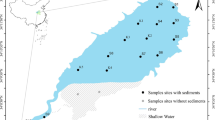
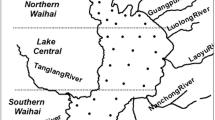
Abstract
Ecological pollution caused by heavy metals released from sediments is a worldwide concern. However, the effect of changes in sediment speciation on their release of heavy metals has not been adequately reported. In this study, the research focused on Pb and Cr in the ice period of Wuliangsuhai. This study analyzed changes in the sediment speciation of Pb and Cr before and after a release experiment using four risk assessment methods while varying the temperature, pH, and salinity of the water column. The results indicated that the total concentration of Pb ranged from 11.17 to 24.25 mg/kg, while for Cr it ranged from 42.26 to 69.68 mg/kg. Both elements exhibited mild contamination. The release of Pb and Cr from sediments increases with increasing water temperature, mainly due to the conversion of the residual fraction of Pb to the Fe–Mn oxide fraction and Cr converting more residual fraction to the organic matter and sulfide fraction. The release of sediment Pb and Cr decreased with increasing pH, with Pb converting more acid extractable fraction to the residual fraction and Cr converting more organic matter and sulfide fraction to the residual fraction. In contrast, the release of Pb and Cr increased and then decreased with increasing salinity. For Pb, the acid extractable fraction was more susceptible to conversion to the residual fraction by environmental influences, whereas for Cr, the organic matter and sulfide fraction were susceptible to conversion to the residual fraction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharchaou, I., Py, J. S., Cambier, S., Loizeau, J. L., Cornelis, G., Rousselle, P., Battaglia, E., & Vignati, D. A. L. (2018). Chromium hazard and risk assessment: New insights from a detailed speciation study in a standard test medium. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 37(4), 983–992. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4044
Aytekin, T. (2022). Evaluation of the effects of nitrilotriacetic acid as a chelating agent on the biochemical toxicity of lead in oreochromis niloticus. Biological Trace Element Research, 200(6), 2908–2914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02973-y
Bakshe, P., Jugade, R. J. W., & Air, & Pollution, S. (2021). Distribution, association, and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals and influencing factors in major industrial stream sediments of Chandrapur District, Central India. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 232, 1–16.
Bastami, K. D., Neyestani, M. R., Raeisi, H., Shafeian, E., Baniamam, M., Shirzadi, A., Esmaeilzadeh, M., Mozaffari, S., & Shahrokhi, B. (2018). Bioavailability and geochemical speciation of phosphorus in surface sediments of the Southern Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 126, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.095
Bing, H., Wu, Y., Zhou, J., Sun, H., Wang, X., & Zhu, H. (2019). Spatial variation of heavy metal contamination in the riparian sediments after two-year flow regulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Science of the Total Environment, 649, 1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.401
Chakraborty, P., Babu, P. R., Vudamala, K., Ramteke, D., & Chennuri, K. (2014). Mercury speciation in coastal sediments from the central east coast of India by modified BCR method. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 81(1), 282–288.
Chang, X., Wang, S., Chen, H., & Guan, X. (2021). Analysis of the main factors affecting salinity in Wuliangsuhai Lake. Paper presented at the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.
Chen, F., Ma, J., Akhtar, S., Khan, Z. I., Ahmad, K., Ashfaq, A., Nawaz, H., & Nadeem, M. (2022). Assessment of chromium toxicity and potential health implications of agriculturally diversely irrigated food crops in the semi-arid regions of South Asia. Agricultural Water Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107833
Du, C., Li, J., Li, G., Li, X., Zhao, C., & Zhang, L. J. E. S. (2022). Distribution and risk assessment on the nutrients and heavy metals in surface sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Environmental Science, 43, 1–16.
Fan, X., Ding, S., Chen, M., Gao, S., Fu, Z., Gong, M., Wang, Y., & Zhang, C. (2019). Mobility of chromium in sediments dominated by macrophytes and cyanobacteria in different zones of Lake Taihu. Science of the Total Environment, 666, 994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.299
Fu, Z., Guo, W., Dang, Z., Hu, Q., Wu, F., Feng, C., Zhao, X., Meng, W., Xing, B., Giesy, J. P. (2017). Refocusing on nonpriority toxic metals in the aquatic environment in China. In: ACS Publications.
Gosnell, K. J., Beck, A. J., Müller, P., Keßler, A., & Achterberg, E. P. J. M. P. B. (2022). Effects of salinity and temperature on seawater dissolution rate of initial detonation agent mercury fulminate. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 185, 114311.
Guo, Y. J., Wang, Y., Liu, Y. G., Hou, L., Yang, G. Y., Li, M. Y., & Wen, G. J. (2018). Effects of environmental factors on arsenic fractions in plateau lakeside wetland sediments. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 27(5), 2029–2040.
He, X., Chen, G., Fang, Z., Liang, W., Li, B., Tang, J., Sun, Y., & Qin, L. (2020). Source identification of chromium in the sediments of the Xiaoqing River and Laizhou Bay: A chromium stable isotope perspective. Environmental Pollution, 264, 114686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114686
Ikem, A., Egiebor, N., & Nyavor, K. J. W. (2003). Trace elements in water, fish and sediment from Tuskegee Lake, Southeastern USA. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 149, 51–75.
Islam, A. R. M. T., Jion, M. M. M. F., Jannat, J. N., Varol, M., Islam, M. A., Khan, R., Idris, A. M., Malafaia, G., & Habib, M. A. (2023). Perception and legacy of soil chromium and lead contamination in an operational small-scale coal mining community. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45, 1–17.
Kapoor, R. T., Bani Mfarrej, M. F., Alam, P., Rinklebe, J., & Ahmad, P. (2022). Accumulation of chromium in plants and its repercussion in animals and humans. Environmental Pollution, 301, 119044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119044
Li, H., Shi, A., Li, M., & Zhang, X. (2013). Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/434012
Liang, R. Z., Gu, Y. G., Li, H. S., Han, Y. J., Niu, J., Su, H., Jordan, R. W., Man, X. T., & Jiang, S. J. (2023). Multi-index assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of the Pearl River estuary intertidal zone. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 186, 114445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114445
Liu, B., Luo, J., Jiang, S., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, X., & Zhou, S. (2021). Geochemical fractionation, bioavailability, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of the largest influent river into Chaohu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution, 290, 118018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118018
Luo, H., Wang, Q., Liu, Z., Wang, S., Long, A., & Yang, Y. (2020). Potential bioremediation effects of seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis on heavy metals in coastal sediment from a typical mariculture zone. Chemosphere, 245, 125636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125636
Lv, J., Li, C., Jia, K., Zhang, S., Shi, X., Zhao, S., & Sun, B. (2017). Impacts of salinity change on the effectiveness of heavy metals in the sediment of Wuliangsuhai. Environmental Sciences, 26(9), 1547–1553.
Ma, W., Tai, L., Qiao, Z., Zhong, L., Wang, Z., Fu, K., & Chen, G. (2018). Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China. Science of the Total Environment, 631, 348–357.
Martín-Torre, M. C., Ruiz, G., Galán, B., & Viguri, J. R. (2015). Generalised mathematical model to estimate Zn, Pb, Cd, Ni, Cu, Cr and As release from contaminated estuarine sediment using pH-static leaching tests. Chemical Engineering Science, 138, 780–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2015.08.053
Mathur, S., Kalaji, H. M., & Jajoo, A. (2016). Investigation of deleterious effects of chromium phytotoxicity and photosynthesis in wheat plant. Photosynthetica, 54(2), 185–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-016-0198-6
Meena, N. K., Prakasam, M., Bhushan, R., Sarkar, S., Diwate, P., & Banerji, U. (2017). Last-five-decade heavy metal pollution records from the Rewalsar Lake, Himachal Pradesh, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 1–10.
Mishra, S., & Bharagava, R. N. (2016). Toxic and genotoxic effects of hexavalent chromium in environment and its bioremediation strategies. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part c, Environmental Carcinogenesis & Ecotoxicology Reviews, 34(1), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2015.1096883
Ouyang, W., Wang, Y., Lin, C., He, M., Hao, F., Liu, H., & Zhu, W. (2018). Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Science of the Total Environment, 637, 208–220.
Peng, C., Huang, Y., Yan, X., Jiang, L., Wu, X., Zhang, W., & Wang, X. (2021). Effect of overlying water pH, temperature, and hydraulic disturbance on heavy metal and nutrient release from drinking water reservoir sediments. Water Environment Research, 93(10), 2135–2148.
Qin, Y., & Tao, Y. (2022). Pollution status of heavy metals and metalloids in Chinese lakes: Distribution, bioaccumulation and risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 248, 114293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114293
Rahman, Z., & Singh, V. P. (2019). The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(7), 419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7528-7
Rosa, M., Prado, C., Chocobar-Ponce, S., Pagano, E., & Prado, F. (2017). Effect of seasonality and Cr(VI) on starch-sucrose partitioning and related enzymes in floating leaves of Salvinia minima. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 118, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.05.014
Shengnan, Z., Xiaohong, S., & Hanmeng, Z. (2018). Simulation on the species of heavy metals in Wuliangsuhai Lake water.
Shi, W., Li, T., Feng, Y., Su, H., & Yang, Q. (2022). Source apportionment and risk assessment for available occurrence forms of heavy metals in Dongdahe Wetland sediments, southwest of China. Science of the Total Environment, 815, 152837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152837
Smith, S. L., MacDonald, D. D., Keenleyside, K. A., Ingersoll, C. G., & Field, L. J. (1996). A preliminary evaluation of sediment quality assessment values for freshwater ecosystems. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 22(3), 624–638.
Soetan, O., Nie, J., & Feng, H. (2022). Preliminary environmental assessment of metal-contaminated sediment dredging in an Urban River, New Jersey, USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 184, 114212.
Song, S., Peng, R., Wang, Y., Cheng, X., Niu, R., & Ruan, H. (2023). Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metal pollution around typical coal gangue hill located in Fengfeng Mining area. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45, 1–22.
Sotelo, T. J., & Satoh, H. (2023). Organic matter removal performance of enhanced sewer self-purification by porous media treating domestic wastewater under various temperatures. Journal of Water and Environment Technology, 21(1), 76–82. https://doi.org/10.2965/jwet.22-107
Sun, H., Yu, R., Liu, X., Cao, Z., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Zhuang, S., Ge, Z., & Zhang, L. J. W. R. (2022). Drivers of spatial and seasonal variations of CO2 and CH4 fluxes at the sediment water interface in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Research, 222, 118916.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Tian, W., Pei, G., Zhao, S., Shi, X., Zhang, H., Sun, B., Song, S., Sun, C., & Ma, H. (2020). Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Water Supply, 20(8), 3779–3790.
Vallius, H. (2015). Quality of the surface sediments of the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 99(1–2), 250–255.
Wang, X., Zhang, L., Zhao, Z., & Cai, Y. (2018). Heavy metal pollution in reservoirs in the hilly area of southern China: Distribution, source apportionment and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 634, 158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.340
Yu, H., Shi, X., Zhao, S., Sun, B., Liu, Y., Arvola, L., Li, G., Wang, Y., Pan, X., Wu, R., & Tian, Z. (2022). Primary productivity of phytoplankton and its influencing factors in cold and arid regions: A case study of Wuliangsuhai Lake. China. Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109545
Zamani Ahmad Mahmoodi, R. (2017). Investigation of heavy metals concentration in surface sediments of Choghakhor wetland. Journal of Environmental Studies, 43(1), 149–161.
Zhang, H., Liang, P., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Bai, Y., Xing, Y., Wei, C., Li, Y., Liu, Y., & Hu, Y. (2022). Spatial distributions and intrinsic influence analysis of Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd and Pb in sediments from the Wuliangsuhai Wetland, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), 10843.
Zhang, Z. Y., Wan, C. Y., Hu, H. Q., Yang, Z. H., Yuan, Y. J., & Zhu, W. (2023). Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 44(2), 770–780. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202203039
Zhao, Y., Zhao, S., Shi, X., Lu, J., Cui, Z., Yu, H., Ye, B., Li, X. (2023). Influence of environmental factors on changes in the speciation of Pb and Cr in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake, during the ice-covered period.
Zhou, J., Zhang, M., Ji, M., Wang, Z., Hou, H., Zhang, J., Huang, X., Hursthouse, A., & Qian, G. (2020). Evaluation of heavy metals stability and phosphate mobility in the remediation of sediment by calcium nitrate. Water Environment Research, 92(7), 1017–1026. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1297
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52060022 and 52260028]; the National Key R&D Program of China [grant numbers 2017YFE0114800 and 2019YFC0409204]. The Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan (2021GG0089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by YZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YZ and SZ, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhao, S., Shi, X. et al. Influence of environmental factors on changes in the speciation of Pb and Cr in sediments of Wuliangsuhai Lake, during the ice-covered period. Environ Geochem Health 46, 116 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01842-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01842-y