Abstract
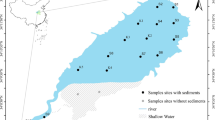
Caohai Lake in Guizhou Province is a plateau wetland lake within a karst geological topography. It is in the lead–zinc enrichment zone in northwestern Guizhou. The potential environmental risk of heavy metals, with high geological background levels, has been attracting attention. In this study, sediments in Caohai Lake were investigated to analyse the overall levels and chemical speciation of heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, and Zn). In addition, the potential ecological risk of environmentally active heavy metals was investigated from the perspective of heavy metal speciation using the ratio of the secondary phase to primary phase combined with the ecological risk assessment code. The results showed that the overall levels of heavy metals in sediments in Caohai Lake were several to hundreds of times higher than the background values. However, the chemical speciation of heavy metals was mostly residual. Among heavy metals, Cd is a typical pollution stress factor in the region, with high total levels and a high proportion of environmentally unstable forms. The mean sediment quality guideline quotient of heavy metals in sediments ranged between 0.2 and 1.6, indicating mild to moderate toxic effects on benthic organisms. From the analysis of the forms that migrate in the environment, the heavy metals in sediments were mostly at the pollution-free or low-risk levels. Cd poses a high environmental risk, with an extremely high regional risk level. Therefore, different forms of heavy metals have different environmental risks. In the environmental impact assessment of heavy metals, it is necessary to consider the environmental activity and bioavailability of different chemical forms of heavy metals. Stability and passivation of Cd forms with high environmental activity should be the focus in the prevention and control of heavy metal pollution in Caohai Lake.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo P, Iavazzo P, Albanese S (2014) Bioavailability and soil to plant transfer factors as indicators of potentially toxic element contamination in agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 500–501:11–22
Ahn Y, Yun HS, Pandi K (2020) Heavy metal speciation with prediction model for heavy metal mobility and risk assessment in mine-affected soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(3):3213–3223
Bao K, Liu JL, You XG (2017) A new comprehensive ecological risk index for risk assessment on Luanhe River, China. Environ Geochem Health 40(5):1965–1978
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang Y (2007) Heavy metals in an impacted wetland system: a typical case from south western China. Sci Total Environ 387(1–3):257–268
Bochatay L, Persson P, Sjöberg S (2000) Metal ion coordination at the water manganite (γ-MnOOH) interface: I. An EXAFS study of cadmium(II). Colloid Interface Sci 229:584–592
Campana O, Blasco J, Simpson SL (2013) Demonstrating the appropriateness of developing sediment quality guidelines based on sediment geochemical properties. Environ Sci Technol 47:7483–7489
Chen JJ, Liu B, Cai LG (2018) Comparison of risk assessment based on the various methods of heavy metals in soil: a case study for the typical field areas in the Jianghan Plain. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 45(6):164–172
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (2014) Background values of soil elements in China. China Environment Publishing Group
Ciszewski D, Grygar TM (2016) A Review of flood-related storage and remobilization of heavy metal pollutants in river systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(7):239
Davutluoglu OI, Seckin G, Ersu CB (2015) Assessment of metal pollution in water and surface sediments of the Seyhan River, Turkey, using different indexes. Soil, Air, Water 39(2):185–194
Han CM, Wang LS, Gong ZQ (2005) Chemical forms of soil heavy metals and their environmental significance. Chin J Ecol 24(12):1499–1502
Hao YP, Miao XY, Liu HW (2021) The variation of heavy metals bioavailability in sediments of Liujiang river basin, SW China associated to their speciations and environmental fluctuations, a field study in typical Karstic river. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(8):3986–4014
Hu J, Zhou SQ, Wu P (2017) Assessment of the distribution, bioavailability and ecological risks of heavy metals in the lake water and surface sediments of the Caohai plateau wetland. China Plos One 12(12):e189295
Hu J, Long YC, Zhou W (2020) Influence of different land use types on hydrochemistry and heavy metals in surface water in the lakeshore zone of the Caohai Wetland. China. Environ Pollut 267:115454
Hu B, Guo PY, Su HT (2021) Fraction distribution and bioavailability of soil heavy metals under different planting patterns in mangrove restoration wetlands in Jinjiang, Fujian. China. Ecol Eng 166:106242
Huang L, Pu X, Pan JF (2013) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of Swan Lake lagoon and Rongcheng Bay in the northern Yellow Sea. Chemosphere 93(9):1957–1964
Impellitteri CA, Saxe JK, Cochran M (2010) Predicting the bioavailability of copper and zinc in soils: modeling the partitioning of potentially bioavailable copper and zinc from soil solid to soil solution. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(6):1380–1386
Kasem R, Karbassi AR, Omidvar B (2020) Stability and speciation of heavy metals and metalloids in Tajan River water, North of Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(4):1899–1906
Ke X, Gui S, Huang H (2017) Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 175:473–481
Lao QB, Su QZ, Liu GQ (2019) Spatial distribution and historical changes in heavy metal in the surface seawater and sediments of Beibu Gulf, China. Mar Pollut Bull 146:427–434
Li HY, Shi AB, Li MY (2013) Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. J Chem 2013:1–11
Liang P, Wu SC, Zhang J (2016) The effects of mariculture on heavy metal distribution in sediments and cultured fish around the Pearl River Delta region, south China. Chemosphere 148:171–177
Liao RH, Wu XG, Wang ZD (2020) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment on the main nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of Lake Gehu, Taihu Basin after removing the aquaculture net. J Lake Sci 33(05):1436–1447
Lin SJ (1987) New progress of neozoic study in Guizhou. Guizhou Geol 4:29–37
Lin SX, Zhang QH, Guo Y (2012) Pollution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Caohai in Guizhou Province, China. J Agro-Environ Sci 31(11):2236–2241
Lin SX, Liu XL, Zhang ZL (2021) Heavy metal pollution characteristic and source apportionment in overlying deposits of Caohai Lake, Guizhou Province. J Agro-Environ Sci 40(2):390–399
Liu JL, Li YL, Zhang B (2009) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Luan River source water. Ecotoxicology 18(6):748–758
Long ER, Field LJ, MacDonald DD (1998) Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:714–727
Lu SY, Jiao W, Jin XC (2010) Heavy metals pollution and its stability assessment of sediments in flowing rivers around lake Taihu. Environ Sci 31(10):2311–2314
Ma XL, Zuo H, Tian MJ (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 144:264–272
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2002) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Marrugo-Negrete J, Pinedo-Hernández J, Díez S (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ Res 154:380–388
Perin G, Craboledda L, Lucchese L (1985) Heavy metal speciation in the sediments of Northern Adriatic sea: a new approach for environ mental toxicity determination. Heavy Metal Environ 2:454–456
Rauret G, LópezSánchez JF, Sahuquillo A (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1(1):167–183
Shen Q, Xiang JM, Zhang MK (2020) Distribution and chemical speciation of heavy metals in various size fractions of aggregates from zonal soil. Int J Environ Analyt Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1781840
Song YL, Zeng Y, Yang HQ (2016) Spatiotemporal distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Caohai, Guizhou, China. Chin J Ecol 35(07):1849–1856
Sun RR, Chen HQ, Li DK (2015) Comparison of ecological risk assessment methods based on the chemical forms of lead in soil. J Saf Environ 22(5):47–51
Sun JW, Yu RL, Hu GR (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and tracing sources by Pb & Sr Isotope in the soil profile of woodland in Quanzhou. Environ Sci 38(4):1566–1575
Wang Y (2005) Comparison of element abundances between the exposed crust of the continent of China and the global average continental upper crust. Geol Bull China 24(10–11):906–915
Wang SH, Wang WW, Jiang X (2013) Heavy metal speciation and stability in the sediment of Lihu Lake. Environ Sci 34(09):3562–3571
Wang K, Zeng XL, Xu DY (2020) Chemical fractions, diffusion flux and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Sci Total Environ 724:138046
Xia PH, Ma L, Sun RG (2020) Evaluation of potential ecological risk, possible sources and controlling factors of heavy metals in surface sediment of Caohai Wetland, China. Sci Total Environ 740:140231–140253
Yu Y, Lv YN, Wang WJ (2020) Spatio-Temporal distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in middle and lower reaches of Le’an river. Environ Sci 41(2):691–701
Yuan GL, Liu C, Chen L (2011) Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J Hazard Mater 185(1):336–345
Zhang FY, Yan BX, Zhu LL (2010) Speciation of heavy metals in sediment of the Songhua River northeast of China. J Agro-Environ Sci 29(1):163–167
Zhang ZL, Tan H, He JL (2018) Distribution characteristics and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Caohai lake in Guizhou. Ecol Environ Sci 27(12):2314–2320
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21767006, 42167054).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21767006,42167054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shaoxia Lin: Original draft/paper writing/funding acquisition. Xiaolan Liu: Data curation. Zhuanling Zhang: Samples collection, analysis. Qinghai Zhang: Writing, review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Liu, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Speciation characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments from Caohai Lake, Guizhou Province. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36, 3929–3944 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02236-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02236-9