Abstract
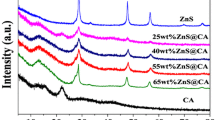
A facile and cost-effective hydrothermal followed by precipitation method is employed to synthesize visible light-driven ZnS-Ag ternary composites supported on carbon aerogel (CA). Extensive studies were conducted on the structural, morphological, and optical properties, confirming the successful formation of ternary nanocomposites. The obtained results evidently demonstrate the successful loading of ZnS and Ag onto the surface of the CA. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis revealed that ZnS and Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) were uniformly distributed on the surface of the CA with an average diameter of 18 nm. The biomass-derived CA, containing a hierarchical porous nano-architecture and an abundant number of –NH2 functional groups on the surface, can greatly prevent the agglomeration, stability and reduce particle size. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis results indicated specific surface areas of 4.62 m2 g−1 for the CA, 48.50 m2 g−1 for the CA/ZnS composite, and 62.62 m2 g−1 for the CA/ZnS-Ag composite. These values demonstrate an increase in surface area upon the incorporation of ZnS and Ag into the CA matrix. Under visible light irradiation, the synthesized CA/ZnS-Ag composites displayed remarkably improved photodegradation efficiency of methylene blue (MB). Among the tested samples, the CA/ZnS-Ag composites exhibited the highest percentage of photodegradation efficiency, surpassing ZnS, CA, and CA/ZnS. The obtained percentages of degradation efficiency for CA, ZnS, CA/ZnS, and CA/ZnS-Ag composites were determined as 26.60%, 52.12%, 68.39%, and 98.64%, respectively. These results highlight the superior photocatalytic performance of the CA/ZnS-Ag composites in the degradation of MB under visible light conditions. The superior efficiency of the CA/ZnS-Ag composite can be attributed to multiple factors, including its elevated specific surface area, inhibition of electron–hole pair recombination, and enhanced photon absorption within the visible light spectrum. The CA/ZnS-Ag composites displayed consistent efficiency over multiple cycles, confirming their stable performance, reusability, and enduring durability, thereby showcasing the robust nature of this composite material.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Aruljothi, C., Balaji, P., Vaishnavi, E., Pazhanivel, T., & Vasuki, T. (2023). Magnetic recyclable CuFe2O4/rGO nanocomposite for the degradation of tetracycline under sunlight irradiation. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 98(8), 1908–1917. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.7408
Aydoghmish, S. M., Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi, S. A., & Saffar-Teluri, A. (2019). Facile synthesis and investigation of NiO–ZnO–Ag nanocomposites as efficient photocatalysts for degradation of methylene blue dye. Ceramics International, 45(12), 14934–14942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.229
Banat, G. B. F., & Abu, H. M. (2023). Photoelectrochemical advanced oxidation processes for simultaneous removal of antibiotics and heavy metal ions in wastewater using 2D-on-2D WS2@CoFe2O4 heteronanostructures. Environmental Pollution, 339, 122753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122753
Bharath, G., Hai, A., Kiruthiga, T., Rambabu, K., Sabri, M. A., Park, J., et al. (2022). Fabrication of Ru–CoFe2O4/RGO hierarchical nanostructures for high-performance photoelectrodes to reduce hazards Cr(VI) into Cr(III) coupled with anodic oxidation of phenols. Chemosphere, 299, 134439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134439
Bharath, G., Rambabu, K., Alqassem, B., Morajkar, P. P., Abu Haija, M., Nadda, A. K., et al. (2023). Fabrication of gold nanodots decorated on 2D tungsten sulfide (Au-WS2) photoanode for simultaneous oxidation of phenol and arsenic (III) from industrial wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 456, 141062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.141062
Bhunia, S. K., & Jana, N. R. (2014). Reduced graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle composite as visible light photocatalyst for degradation of colorless endocrine disruptors. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 6(22), 20085–20092. https://doi.org/10.1021/am505677x
Deng, J., Gu, Z., Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Tong, Y., Meng, F., et al. (2023). Efficient purification of graphite industry wastewater by a combined neutralization-coagulation-flocculation process strategy: Performance of flocculant combinations and defluoridation mechanism. Separation and Purification Technology, 326, 124771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124771
Dixit, N., & Soni, H. P. (2014). Tuning optical properties of ZnS nanoparticles in micellar medium at different pH. Superlattices and Microstructures, 65, 344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2013.11.018
Fan, S., Chen, J., Tian, L., Fan, C., Xu, W., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Construction of a recyclable chitosan-based aerogel-supported TiO2 catalyst for treating high-concentration surfactants. Composites Part b: Engineering, 251, 110475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110475
Fan, T., Fu, T., Xu, Q., & Gjoni, G. (2022). Research on the purification of environmental pollution by biomaterials and its treatment methods in the development of rural cultural and creative industries. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications, 2022, e1594081. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1594081
Fatnassi, A., Cammarano, C., Oliviero, E., Hulea, V., & Brun, N. (2022). Carbon-aerogel-supported noble-metal nanoparticles as hydrogenation catalysts. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 5(10), 14227–14234. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.2c03313
Feng, Y., Feng, N., Zhang, G., & Du, G. (2013). One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of ZnS-reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic properties. CrystEngComm, 16(2), 214–222. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE41423J
Gong, H., Hajizadeh, S., Liu, W., & Ye, L. (2021). Imprinted polymer beads loaded with silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 4(3), 2829–2838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00045
Govarthanan, M., Selvankumar, T., Manoharan, K., Rathika, R., Shanthi, K., Lee, K.-J., et al. (2014). Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using panchakavya, an Indian traditional farming formulating agent. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 9, 1593–1599. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S58932
Haripriyan, U., Arun, J., Gopinath, K. P., Mythili, R., Kim, W., & Govarthanan, M. (2022). A mini-review on innovative strategies for simultaneous microbial bioremediation of toxic heavy metals and dyes from wastewater. Archives of Microbiology, 205(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03367-x
Jeyaram, J., Varadharajan, K., Singaram, B., & Rajendhran, R. (2017). Optical, photoconducting, thermal and anisotropic mechanical behaviours of Benzimidazolium salicylate single crystals. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 2(4), 445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.09.004
Jin, Y., Wu, M., Zhao, G., & Li, M. (2011). Photocatalysis-enhanced electrosorption process for degradation of high-concentration dye wastewater on TiO2/carbon aerogel. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168(3), 1248–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.026
Kameli, S., & Mehrizad, A. (2019). Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of Ag-ZnS/rGO and its utilization in photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light irradiation. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 95(2), 512–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12998
Kandasamy, M., Vasudevan, V., Thangavelu, P., Parasuraman, B., Govindasamy, M., Habila, M. A., et al. (2023). Synthesis of a hybrid phase FeCoWO4/g-C3N4 heterojunction composite for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of MB under visible light. ChemistrySelect, 8(45), e202302715. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202302715
Kim, W. J., Pradhan, D., Min, B.-K., & Sohn, Y. (2014). Adsorption/photocatalytic activity and fundamental natures of BiOCl and BiOClxI1x prepared in water and ethylene glycol environments, and Ag and Au-doping effects. Applied Catalysis b: Environmental, 147, 711–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.008
Krishnan, R. Y., Manikandan, S., Subbaiya, R., Karmegam, N., Kim, W., & Govarthanan, M. (2023). Recent approaches and advanced wastewater treatment technologies for mitigating emerging microplastics contamination—A critical review. Science of the Total Environment, 858, 159681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159681
Li, J.-X., Zhang, R.-L., Pan, Z.-J., Liao, Y., Xiong, C.-B., Chen, M.-L., et al. (2021). Preparation of CdS@C photocatalyst using phytoaccumulation Cd recycled from contaminated wastewater. Frontiers in Chemistry, 9, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.717210
Li, X., Yang, S., Sun, J., He, P., Xu, X., & Ding, G. (2014). Tungsten oxide nanowire-reduced graphene oxide aerogel for high-efficiency visible light photocatalysis. Carbon, 78, 38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.06.034
Liu, R., Yuan, J., Huang, L., Yu, S., Zhao, Y., Duan, C., & Jiang, H. (2024). Synergistic enhancement of coal slurry water sedimentation and dehydration process using PDMDAAC/PAM. Journal of Cleaner Production, 434, 140160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140160
Liu, X.-D., Chen, K., Ma, S., Hao, Z.-H., Liang, S., Zhou, L., & Wang, Q.-Q. (2019b). Synthesis of Au/CdSe Janus nanoparticles with efficient charge transfer for improving photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Nanoscale Research Letters, 14(1), 349. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-3185-6
Liu, X., Xu, J., Ni, Z., Wang, R., You, J., & Guo, R. (2019a). Adsorption and visible-light-driven photocatalytic properties of Ag3PO4/WO3 composites: A discussion of the mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 356, 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.001
Lu, J., Hu, H., Yang, S., Shanmugam, P., Wei, W., Selvaraj, M., & Xie, J. (2018). ZnS@carbonaceous aerogel composites fabricated in production of hydrogen and for removal of organic pollutants. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 29(10), 8523–8534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8866-x
Ma, L., Ai, X., Lu, Y., Yan, S., & Wu, X. S. (2020). Development of a new synthetic strategy for highly reduced graphene oxide-CdS quantum-dot nanocomposites and their photocatalytic activity. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 828, 154406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154406
Mao, M., Jiang, L., Wu, L., Zhang, M., & Wang, T. (2015). The structure control of ZnS/graphene composites and their excellent properties for lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3(25), 13384–13389. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA01501D
Messalti, A. S., El-Ghozzi, M., Zambon, D., Mahiou, R., & Setifi, Z. (2021). Investigating photoluminescence properties of Ca-doped ZnS nanoparticles prepared via hydrothermal method. Journal of Luminescence, 238, 118227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118227
Mohamed, M. J. S., Shenoy, U. S., & Bhat, D. K. (2018). Novel NRGO-CoWO4-Fe2O3 nanocomposite as an efficient catalyst for dye degradation and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 208, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.01.012
Munusamy, S., Mandlimath, T.R., Swetha, P., Al-Sehemi, A.G., Pannipara, M., Koppala, S., Shanmugam, P., Boonyuen, S., Pothu, R., & Boddula, R. (2023). Nitrogen-doped carbon dots: Recent developments in its fluorescent sensor applications. Environmental Research, 231, 116046.
Ngullie, R. C., Bhuvaneswari, K., Shanmugam, P., Boonyuen, S., Smith, S. M., & Sathishkumar, M. (2022). Magnetically RECOVERABLE BIOMASS-DERIVED carbon-aerogel supported ZnO (ZnO/MNC) composites for the photodegradation of methylene blue. Catalysts, 12(9), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12091073
Palve, A. M., & Kokil, D. N. (2019). One-pot synthesis of ZnS-rGO nanocomposites using single-source molecular precursor for photodegradation of methylene blue and reduction towards toxic Cr(VI) under solar light. Materials Research Express, 6(10), 105536. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab408f
Parasuraman, B., Kandasamy, B., Murugan, I., Alsalhi, M. S., Asemi, N., Thangavelu, P., & Perumal, S. (2023a). Designing the heterostructured FeWO4/FeS2 nanocomposites for an enhanced photocatalytic organic dye degradation. Chemosphere, 334, 138979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138979
Parasuraman, B., Shanmugam, P., Govindasamy, P., Nangan, S., Gnanasekaran, L., & Thangavelu, P. (2023b). Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline contaminated wastewater over Bi2S3/BiWO6/rGO ternary nanocomposite under visible light irradiation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 25, 105249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2023.105249
Park, Y., Na, Y., Pradhan, D., Min, B.-K., & Sohn, Y. (2014). Adsorption and UV/Visible photocatalytic performance of BiOI for methyl orange, Rhodamine B and methylene blue: Ag and Ti-loading effects. CrystEngComm, 16(15), 3155–3167. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42654H
Patel, K., Deshpande, M. P., & Chaki, S. H. (2017). Effect of Ag on structural, optical and luminescence properties of ZnS nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted chemical route. Applied Physics A, 123(5), 367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0980-8
Prasad, S., Shanmugam, P., Bhuvaneswari, K., Palanisamy, G., Pazhanivel, T., Arunkumar, T., et al. (2020). Rod-shaped carbon aerogel-assisted CdS nanocomposite for the removal of methylene blue dye and colorless phenol. Crystals, 10(4), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10040300
Qin, Y., Zhao, W., Sun, Z., Liu, X., Shi, G., Liu, Z., et al. (2019). Photocatalytic and adsorption property of ZnS–TiO2/RGO ternary composites for methylene blue degradation. Adsorption Science and Technology, 37(9–10), 764–776. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418810932
Raju, M., Parasuraman, B., Govindasamy, P., Thangavelu, P., & Duraisamy, S. (2023). Improved anti-diabetic and anticancer activities of green synthesized CuO nanoparticles derived from Tabernaemontana divaricate leaf extract. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26261-5
Ranjith, R., Karmegam, N., Alsawalha, M., Hu, X., & Jothimani, K. (2023a). Construction of g-C3N4/CdS/BiVO4 ternary nanocomposite with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity toward methylene blue dye degradation in the aqueous phase. Journal of Environmental Management, 330, 117132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117132
Ranjith, R., Vignesh, S., Balachandar, R., Suganthi, S., Raj, V., Ramasundaram, S., et al. (2023b). Construction of novel g-C3N4 coupled efficient Bi2O3 nanoparticles for improved Z-scheme photocatalytic removal of environmental wastewater contaminant: Insight mechanism. Journal of Environmental Management, 330, 117134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117134
Ren, Y., Xu, Q., Zhang, J., Yang, H., Wang, B., Yang, D., et al. (2014). Functionalization of biomass carbonaceous aerogels: Selective preparation of MnO2@CA composites for supercapacitors. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 6(12), 9689–9697. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502035g
Sacco, O., Vaiano, V., Sannino, D., Picca, R. A., & Cioffi, N. (2019). Ag modified ZnS for photocatalytic water pollutants degradation: Influence of metal loading and preparation method. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 537, 671–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.11.073
Sadaqat, A., Ali, G., Ali, Z., Iftikhar, F. J., Hasan, M., & ul. (2021). Synergetic effect of binary ZnS:SnS composites with reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes as anodes for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 4(12), 13868–13877. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.1c02639
Selvi, S., Rajendran, R., Barathi, D., & Jayamani, N. (2021). Facile synthesis of CeO2/CoWO4 hybrid nanocomposites for high photocatalytic performance and investigation of antimicrobial activity. Journal of Electronic Materials, 50(5), 2890–2902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08729-z
Shanmugam, P., Ngullie, R. C., Meejoo Smith, S., Boonyuen, S., Boddula, R., & Pothu, R. (2023a). Visible-light induced photocatalytic removal of methylene blue dye by copper oxide decorated zinc oxide nanorods. Materials Science for Energy Technologies, 6, 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2023.03.001
Shanmugam, P., Smith, S. M., Boonyuen, S., & Luengnaruemitchai, A. (2023b). In-situ development of boron doped g-C3N4 supported SBA-15 nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline. Environmental Research, 224, 115496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115496
Shanmugam, P., Wei, W., Qian, K., Jiang, Z., Lu, J., & Xie, J. (2019). Efficient removal of erichrome black T with biomass-derived magnetic carbonaceous aerogel sponge. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 248, 114387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2019.114387
Sivaranjani, T., Rajakarthihan, S., Bharath, G., Haija, M. A., & Banat, F. (2023). An advanced photo-oxidation process for pharmaceuticals using plasmon-assisted Ag-CoFe2O4 photocatalysts. Chemosphere, 341, 139984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139984
Subbulakshmi, A., Durgadevi, S., Anitha, S., Govarthanan, M., Biruntha, M., Rameshthangam, P., & Kumar, P. (2023). Biogenic gold nanoparticles from Gelidiella acerosa: Bactericidal and photocatalytic degradation of two commercial dyes. Applied Nanoscience, 13(6), 4033–4042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-022-02693-2
Thanigaivel, S., Vickram, S., Manikandan, S., Deena, S. R., Subbaiya, R., Karmegam, N., et al. (2022). Sustainability and carbon neutralization trends in microalgae bioenergy production from wastewater treatment: A review. Bioresource Technology, 364, 128057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128057
Thommes, M., & Cychosz, K. A. (2014). Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials: Progress and challenges. Adsorption, 20(2), 233–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9606-z
Venugopal, V., Balaji, D., Preeyanghaa, M., Moon, C. J., Neppolian, B., Muthusamy, G., et al. (2023). Synergistic combination of BiFeO3 nanorods and CeVO4 nanoparticles for enhanced visible light driven photocatalytic activity. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 72, 531–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2023.04.024
Vignesh, S., Palanisamy, G., Srinivasan, M., Elavarasan, N., Bhuvaneswari, K., Venkatesh, G., et al. (2021). Fabricating SnO2 and Cu2O anchored on g-C3N4 nanocomposites for superior photocatalytic various organic pollutants degradation under simulated sunlight exposure. Diamond and Related Materials, 120, 108606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108606
Wang, G., Huang, B., Li, Z., Lou, Z., Wang, Z., Dai, Y., & Whangbo, M.-H. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of ZnS with controlled amount of S vacancies for photocatalytic H2 production under visible light. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 8544. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08544
Wang, X., Zhou, J., Zhao, S., Chen, X., & Yu, Y. (2018). Synergistic effect of adsorption and visible-light photocatalysis for organic pollutant removal over BiVO4/carbon sphere nanocomposites. Applied Surface Science, 453, 394–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.073
Xu, W.-T., Ma, L., Ke, F., Peng, F.-M., Xu, G.-S., Shen, Y.-H., et al. (2014). Metal–organic frameworks MIL-88A hexagonal microrods as a new photocatalyst for efficient decolorization of methylene blue dye. Dalton Transactions, 43(9), 3792–3798. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3DT52574K
Yan, N., Zhou, Y., Zheng, Y., Qiao, S., Yu, Q., Li, Z., & Lu, H. (2015). Antibacterial properties and cytocompatibility of bio-based nanostructured carbon aerogels derived from silver nanoparticles deposited onto bacterial cellulose. RSC Advances, 5(118), 97467–97476. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15485E
Zhang, P., Yin, L., Yang, X., Wang, J., Chi, M., & Qiu, J. (2023a). Cotton-derived 3D carbon fiber aerogel to in situ support Bi2O3 nanoparticles as a separation-free photocatalyst for antibiotic removal. Carbon, 201, 110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.09.012
Zhang, Y., Liu, F., Zhong, L., Dong, Z., Chen, C., & Xu, Z. (2023b). Reusable and environmentally friendly cellulose nanofiber/titanium dioxide/chitosan aerogel photocatalyst for efficient degradation of tetracycline. Applied Surface Science, 641, 158425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.158425
Zhu, W., Han, M., Kim, D., Zhang, Y., Kwon, G., You, J., et al. (2022). Facile preparation of nanocellulose/Zn-MOF-based catalytic filter for water purification by oxidation process. Environmental Research, 205, 112417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112417
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Thammasat University Postdoctoral Fellowship (B.E.2564), Thailand Science Research and Innovation Fundamental Fund fiscal year 2023. The authors express their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2024R68) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS contributed to conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft and visualization. SB done supervision, data curation, project administration and writing—review and editing. BP performed validation, review and editing, PT and MSA done review and resources, ALTZ done review and editing and VA done data curation and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shanmugam, P., Parasuraman, B., Boonyuen, S. et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic application of ZnS-Ag composites based on biomass-derived carbon aerogel for the visible light degradation of methylene blue. Environ Geochem Health 46, 92 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01871-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01871-1