Abstract
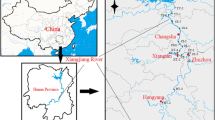
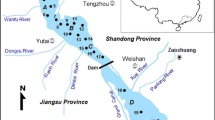
To understand the potential risks of heavy metals, including their bioavailability and toxicity, 15 surface sediment samples were collected from Luhun Reservoir in Luoyang city, China. Total concentrations and chemical fractions of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were analyzed. Various rating methods were used to evaluate the degree, risk, and toxicity of the heavy metal pollution. Results showed that Cd and Pb were preferentially associated with exchangeable (55.77–69.76%) and reducible (53.54–69.43%) fractions, respectively, and therefore exhibited high potential availability. Cr (57.14–86.56%) and Ni (32.21–72.77%) occurred primarily in the residual fraction. Metal concentrations in the effective fraction of the sediment decreased in the order: Cd (96.32%) > Pb (91.61%) > Cu (64.54%) > Zn (57.23%) > Ni (41.51%) > Cr (21.68%). Risk assessment indicated that the risk for Cd is extremely high (62.96%); Cu, Pb, and Zn are ranked as medium risk. Based on the potential ecological risk index, these metals (especially Cd) showed higher potential risk near the dam region. Toxic unit values (2.89–6.05) in more than 60% of sediment sites exceeded a value of 4, and Pb had a relatively higher contribution (1.06–2.65). Cd and Pb are the main contaminants in sediments of Luhun Reservoir and should be paid more attention in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai JH, Jia J, Zhang GL, Zhao QQ, Lu QQ, Cui BS, Liu XH (2016) Spatial and temporal dynamics of heavy metal pollution and source identification in sediment cores from the short-term flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta. Environ Pollut 219:379–388
Bettinelli M, Beone GM, Spezia S, Baffi C (2000) Determination of heavy metals in soils and sediments by microwave-assisted digestion and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry analysis. Anal Chim Acta 424:289–296
Bing HJ, Wu YH, Zhou J, Sun HY, Wang XX, Zhu H (2019) Spatial variation of heavy metal contamination in the riparian sediments after two-year flow regulation in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci Total Environ 649:1004–1016
Chai L, Li H, Yang Z et al (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:874–885
Delgado J, Barba-Brioso C, Nieto JM, Boski T (2011) Speciation and ecological risk of toxic elements in estuarine sediments affected by multiple anthropogenic contributions (Guadiana saltmarshes, SW Iberian Peninsula): I. Surficial sediments. Sci Total Environ 409:3666–3679
Fan WH, Wang W-X, Chen JS, Li XD, Yen Y-F (2002) Cu, Ni, and Pb speciation in surface sediments from a contaminated bay of northern China. Mar Pollut Bull 44:816–832
Fernandes MC, Nayak GN (2015) Speciation of metals and their distribution in tropical estuarine mudflat sediments, southwest coast of India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:68–75
Guillén MT, Delgado J, Albanese S, Nieto JM, Lima A, De Vivo B (2012) Heavy metals fractionation and multivariate statistical techniques to evaluate the environmental risk in soils of Huelva Township (SW Iberian Peninsula). J Geochem Explor 119-120:32–43
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Huang LL, Pu XM, Pan JF, Wang B (2013) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of Swan Lake lagoon and Rongcheng Bay in the northern Yellow Sea. Chemosphere 93:1957–1964
Ji ZH, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Chen T, Long ZW, Li M, Pei YS (2019) Distribution, ecological risk and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake, Northern China. Chemosphere 237:124425
Jia XW, Wang C, Zeng XY, Yu ZQ, Sheng GY, Fu JM (2014) The occurrence, accumulation and preliminary risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from the main tributaries in the Three Gorges Reservoir. GEOCHIMICA 43(2):174–179
Li YH, Lin YP, Wang L (2017) Distribution of heavy metals in seafloor sediments on the East China Sea inner shelf: seasonal variations and typhoon impact. Mar Pollut Bull 129(2)
Li H, Chai LY, Yang ZH, Liao Q, Liu Y, Ouyang B (2019) Seasonal and spatial contamination statuses and ecological risk of sediment cores highly contaminated by heavy metals and metalloids in the Xiangjiang River. Environ Geochem Health 41:1617–1633
Liu JL, Li YL, Zhang B, Cao JL, Cao ZG, Domagalski J (2009) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Luan River source water. Ecotoxicology 18:748–758
Ma XL, Zuo H, Tian MJ, Zhang L, Meng J, Zhou X, Min N, Chang X, Liu Y (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 144:264–272
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Abas MR, Sobhanzadeh E (2011) Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J Hazard Mater 192:402–410
Pignotti E, Guerra R, Covelli S, Fabbri E, Dinelli E (2018) Sediment quality assessment in a coastal lagoon (Ravenna, NE Italy) based on SEM-AVS and sequential extraction procedure. Sci Total Environ 635:216–227
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Shah MH (2014) Dissolved concentrations, sources, and risk evaluation of selected metals in surface water from Mangla Lake, Pakistan. Sci World J 2014:948396
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Akhter G, Shah MH (2018) Fractionation, bioavailability, contamination and environmental risk of heavy metals in the sediments from a freshwater reservoir, Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 184:199–208
Sheng Q, Wang HX, Hu YH, Cai CN (2009) Study on soil background value and reference value in Henan Section of Yellow River. J Anhui Agric Sci 37:8647–8650
Siddiqui Ekabal, Pandey Jitendra (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water and surface sediment and evaluation of ecological risks associated with sediment contamination in the Ganga River: a basin-scale study. 26:10926-10940
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Soliman NF, El Zokm GM, Okbah MA (2018) Risk assessment and chemical fractionation of selected elements in surface sediments from Lake Qarun, Egypt using modified BCR technique. Chemosphere 191:262–271
Sun H, Tan CY, Huang DY, Wan DJ, Liu LK, Yang Y, Yu X (2011) Effects of soil organic matter on the accumulation, availability and chemical speciation of heavy metal. J Nat Sci Hunan Normal Univ 34(4):82–87
Sundaray SK, Nayak BB, Lin S, Bhatta D (2011) Geochemical speciation and risk assessment of heavy metals in the river estuarine sediments - a case study: Mahanadi basin, India. J Hazard Mater 186:1837–1846
Tang WZ, Shan BQ, Zhang H, Zhu X, Li S (2016) Heavy metal speciation, risk, and bioavailability in the sediments of rivers with different pollution sources and intensity. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:23630–23637
Tang WZ, Zhang WQ, Yu Z, Zhang H, Shan BQ (2017) Basin-scale comprehensive assessment of cadmium pollution, risk, and toxicity in riverine sediments of the Haihe Basin in north China. Ecol Indic 81:295–301
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang C, Liu SL, Zhao QH, Deng L, Dong SK (2012) Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:32–39
Wang GQ, A YL, Jiang H, Fu Q, Zheng BH (2015a) Modeling the source contribution of heavy metals in surficial sediment and analysis of their historical changes in the vertical sediments of a drinking water reservoir. J Hydrol 520:37–51
Wang YQ, Yang LY, Kong LH, Liu EF, Wang LF, Zhu JG (2015b) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 125:200–205
Wang JZ, Peng SC, Chen TH, Zhang L (2015c) Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(1):307–314
Wang WW, Wang SH, Chen JY, Jiang X, Zheng BH (2019) Combined use of diffusive gradients in thin film, high-resolution dialysis technique and traditional methods to assess pollution and bioavailability of sediment metals of lake wetlands in Taihu Lake Basin. Sci Total Environ 671:28–40
Wen SF, Shan BQ, Zhang H (2012) Spatial distribution character of phosphorus fractions in surface sediment from Chaohu Lake. Environ Sci 33(7):2322–2329
Yang ZF, Wang Y, Shen ZY, Niu JF, Tang ZW (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J Hazard Mater 166:1186–1194
Yang LQ, Liu GM, Di L, Wu XY, You WH, Huang B (2019) Occurrence, speciation, and risks of trace metals in soils of greenhouse vegetable production from the vicinity of industrial areas in the Yangtze River Delta. China Environ Sci Pollut R 26:8696–8708
Yu H, Zhang WB, Yu JP (2011) Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hongze Lake. Environ Sci 32:437–444
Yu C-C, Zhao W-T, Gao X-F, Cheng S-G, Xie D, Ma P-T (2018) Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of metals in drinking water sources from the Luhun Reservoir. Environ Sci 39:89–98
Zhang C, Shan BQ, Tang WZ, Dong LX, Zhang WQ, Pei YS (2017) Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:263–271
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41907267 and 51979107), the Henan Province University Scientific and Technological Innovation Team (Grant No. 18IRTSTHN009), and the Foundation for University Key Youth Teachers of Henan Province of China (Grant No. 2018GGJS077). We thank Kathryn Sole, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 39.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Song, G., Zhang, C. et al. Chemical fractionation and risk assessment of surface sediments in Luhun Reservoir, Luoyang city, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 35319–35329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09512-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09512-7