Abstract
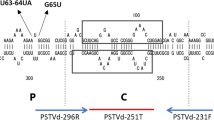
Potato spindle tuber viroid (PSTVd) is an important pathogen that severely affects tomato and potato production. Several Solanaceae species are naturally and experimentally susceptible to PSTVd, implying that Solanaceae weeds can be a reservoir of PSTVd through infected seeds in crop fields. To determine whether PSTVd is seed-transmissible in solanaceous weed species, we examined seed transmission rates and localization of PSTVd in the reproductive organs of Solanum nigrum and Physalis angulata. The results revealed that the seed transmission rate of PSTVd was 0%–50% and 89.7%–100% in S. nigrum and P. angulata, respectively, suggesting that these weed species act as reservoirs of PSTVd, and their seed seems to be an important source of PSTVd. While the seed transmission rate in S. nigrum was 0%–8% for PSTVd isolate VP35, it was 10.5%–50% for isolate VP72-1. In situ hybridization analysis showed that isolate VP72-1 (but not VP35) successfully invaded the ovule and embryo of S. nigrum, suggesting that the transmission rate in S. nigrum might depend on the distribution pattern of PSTVd in ovules and embryos. This is the first report to show the distribution patterns of a viroid in the reproductive organs of solanaceous weed species during their developmental stages.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not relevant.
References
Behjatnia, S. A. A., Dry, I. B., Krake, L. R., Conde, B. D., Connelly, M. I., Randles, J. W., & Rezaian, M. A. (1996). New potato spindle tuber viroid and tomato leaf curl geminivirus strains from a wild Solanum sp. Phytopathology, 86, 880–886. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-86-880
Chaudhary, P., Kumari, R., Singh, B., Hallan, V., & Nagpal, A. K. (2019). First report of potato virus M, potato virus Y and cucumber mosaic virus infection in Solanum nigrum in India. Journal Plant Pathology, 101, 419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-0194-8
Di Serio, F., Li, S. F., Pallás, V., Owens, R. A., Randles, J. W., Sano, T., Verhoeven, J. T. J., Vidalakis, G., & Flores, R. (2017). Viroid taxonomy. In A. Hadidi, R. Flores, J. Randles, & P. Palukaitis (Eds.), Viroids and Satellites (pp. 135–148). Academic Press
Hosokawa, M., Matsushita, M., Uchida, H., & Yazawa, S. (2006). Direct RT-PCR method for detecting two chrysanthemum viroids using minimal amounts of plant tissue. Journal of Virological Methods, 131, 28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.07.001
Mackie, A. E., Rodoni, B. C., Barbetti, M. J., McKirdy, S. J., & Jones, R. A. C. (2016). Potato spindle tuber viroid: Alternative host reservoirs and strain found in a remote subtropical irrigation area. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 145, 433–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0857-2
Matsushita, Y., & Tsuda, S. (2014). Distribution of potato spindle tuber viroid in reproductive organs of petunia during its developmental stages. Phytopathology, 104(9), 964–969. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-10-13-0294-R
Matsushita, Y., & Tsuda, S. (2016). Seed transmission of potato spindle tuber viroid, tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid, tomato apical stunt viroid, and Columnea latent viroid in horticultural plants. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 145, 1007–1011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0868-z
Matsushita, Y., Usugi, T., & Tsuda, S. (2011). Distribution of tomato chlorotic dwarf viroid in floral organs of tomato. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 130, 441–447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9766-6
Matsushita, Y., Yanagisawa, H., & Sano, T. (2018). Vertical and horizontal transmission of pospiviroids. Viruses, 10(2), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120706
Matsushita, Y., Yanagisawa, H., Khiutti, A., Mironenko, N., Ohto, Y., & Afanasenko, O. (2021). Genetic diversity and pathogenicity of potato spindle tuber viroid and chrysanthemum stunt viroid isolates in Russia. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 161, 529–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02339-z
Mironenko, N., Khiutti, A., Kyrova, E., Lashina, N., & Afanasenko, O. (2022). Solanum nigrum L. is a potato spindle tuber viroid reservoir. Proceedings on Applied Botany, Genetics and Breeding, 183(3), 194–203. https://doi.org/10.30901/2227-8834-2022-3-194-203
Sager, R., & Lee, J.-Y. (2014). Plasmodesmata in integrated cell signalling insights from development and environmental signals and stresses. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65(22), 6337–6358. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru365
Sainte-Marie, G. (1962). A paraffin embedding technique for studies employing immunofluorescence. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, 10(3), 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1177/10.3.250
Singh, R. P. (1973). Experimental host range of the potato spindle tuber ‘virus.’ American Potato Journal, 50, 111–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857207
Škarić, D. (2017). Viroid Biology. In A. Hadidi, R. Flores, J. W. Randles, & P. Palukatis (Eds.), Viroids and Satellites (pp. 53–61). United Kingdom.
Tsushima, T., & Sano, T. (2018). A point-mutation of Coleus blumei viroid 1 switches the potential to transmit through seed. Journal of General Virology, 99(3), 393–401. https://doi.org/10.1099/jgv.0.001013
Verhoeven, J. T. J., Botermans, M., & Roenhorst, J. W. (2009). First report of potato spindle tuber viroid in cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana) from Turkey and Germany. Plant Disease, 93(3), 316. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-93-3-0316A
Verhoeven, J. T. J., Hammond, W. R., & Stancanelli, G. (2017). Economic Significance of Viroids in Ornamental Crops. In A. Hadidi, R. Flores, J. W. Randles, & P. Palukatis (Eds.), Viroids and Satellites (pp. 27–38). Academic Press/Elsevier: United Kingdom.
Ward, L. I., Tang, J., Veerakone, S., Quinn, B. D., Harper, S. J., Delmiglio, C., & Clover, G. R. G. (2010). First report of Potato spindle tuber viroid in cape gooseberry (Physalis peruviana) in New Zealand. Plant Disease, 94, 479. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-94-4-0479A
Werner, D., Gerlitz, N., & Stadler, R. (2011). A dual switch in phloem unloading during ovule development in Arabidopsis. Protoplasma, 248(1), 225–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-010-0223-8
Yanagisawa, H., Matsushita, Y., Khiutti, A., Mironenko, N., Ohto, Y., & Afanasenko, O. (2021). Occurrence and distribution of viruses infecting potato in Russia. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 73, 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13476
Zhong, X., Archual, A. J., Amin, A. A., & Ding, B. A. (2008). Genomic map of viroid RNA motifs critical for replication and systemic trafficking. The Plant Cell, 20(1), 35–47. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.056606
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Y. Narita, K. Nakata, and Y. Matsumura for preparing the experimental materials and Y. Tomitaka for the statistical analysis. This study was partially supported by the Strategic International Collaborative Research Project (No. J008837) promoted and administered by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, Tokyo, Japan.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Strategic International Collaborative Research Project (No. J008837) promoted and administered by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed to the conception and design of this study. Matsushita and Kubota performed data collection and analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Matsushita. Both authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita, Y., Kubota, K. Seed transmission of potato spindle tuber viroid and its distribution in reproductive organs in Solanaceae weed species. Eur J Plant Pathol 167, 315–322 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02707-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02707-x