Abstract
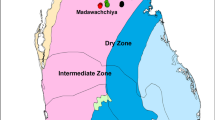
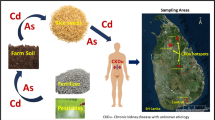
Environmental exposure to trace elements has been widely suspected as an etiological factor for the emergence of chronic kidney disease of undetermined origin (CKDu) that prevails in certain districts of the dry zone areas of Sri Lanka. Contaminated rice can be act as a host for potentially toxic trace elements that ultimately led to health hazards; thus, rice soils were investigated in detail, giving particular attentions to identified CKDu hotspots. A total of 102 rice soil samples were collected from main climatic zones viz. wet and dry zones including CKDu hotspots. In addition to pH, electrical conductivity and cation exchange capacity, acid extracted major and trace element contents in rice soils were determined by using ICP-MS. Significant differences were observed for Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, and Pb contents between climatic zones. Arsenic and Pb contents in soils were lower than the levels reported in soils from other regions of the world, though significantly higher contents were observed in CKDu regions compared to non-endemic wet zone regions. Calculation of enrichment factor revealed that soils in both dry and wet zones were moderately enriched with As, Cd, and Pb, suggesting an influence of anthropogenic processes. Twenty percent of the wet zone samples showed significant enrichment of Ni, Cu, and Zn. Geo-accumulation index assorted that the studied soil samples were uncontaminated to moderately contaminated, implying that rice soils in both climatic zones are not alarmingly contaminated with toxic trace elements. However, regular and continuous monitoring of rice soil quality is extremely important.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data set used or analyzed during the current study is not publicly available due to the pending postgraduate examination (SB), but are available with the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
References
Abraham, G., Varughese, S., Thandavan, T., Iyengar, A., Fernando, E., Naqvi, S. A., et al. (2016). Chronic kidney disease hotspots in developing countries in South Asia. Clinical Kidney Journal, 9(1), 135–141.
Adriano, D. (2001). Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability and Risks of Metals. Springer.
Alloway, B. J. (1990). The origins of heavy metals in soils. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (pp. 33–39). Blackie & Glasgow.
Alloway, B. J. (2013). Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils: Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (pp. 11–50). Springer.
Anupama, Y. J., Sankarasubbaiyan, S., & Taduri, G. (2020). Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology: Case definition for India–a perspective. Indian Journal of Nephrology, 30(4), 236.
Athuraliya, N. T. C., Abeysekera, T. D. J., Amerasinghe, P. H., Kumarasiri, R., Bandara, P., Karunaratne, U., et al. (2011). Uncertain etiologies of proteinuric-chronic kidney disease in rural Sri Lanka. Kidney International, 80(11), 1212–1221.
Aydinalp, C., & Katkat, A. V. (2004). The comparison of extraction methods for evaluating some heavy metals in polluted soils. Plant Soil and Environment, 50(5), 212–217.
Balasoiu, C. F., Zagury, G. J., & Deschenes, L. (2001). Partitioning and speciation of chromium, copper, and arsenic in CCA-contaminated soils: Influence of soil composition. Science of the Total Environment, 280(1–3), 239–255.
Balasooriya, S., Munasinghe, H., Herath, A. T., Diyabalanage, S., Ileperuma, O. A., Manthrithilake, H., et al. (2020). Possible links between groundwater geochemistry and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): an investigation from the Ginnoruwa region in Sri Lanka. Exposure and Health, 12, 823–834.
Bandara, J. M. R. S., Senevirathna, D. M. A. N., Dasanayake, D. M. R. S. B., Herath, V., Bandara, J. M. R. P., Abeysekara, T., et al. (2008). Chronic renal failure among farm families in cascade irrigation systems in Sri Lanka associated with elevated dietary cadmium levels in rice and freshwater fish (Tilapia). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 30(5), 465–478.
Barbieri, M. (2016). The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 5(1), 1–4.
CCME (2007). (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment) Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health. National Guideline and Standards (pp. 7). Quebec, Canada: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment.
Chandrajith, R., Dissanayake, C. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (2005a). The abundances of rarer trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka. Chemosphere, 58(10), 1415–1420.
Chandrajith, R., Dissanayake, C. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (2005b). Geochemistry of trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka–implications for iodine deficiency disorders (IDD). Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27(1), 55–64.
Chandrajith, R., Nanayakkara, S., Itai, K., Aturaliya, T. N. C., Dissanayake, C. B., Abeysekera, T., et al. (2011). Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology (CKDue) in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(3), 267–278.
Chandrajith, R., Seneviratna, S., Wickramaarachchi, K., Attanayake, T., Aturaliya, T. N. C., & Dissanayake, C. B. (2010). Natural radionuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: Study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(1), 193–201.
Charlatchka, R., & Cambier, P. (2000). Influence of reducing conditions on solubility of trace metals in contaminated soils. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 118(1–2), 143–168.
Chen, H., Teng, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2015). Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Science of the Total Environment, 512, 143–153.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Chandrajith, R. (2009). Phosphate mineral fertilizers, trace metals and human health. Journal of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka, 37(3), 153–165.
Diyabalanage, S., Navarathna, T., Abeysundara, H. T. K., Rajapakse, S., & Chandrajith, R. (2016). Trace elements in native and improved paddy rice from different climatic regions of Sri Lanka: Implications for public health. Springerplus, 5(1), 1864.
DOA (2020). Rice Cultivation. Colombo, Sri Lanka: Rice Research and Development Institute, Department of Agriculture, Sri Lanka.
Dolenec, T., Serafimovski, T., Tasev, G., Dobnikar, M., Dolenec, M., & Rogan, N. (2007). Major and trace elements in paddy soil contaminated by Pb–Zn mining: A case study of Kočani Field. Macedonia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(1), 21–32.
Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, J., Vandecasteele, B., Meers, E., & Tack, F. M. G. (2009). Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 407(13), 3972–3985.
El Nahas, A. M., & Bello, A. K. (2005). Chronic kidney disease: The global challenge. The Lancet, 365(9456), 331–340.
Essington, M. E. (2015). Soil and Water Chemistry: An Integrative Approach (2nd ed.). CRC Press LLC.
Fageria, N. K., Carvalho, G. D., Santos, A. B., Ferreira, E. P. B., & Knupp, A. M. (2011). Chemistry of lowland rice soils and nutrient availability. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 42(16), 1913–1933.
Favre, F., Tessier, D., Abdelmoula, M., Génin, J.-M., Gates, W. P., & Boivin, P. (2002). Iron reduction and changes in cation exchange capacity in intermittently waterlogged soil. European Journal of Soil Science, 53(2), 175–183.
Fernando, B. N. T. W., Sudeshika, T. S. H., Hettiarachchi, T. W., Badurdeen, Z., Abeysekara, T. D. J., Abeysundara, H. T. K., et al. (2020). Evaluation of biochemical profile of Chronic Kidney Disease of uncertain etiology in Sri Lanka. Plos one, 15(5), e0232522. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.023252.2
Fordyce, F. M., Johnson, C. C., Navaratna, U. R. B., Appleton, J. D., & Dissanayake, C. B. (2000). Selenium and iodine in soil, rice and drinking water in relation to endemic goitre in Sri Lanka. Science of the Total Environment, 263(1–3), 127–141.
Gilbert, P. J., Polya, D. A., & Cooke, D. A. (2015). Arsenic hazard in Cambodian rice from a market-based survey with a case study of Preak Russey village. Kandal Province. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(4), 757–766.
Hang, X., Wang, H., Zhou, J., Ma, C., Du, C., & Chen, X. (2009). Risk assessment of potentially toxic element pollution in soils and rice (Oryza sativa) in a typical area of the Yangtze River Delta. Environmental Pollution, 157(8–9), 2542–2549.
Hettiarachchi, G. M., Ryan, J. A., Chaney, R. L., & La Fleur, C. M. (2003). Sorption and desorption of cadmium by different fractions of biosolids-amended soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32(5), 1684–1693.
Impellitteri, C. A., Lu, Y., Saxe, J. K., Allen, H. E., & Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M. (2002). Correlation of the partitioning of dissolved organic matter fractions with the desorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from 18 Dutch soils. Environment International, 28(5), 401–410.
Jayatilake, N., Mendis, S., Maheepala, P., & Mehta, F. R. (2013). Chronic kidney disease of uncertain aetiology: Prevalence and causative factors in a developing country. BMC Nephrology, 14(1), 180.
Johri, N., Jacquillet, G., & Unwin, R. (2010). Heavy metal poisoning: The effects of cadmium on the kidney. BioMetals, 23(5), 783–792.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants (4th ed.). CRC Press.
Kamel, E. G., & EL-Minshawy, O. (2010). Environmental factors incriminated in the development of end stage renal disease in El-Minia Governorate, Upper Egypt. Journal of Nephro-urology 2(3), 431–437.
Khanam, R., Kumar, A., Nayak, A. K., Shahid, M., Tripathi, R., Vijayakumar, S., et al. (2020). Metal (loid) s (As, Hg, Se, Pb and Cd) in paddy soil: Bioavailability and potential risk to human health. Science of the Total Environment, 699, 134330.
Kirthisinghe, J. P., Kumaragamage, D., & Sultanbava, F. (2007). Evaluation of site-specific fertilizer recommendation for cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) in two locations in Sri Lanka. Tropical Agricultural Research, 19, 229–239.
Kosolsaksakul, P., Farmer, J. G., Oliver, I. W., & Graham, M. C. (2014). Geochemical associations and availability of cadmium (Cd) in a paddy field system, northwestern Thailand. Environmental Pollution, 187, 153–161.
Kowalska, J. B., Mazurek, R., Gąsiorek, M., & Zaleski, T. (2018). Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40(6), 2395–2420.
Krishnamurti, G. S. R., & Naidu, R. (2003). Solid–solution equilibria of cadmium in soils. Geoderma, 113(1–2), 17–30.
Lapegue, J. (2000). Chemical risks associated to the consumption of groundwater: The specificity of chronic renal failure in eastern areas of Sri Lanka. Trincomalee, Sri Lanka: Action Contre la Faim.
Liu, J., Li, K., Xu, J., Zhang, Z., Ma, T., Lu, X., et al. (2003). Lead toxicity, uptake, and translocation in different rice cultivars. Plant Science, 165(4), 793–802.
Mazurek, R., Kowalska, J., Gąsiorek, M., Zadrożny, P., Józefowska, A., Zaleski, T., et al. (2017). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere, 168, 839–850.
McLaughlin, M. J., Parker, D. R., & Clarke, J. M. (1999). Metals and micronutrients–food safety issues. Field Crops Research, 60(1–2), 143–163.
Molina, M., Aburto, F., Calderón, R., Cazanga, M., & Escudey, M. (2009). Trace element composition of selected fertilizers used in Chile: Phosphorus fertilizers as a source of long-term soil contamination. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 18(4), 497–511.
Müller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins-Veränderungen seit 1971. Umschau, 24, 773–778.
Nanayakkara, S., Senevirathna, S. T. M. L. D., Harada, K. H., Chandrajith, R., Hitomi, T., Abeysekera, T., et al. (2019). Systematic evaluation of exposure to trace elements and minerals in patients with chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 54, 206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.04.019
Nanayakkara, S., Senevirathna, S. T., Karunaratne, U., Chandrajith, R., Harada, K. H., Hitomi, T., et al. (2012). Evidence of tubular damage in the very early stage of chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology in the North Central Province of Sri Lanka: A cross-sectional study. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 17(2), 109–117.
Nguyen, T. P., Ruppert, H., Pasold, T., & Sauer, B. (2020). Paddy soil geochemistry, uptake of trace elements by rice grains (Oryza sativa) and resulting health risks in the Mekong River Delta. Vietnam. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(8), 2377–2397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00456-7
Norra, S., Berner, Z. A., Agarwala, P., Wagner, F., Chandrasekharam, D., & Stüben, D. (2005). Impact of irrigation with As rich groundwater on soil and crops: A geochemical case study in West Bengal Delta Plain. India. Applied Geochemistry, 20(10), 1890–1906.
O’Donnell, J. K., Tobey, M., Weiner, D. E., Stevens, L. A., Johnson, S., Stringham, P., et al. (2011). Prevalence of and risk factors for chronic kidney disease in rural Nicaragua. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 26(9), 2798–2805.
Olsen, S. R. (1954). Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate (Vol. 939): US Department of Agriculture.
Oorts, K. (2013). Copper. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils: Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability (pp. 367–394). Springer, Dordrecht.
Peralta-Videa, J. R., Lopez, M. L., Narayan, M., Saupe, G., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. (2009). The biochemistry of environmental heavy metal uptake by plants: Implications for the food chain. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 41(8–9), 1665–1677.
Rafique, N., & Tariq, S. R. (2016). Distribution and source apportionment studies of heavy metals in soil of cotton/wheat fields. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(5), 309.
Rango, T., Jeuland, M., Manthrithilake, H., & McCornick, P. (2015). Nephrotoxic contaminants in drinking water and urine, and chronic kidney disease in rural Sri Lanka. Science of the Total Environment, 518, 574–585.
Ratnayake, R. R., Perera, B. M. A. C. A., Rajapaksha, R. P. S. K., Ekanayake, E. M. H. G. S., Kumara, R. K. G. K., & Gunaratne, H. M. A. C. (2017). Soil carbon sequestration and nutrient status of tropical rice based cropping systems: Rice-Rice, Rice-Soya, Rice-Onion and Rice-Tobacco in Sri Lanka. CATENA, 150, 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.006
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(24), 5084–5091.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Science of the Total Environment, 337(1–3), 91–107.
Reimann, C., Filzmoser, P., & Garrett, R. G. (2002). Factor analysis applied to regional geochemical data: Problems and possibilities. Applied Geochemistry, 17(3), 185–206.
Rhoades, J. D. (1983). Cation Exchange Capacity. In A. L. Page (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties (2nd edition ed., pp. 149–157, Agronomy Monographs). USA: American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Soil Science Society of America, Inc.
Rosemary, F., Vitharana, U. W. A., Indraratne, S. P., & Weerasooriya, S. V. R. (2014). Concentrations of trace metals in selected land uses of a dry zone soil catena of Sri Lanka. Tropical Agricultural Research, 25(4), 512–522.
Sabolić, I. (2006). Common mechanisms in nephropathy induced by toxic metals. Nephron Physiology, 104(3), 107-p114.
Sanjeevani, U. K. P. S., Indraratne, S. P., Weerasooriya, R., & Rosemary, F. (2015). Baseline concentrations of some trace elements in Alfisols of Sri Lanka. Geoderma Regional, 4, 73–78.
Singh, N., Gupta, V. K., Kumar, A., & Sharma, B. (2017). Synergistic effects of heavy metals and pesticides in living systems. Frontiers in Chemistry, 5, 70.
Sirisena, D., & Suriyagoda, L. D. B. (2018). Toward sustainable phosphorus management in Sri Lankan rice and vegetable-based cropping systems: A review. Agriculture and Natural Resources, 52(1), 9–15.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17(5), 517–568.
Srivastav, A. L. (2020). Chemical fertilizers and pesticides: Role in groundwater contamination. In M.N.V. Pasad (Ed.), Agrochemicals detection, treatment and remediation (pp. 143–159): Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2018-0-02947-3.
Tatapudi, R. R., Rentala, S., Gullipalli, P., Komarraju, A. L., Singh, A. K., Tatapudi, V. S., et al. (2019). High prevalence of CKD of unknown etiology in Uddanam. India. Kidney International Reports, 4(3), 380–389.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2), 241–265.
Tiessen, H. J. W. B., & Moir, J. O. (1993). Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 7, 5–229.
Tóth, G., Hermann, T., Da Silva, M. R., & Montanarella, L. (2016). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environment International, 88, 299–309.
Van Kauwenbergh, S. J. Cadmium content of phosphate rocks and fertilizers. In International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA) Technical Conference, Chennai, India, 2002
Van Dervort, D. R., López, D. L., Orantes, C. M., & Rodríguez, D. S. (2014). Spatial distribution of unspecified chronic kidney disease in El Salvador by crop area cultivated and ambient temperature. MEDICC Review, 16, 31–38.
Vithanage, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Wijesekara, H., Weerarathne, N., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Effects of soil type and fertilizer on As speciation in rice paddy contaminated with As-containing pesticide. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(2), 837–847.
Weerasooriya, R., Tobschall, H. J., Wijesekara, H. K. D. K., Arachchige, E. K. I. A. U. K., & Pathirathne, K. A. S. (2003). On the mechanistic modeling of As (III) adsorption on gibbsite. Chemosphere, 51(9), 1001–1013.
Wijetunge, S., Ratnatunga, N. V. I., Abeysekera, D. T. D. J., Wazil, A. W. M., Selvarajah, M., & Ratnatunga, C. N. (2013). Retrospective analysis of renal histology in asymptomatic patients with probable chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka. Ceylon Medical Journal, 58(4), 142–147.
Swaddiwudhipong, W., Limpatanachote, P., Krintratun, S., & Padungtod, C. (2007). Cadmium-exposed population in Mae Sot District, Tak Province: 1. Prevalence of high urinary cadmium levels in the adults. J Med Assoc Thailand, 90(1), 143–148.
Yongming, H., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355(1–3), 176–186.
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. L. (2002). Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 54(6), 1051–1070.
Acknowledgements
This research work was conducted with financial support from the National Research Council, Sri Lanka (Grant NRC TO 14-05). Prof. R.B. Mapa is acknowledged for his numerous supports.
Funding
National Research Council, Sri Lanka (Grant NRC TO 14–05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB carried out the study, laboratory analyses, data curation, preliminary data interpretation, draft preparation. SD contributed for statistical analyses, data visualization, and draft preparation. OI designed the study edited the manuscript. SKY supervised the project. RC designed the study, acquired funding, and finalized the final version of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasooriya, S., Diyabalanage, S., Yatigammana, S.K. et al. Major and trace elements in rice paddy soils in Sri Lanka with special emphasis on regions with endemic chronic kidney disease of undetermined origin. Environ Geochem Health 44, 1841–1855 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01036-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01036-4