Abstract
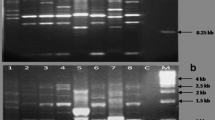
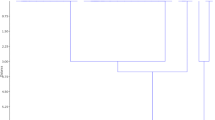
Bacterial leaf blight caused (BLB) by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) is the most serious biotic constraint of rice in Udham Singh Nagar (U.S. Nagar), India. We have experienced severe BLB outbreaks, causing total crop failure during 2007–2010. The severity of losses incurred due to BLB in U.S. Nagar necessitates the development of an ecology-conscious, effective and durable management strategy. Our interests here were focused to obtain information on the haplotypic and pathogenic variability of Xoo to develop effective breeding strategy for BLB resistance. Our results indicate that the currently existing population of Xoo in U.S. Nagar is highly virulent and genetically diverse. Twenty one haplotypes were detected among a collection of 193 strains by each of the PCR technique used i.e. rep-PCR and IS-PCR. The high value of total haplotypic diversity (HT =0.79) reflected the genetic heterogeneity of Xoo population infecting popular varieties. Strains responsible for severe BLB outbreaks were grouped into eight distinct lineages with significant bootstrap values (p > 75). Virulence assay revealed the presence of 11 pathotypes. The interaction of lines with strains was found significant (p < 0.01) confirming the pathogenic specialization of Xoo in U.S. Nagar. Most of the single major resistance genes used in rice breeding program at International Rice research Institute (IRRI) was defeated by Xoo strains, at the same time; effectiveness of Xa21 to all the pathotypes is encouraging. The potential of Xa21 alone or in combination with xa13 and xa5 could be exploited for pyramiding into well-adapted rice cultivars for the effective management of the pathogen in this region. This is the first report on the population structure of Xoo in U.S. Nagar, India.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, T. B., Vera Cruz, C. M., Zhang, Q., Nelson, R. J., Skinner, D. Z., Mew, T. W., et al. (1995). Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Asia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61, 966–971.
Adhikari, T. B., Basnyat, R. C., Mew, T. W., et al. (1999a). Virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae on rice lines containing single resistance genes and gene combinations. Plant Disease, 83, 46–50.
Adhikari, T. B., Mew, T. W., Leach, J. E., et al. (1999b). Genotypic and pathotypic diversity in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Nepal. Phytopathology, 89, 687–694.
Ardales, E. Y., Leung, H., Vera Cruz, C. M., Mew, T. W., Leach, J. E., Nelson, R. J., et al. (1995). Hierarchical analysis of spatial variation of the rice bacterial blight pathogen across diverse agroecosystems in the Philippines. Phytopathology, 86(3), 241–252.
Caten, C. E. (1987). The concept of race in plant pathology. In M. S. Wolfe & C. E. Caten (Eds.), Populations of plant pathogens: Their dynamics and genetics (pp. 21–37). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Chen, X. M., Line, R. F., Leung, H., et al. (1993). Relationship between virulence variation and DNA polymorphism in Puccinia striiformis. Phytopathology, 83, 1489–1497.
Choi, J. E., Kang, H. K., Lee, D. G., et al. (1996). Classification of Korean strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae on the basis of their virulence to Korean, Japanese, and IRRI differential varieties. Korean Journal of Plant Pathology, 12, 202–208.
Collard, B. C. Y., Vera Cruz, C. M., McNally, K. L., Virk, P. S., Mackill, D. J., et al. (2008). Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: current status and future considerations. International Jounal of Plant Genomics. doi:10.1155/2008/524847.
Cottyn, B., & Mew, T. (2004). Bacterial blight of rice. In: Encyclopedia of Plant and Crop Science. Marcel Dekker, Inc., doi:10.1081/E-EPCS 120010586.
De Bruijn, F. L. (1992). Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti strains and other soil bacteria. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 58, 2180–2187.
Devadath, S. (1983). A strain of oryzae barthii an African wild rice immune to bacterial blight of rice. Current Science, 52, 27–28.
Dinh, H. D., Oanh, N. K., Toan, N. D., Du, P., Loan, L. C., et al. (2008). Pathotype profile of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains from the rice ecosystem in Cuulong Rever Delta. Omonrice, 16, 34–40.
Finckh, M. R., & Nelson, R. J. (1999). Phylogenetic and pathotypic analysis of rice bacterial blight Race 3. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 105, 743–751.
George, M. L. C., Bustaman, M., Cruz, W. T., Leach, J. E., Nelson, R. J., et al. (1997). Movement of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Southeast Asia detected using PCR-based DNA fingerprinting. Phytopathology, 87, 302–309.
Gnanamanickam, S. S., Priyadarisini, V. B., Narayanan, P. V., Kavitha, S., et al. (1999). An overview of bacterial blight disease of rice and strategies for its management. Current Science, 77(11), 1435–1443.
Gonzalez, C., Szurek, B., Manceau, C., Mathieu, T., Sere, Y., Verdier, V., et al. (2007). Molecularand pathotypic characterization of new Xanthomonas oryzae strains from West Africa. Molecular Plant Microbe, 20, 534–546.
Gupta, V. S., Rajebhosale, M. D., Sodhi, M., Singh, S., Gnanamanickam, S. S., Dhaliwal, H. S., et al. (2001). Assessment of genetic variability and strain identification of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae using RAPD-PCR and IS1112- based PCR. Current Science, 80(8), 1043–1048.
Hassankiadeh, A. A., Kazempour, M. N., Dehkaei, F. P., Rahimian, H., et al. (2011). Detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae from rice seeds through bio-pcr technique in paddy fields of guilan province in Northern Iran. Agricultura Tropica et Subtropica, 44(2), 71–76.
Hulton, C. S. J., Higgins, C. F., Sharp, P. M., et al. (1991). ERIC Sequences: a novel family of repetitive elements in the genomes of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria. Molecular Microbiology, 5, 825–834.
Iyer-Pascuzzi, A. S., & McCouch, S. R. (2004). The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions, 17, 1348–1354.
Iyer-Pascuzzi, A. S., & McCouch, S. R. (2007). Recessive resistance genes and the Oryza sativa-Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae pathosystem. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 20(7), 731–739.
Jalaluddin, M., Yamamoto, T., Nakai, H., Tsuyumu, S., et al. (2005). Pathogenic variability and DNA fingerprinting of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae from Bangladesh. Sabrao Journal of Breeding and Genetics, 37(1), 1–11.
Jeung, J. U., Heu, S. G., Shin, M. S., Vera Cruz, C. M., Jena, K. K., et al. (2006). Dynamics of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Populations in Korea and Their Relationship to Known Bacterial Blight Resistance Genes. Phytopathology, 96, 867–876.
Jyufuku, S., Furuya, N., Goto, T., Tsuchiya, K., Yoshimura, A., et al. (2009). Pathogenic and Genetic Diversity in Asian Strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Journal Faculty Agriculture, 4(1), 19–23.
Kameswara, K. R., Lakshminarasub, M., Jena, K. K., et al. (2002). DNA markers and marker-assisted breeding for durable resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Biotechnology Advances, 20, 33–47.
Kauffman, H. E., Reddy, A. P. K., Hsieh, S. P. Y., Merca, S. D., et al. (1973). An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Disease Reporter, 57, 537–541.
Ladha, D. L., & Rabindran, R. (2012). Molecular Variability in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae isolates of Tamil Nadu. Indian Journal of Plant Protection, 40(2), 123–128.
Lang, J. M., Hamilton, J. P., Diaz, M. G. Q., Van Sluys, M. A., Burgos, M. R. G., Vera Cruz, C. M., et al. (2010). Genomics-based diagnostic marker development for Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and X. oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant Disease, 94, 311–319.
Leach, J. E., Rhoads, M. L., Vera Cruz, C. M., White, F. F., Mew, T. W., Leung, H., et al. (1992). Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae within a repetitive DNA element. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 58, 2188–2195.
Lee, S. W., Choi, S. H., Han, S. S., Lee, D. G., Lee, B. Y., et al. (1999). Distribution of Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae strains virulent to Xa21 in Korea. Phytopathology, 89, 928–933.
Lee, S. W., Han, S. W., Sririyanum, M., Park, C. J., Seo, Y. U., Ronald, P. C., et al. (2009). A Type I–secreted, sulfated peptide triggers XA21-mediated innate immunity. Science, 326, 850–853.
Leung, H., Nelson, R. J., Leach, J. E., et al. (1993). Population structure of plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. Advances in Plant Pathology, 10, 157–250.
Leung, H., Wu, J., Liu, B., Bustaman, M., Sridhar, R., Singh, K., Redona, E.D., Quang, V.D., Zheng, K., Bernardo, M., Wang, G., Leach, J., Choi, I.R., Vera Cruz, C.M., et al. (2004). Sustainable disease resistance in rice: current and future strategies. In: Fischer, T., Turner, N., Angus, J., et al. (Eds.), Proc. 4th International Crop Science Congress. Brisbane, Australia, 26 September–1 October (Published on CD-ROM).
Liu, H. X., Liu, F. Q., Hu, B. S., Yang, W. F., Chen, Z. Y., Xu, Z. G., et al. (2004). Virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae on rice Near-isogenic lines with single resistance gene and pyramiding lines in China. Agricultural Sciences in China, 3, 764–769.
Liu, H., Yang, W., Hu, B., Liu, F., et al. (2007). Virulence analysis and race classification of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae in China. Journal of Phytopathology, 155, 129–135.
Lore, J.S., Vikal, Y., Hunjan, M.S., Goel, R.K., Bharaj, T.S., Raina, G.L., et al. (2011). Genotypic and pathotypic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae, the cause of b a c t e r i a l blight of rice in Punjab State of India. Journal of Phytopathology, 1-9.
Louws, F. J., Dennis, W., Christ, F., et al. (1994). Specific genomic fingerprints of phytopathogenic xanthomonas and pseudomonas pathovars and strains generated with repetitive sequences and PCR. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60(7), 2286–229.
Mani, S.C., Agrawal, P.K., Singh, D.K., et al. (2011). Status Paper on Rice in Uttarakhand, (pp. 1-29) Directorate of Rice Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad.
Mannan, S., Malik, S. A., Ahamad, I., Mirza, J. I., Akhtar, M. A., et al. (2009). Studies on virulence reactions of local strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41(1), 391–402.
Mew, T. W. (1987). Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 25, 359–382.
Mew, T. W., Bridge, J., Hibino, H., Bonman, J. M., & Merca, S. D. (1988). Rice pathogens of quarantine importance. In Rice seed health (pp. 101–115). Los Banos: The International Rice Research Institute.
Mew, T. W., Vera Cruz, C. M., Medalla, E. S., et al. (1992). Changes in race frequency of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in response to rice cultivars planted in the Philippines. Plant Disease, 76, 1029–1032.
Mundt, C. C., Nieva, L. P., Vera Cruz, C. M., et al. (2001). Variation for aggressiveness within and between lineages of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Pathology, 51(2), 163–168.
Nayak, D., Bose, L. K., Singh, U. D., Singh, S., Nayak, P., et al. (2008). Measurement of genetic diversity of virulence in populations of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in India. Communications in Biometry and Crop Science, 3(1), 16–28.
Nei, M. (1973). Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided population. USA: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
Nelson, R. J., Baraoidan, M. R., Vera Cruz, C. M., Yap, I. V., Leach, J. E., Mew, T. W., et al. (1994). Relationship between phylogeny and pathotypes for the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60, 3275–3283.
Niño-Liu, D. O., Ronald, P. C., Bogdanove, A. J., et al. (2006). Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Molecular Plant Pathology, 7(5), 303–324.
Noda, T., Yamamoto, T., Kaku, H., Horino, O., et al. (1996). Geographical distribution of pathogenic races of Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae in Japan in 1991 and 1993. Annals of the Phytopathological Society of Japan, 62, 549–553.
Noda, T., Li, C., Li, J., Ochiai, H., Ise, K., Kaku, H., et al. (2001). Pathogenic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains from Yunnan province, China. JARQ, 35(2), 97–103.
Ntsys PC version 2.11 s; Rohlf FJ, 2000 NTSYS-pc Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System Version 2.1. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York, USA.
Ochiai, H., Horino, O., Miyajima, K., Kaku, H., et al. (2000). Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains from Sri Lanka. Phytopathology, 90, 415–421.
Raymundo, A. K., Briones, A. M., Ardales, E. Y., Perez, M. T., Fernandez, L. C., Leach, J. F., et al. (1999). Analysis of DNA polymorphism and virulence in Philippine strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant Disease, 83, 434–440.
Reddy, A.P.K. (1980). Report on bacterial leaf blight epidemic of rice in Punjab. All India Coordinate Rice Improvement Project, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, India (pp.1-30).
Sakthivel, N., Mortensen, C. N., Mathur, S. B., et al. (2001). Detection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in artificially inoculated and naturally infected rice seeds and plants by molecular techniques. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 435–441.
Shahrestani, A. T., Kazempour, M. N., Ebadie, A. A., Elahinia, S. A., et al. (2012). Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice fields of Guilan Province (Iran) using RAPD markers. Agricultura Tropica Et Subtropica, 45(2), 60–65.
Shanti, M. L., Varma, C. M. K., Premalatha, P., Devi, G. L., Zehr, U., Freeman, W., et al. (2010). Understanding the bacterial blight pathogen combining pathotyping and molecular marker studies. International Journal of Plant Pathology, 1(2), 58–68.
Shanty, M. L., George, M. L. C., Vera Cruz, C. M., Bernardo, M. A., Nelson, R. J., Leung, H., et al. (2001). Identification of resistance genes effective against rice bacterial blight pathogen in eastern India. Plant Disease, 85(5), 506–512.
Singh, S., Sidhu, J. S., Huang, N., Vikal, Y., Li, Z., Brar, D. S., et al. (2001). Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes (xa5, xa13 and Xa21) using marker-assisted selection into indica rice cultivar PR106. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 102(6), 1011–1015.
Sneath, P. H. A., & Sokal, R. R. (1973). Numerical taxonomy. San Francisco: W.H. freeman and Co.
Song, W. Y., Wang, G. L., Chen, L. L., Kim, H. S., Pi, L. Y., Holsten, T., et al. (1995). A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science, 270, 1804–1806.
Sundaram, R. M., Vishnupriya, M. R., Biradar, S. K., Laha, G. S., Shobharani, N., Sarma, M. P., et al. (2008). Marker assisted introgression of bacterial blight resistance Sambha Mahsuri, an elite indica rice variety. Euphytica, 160, 411–422.
Sundaram, R. M., Vishnupriya, M. R., Laha, G. S., Rani, N. S., Rao, P. S., Balachandran, S. M., et al. (2009). Introduction of bacterial blight resistance into Triguna, a high yielding, mid-early duration rice variety. Biotechnology Journal, 4, 400–407.
Valérie Verdier, V., Vera Cruz, C., Leach, J. E., et al. (2011). Controlling rice bacterial blight in Africa: needs and prospects. Journal of Biotechnology. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.09.020.
Vera Cruz, C. M., Ardales, E. Y., Skinner, D. Z., Talag, J., Nelson, R. J., Louws, F. J., et al. (1996). Measurement of haplotypic variation in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae within a single field by rep- PCR and RFLP analysis. Phytopathology, 86(12), 1352–1359.
Vera Cruz, C. M., Bai, J., Leung, I., Nelson, H., Mew, R. J., Leach, J. E., et al. (2000). Predicting durability of a disease resistance gene based on an assessment of the fitness loss and epidemiological consequences of avirulence gene mutation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(25), 13500–13505.
Versalovic, J., Koeuth, T., Lupski, J. R., et al. (1991). Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Research, 19, 406–409.
Wang, G. L., Song, W. Y., Ruan, D. L., Sideris, S., Ronald, P. C., et al. (1996). The cloned gene, Xa21, confers resistance to multiple Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains in transgenic plants. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 9, 850–855.
Wang, C., Wen, G., Lin, X., Liu, X., Zhang, D., et al. (2009). Identification and fine mapping of new bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa31 (t) in rice. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 123, 235–240.
White, F. F., & Yang, B. (2009). Host and pathogen factors controlling the rice- Xanthomonas oryzae interaction. Plant Physiology, 150, 1677–1686.
Yap, I. V., & Nelson, R. J. (1996). WinBoot: A program for performing bootstrap analysis of binary data to determine the confidence limits of UPGMA-based dendrograms (IRRI Disc. Ser. No. 14). Manila: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Vice Chancellor, G. B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar, India for providing the necessary facilities
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Singh, B. & Kumar, J. DNA typing and virulence determination of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae population for the management of bacterial leaf blight of rice in Udham Singh Nagar, India. Eur J Plant Pathol 138, 847–862 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0358-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0358-5