboom RL, Portier L, Gerssen A (2019) BPA, BADGE and analogues: a new multi-analyte LC-ESI-MS/MS method for their determination and their in vitro (anti)estrogenic and (anti)androgenic properties. Chemosphere 221:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.189
Vogel SA (2009) The politics of plastics: the making and unmaking of bisphenol a “safety”. Am J Public Health 99(Suppl 3):S559–S566. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2008.159228
Wang Z, Liu H, Liu S (2017) Low-dose bisphenol A exposure: a seemingly instigating carcinogenic effect on breast cancer. Adv Sci (Weinh) 4:1600248. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201600248
Wang C, He J, Xu T, Han H, Zhu Z, Meng L, Pang Q, Fan R (2021) Bisphenol A(BPA), BPS and BPB-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis mediated by mitochondria in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111299
Xing L, Zhang Q, Sun X, Zhu H, Zhang S, Xu H (2018) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in surface water and sediment from a shallow freshwater Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 636:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.320
Xu W, Yan W, Huang W, Miao L, Zhong L (2014) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the Pearl River Delta and coastal environment: sources, transfer, and implications. Environ Geochem Health 36:1095–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9618-3
Yamazaki E, Yamashita N, Taniyasu S, Lam J, Lam PK, Moon HB, Jeong Y, Kannan P, Achyuthan H, Munuswamy N, Kannan K (2015) Bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues including BPS and BPF in surface water samples from Japan, China, Korea and India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.029
Yan Z, Liu Y, Yan K, Wu S, Han Z, Guo R, Chen M, Yang Q, Zhang S, Chen J (2017) Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk. Chemosphere 184:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.010
Yang Y, Lu L, Zhang J, Yang Y, Wu Y, Shao B (2014) Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenols in environmental water and solid samples by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1328:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.12.074
Yue S, Yu J, Kong Y, Chen H, Mao M, Ji C, Shao S, Zhu J, Gu J, Zhao M (2019) Metabolomic modulations of HepG2 cells exposed to bisphenol analogues. Environ Int 129:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.008
Zhang L, Fang P, Yang L, Zhang J, Wang X (2013a) Rapid method for the separation and recovery of endocrine-disrupting compound bisphenol AP from wastewater. LANGMUIR 29:3968–3975. https://doi.org/10.1021/la304792m
Zhang L, Pan F, Liu X, Yang L, Jiang X, Yang J, Shi W (2013b) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as sorbent for recovery of endocrine disrupting compound-bisphenol F from wastewater. Chem Eng J 218:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.046
Zhang P, Ali Shah SA, Gao F, Sun H, Cui Z, Cheng J, Zhang J (2019a) Latent curing epoxy systems with reduced curing temperature and improved stability. Thermochim Acta 676:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.03.022
Zhang H, Zhang Y, Li J, Yang M (2019b) Occurrence and exposure assessment of bisphenol analogues in source water and drinking water in China. Sci Total Environ 655:607–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.053
Zhao X, Qiu W, Zheng Y, Xiong J, Gao C, Hu S (2019) Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues, parabens and their metabolites in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.083
Zhao X, Zhang H, Chen ZL, Wang XC, Shen JM (2020) Spatial and temporal distributions of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from the Lanzhou section of the Yellow River, China. Arab J Geosci 13:1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06122-y
Zhou LJ, Li J, Zhang Y, Kong L, Jin M, Yang X, Wu QL (2019) Trends in the occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in shallow lakes in the lower-middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109511
Zhou N, Liu Y, Cao S, Guo R, Ma Y, Chen J (2020) Biodegradation of bisphenol compounds in the surface water of Taihu Lake and the effect of humic acids. Sci Total Environ 723:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138164
Funding
This study is supported by the Environmental Protection Research Project of Jiangsu Province (2018002). This research work is supported by State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Monitoring and Analysis for Organic Pollutants in Surface Water, Jiangsu Environmental Monitoring Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiuxu Wang, data analysis, writing (original draft); Qiyan Feng, funding acquisition, resources, and supervision; Guanjiu Hu, funding acquisition, resources, and supervision; Xueqiang Zhu, writing (review and editing) and supervision; Yuan Zhang, supervision; Zhanqi Gao, supervision; Qingjun Meng, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hongwen Sun
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 41.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ., Zhang, Y., Feng, Q. et al. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of bisphenol analogues in Luoma Lake and its inflow rivers in Jiangsu Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 1430–1445 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15711-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15711-7