Abstract
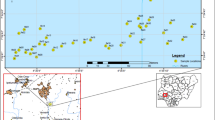
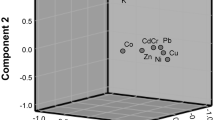
The rising number of chronic kidney disease patients with no identifiable cause (CKD of uncertain aetiology), prevalent in some areas of the dry zone of Sri Lanka is suspected to be related to the environmental exposure to heavy metals. Agricultural soils are well recognized as being contaminated with potentially toxic metals from various forms of fertilizers and agro-chemicals, which could easily enter the human body through the food chain. The objective of this paper is to determine the content of heavy metals and activity concentration of background radionuclides such as K-40, Ra-226 and Th-232, in rice field soils. Rice farming is the most common agricultural practice in the affected region and possible heavy metal sources such as fertilizers are applied in abundance in the rice fields. Soils collected from a rice field in a non-CKD region was used for the comparison. In dry zone soils, Ca, K, Ba, Pb and Zr contents were higher and Fe, Mn, Cr, Ni and Zn contents were lower compared to that of soils from the wet zone non-CKD region. However, the activity concentration of soils was mostly the same in all samples, except for the K-40 contents of the soils, which were higher in the rice field soils compared to the undisturbed forest soils and also to the world averages. The mean U content was 3.6 mg/kg in the studied soils, although extremely high uranium contents were found in some fertilizer samples particularly in the triple superphosphates. Most uranium applied via fertilizer could contaminate the drinking water sources and even low uranium concentrations in drinking water may cause nephrotoxic effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aturaliya TNC, Abeysekera DTDJ, Amerasinghe PH, Kumarasiri PV, Bandara P (2006) Towards understanding of chronic kidney disease of North Central Province. Proceedings of Annual Scientific Sessions of Sri Lanka Medical Association, 2006
Barbarick KA, Ippolito JA, Westfall G (1995) Biosolids effect on phosphorus, copper, zinc, nickel and molybdenum concentrations in dryland wheat. J Environ Qual 24:608–611
Beretka J, Mathew PJ (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, waste and byproducts. Health Phys 48:87–95. doi:10.1097/00004032-198501000-00007
Cao ZH, Hu ZY (2000) Copper contamination in paddy soils irrigated with wastewater. Chemosphere 41:3–6. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00383-5
Chandrajith R, Dissanayake CB, Tobschall HJ (2005a) The abundances of some rarer trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka. Chemosphere 58(10):1415–1420. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.09.090
Chandrajith R, Dissanayake CB, Tobschall HJ (2005b) Geochemistry of trace elements in paddy (rice) soils of Sri Lanka: implications on iodine deficiency disorders (IDD). Environ Geochem Health 27(1):55–64. doi:10.1007/s10653-004-2290-2
Chen W, Chang AC, Wu L (2007) Assessing long-term environmental risks of trace elements in phosphate fertilizers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:48–58. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.12.013
Dissanayake CB (1996) Water quality and dental health in the dry zone of Sri Lanka. In: Appleton JD, Fuge R, McCall GJH (eds) Environmental geochemistry and health. Geological Society Special Publication, UK, pp 131–140
Dissanayake CB, Chandrajith R (1999) Medical geochemistry of tropical environments. Earth Sci Rev 7:219–258. doi:10.1016/S0012-8252(99)00033-1
Dissanayake CB, Chandrajith R (2006) Inorganic aspects of medical geology. Z dt Ges Geowiss 157(3):9–18
Ganashan P, Balendira S, Dassanayake MD (1996) Sri Lanka country report to the FAO: International technical conference on plant genetic resources. FAO, Leipzig, p 96
Ghosh D, Deb A, Bera S, Sengupta R, Patra KK (2008) Measurement of natural radioactivity in chemical fertilizer and agricultural soil: evidence of high alpha activity. Environ Geochem Health 30:79–86. doi:10.1007/s10653-007-9114-0
Haleem AS, Sroor A, El-Bahi SM, Zohny E (2001) Heavy metals and rare earth elements in phosphate fertilizer components using instrumental neutron activation analysis. Appl Radiat Isot 55:569–573. doi:10.1016/S0969-8043(01)00098-7
Kurttio P, Auvinen A, Saloven L, Saha H, Pekkanen J, Makelainen I, Vaisanen SB, Penttila IM, Komulainen H (2002) Renal effects of uranium in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 110(4):337–342
Makweba WM, Holm E (1993) The natural radioactivity of the rock phosphate, phosphatic products and their environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 133(1–2):99–110. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(93)90115-M
Mermut AR, Jain JC, Song L, Kerrich R, Kozak L, Jana S (1996) Trace element concentrations of selected soils and fertilizers in Saskatchewan Canada. J Environ Qual 25:845–853
Mortvedt JJ (1996) Heavy metal contaminants in inorganic and organic fertilizers. Fertil Res 43:55–61. doi:10.1007/BF00747683
Navaratne URB, Dissanayake CB, Perera PSA (1994) The geochemistry of alkali and alkaline earth metals in soils of the Central Province of Sri Lanka. J Geol Soc Sri Lanka 5:105–113
NCRP (1984) Exposures from the uranium series with emphasis on radon and its daughters. Report (No 77) Bethesda MD National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP)
Panabokke CR (1996) Soils and agro-ecological environments of Sri Lanka. NARESA, Colombo, p 220
Sam AK, Holm E (1995) The natural radioactivity in phosphate deposits from Sudan. Sci Total Environ 162(2–3):173–178. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04452-7
Takeda A, Tsukuda H, Takaku Y, Hisamatsu S, Nanzyo M (2006) Accumulation of uranium derived from long-term fertilizer applications in a cultivated Andisol. Sci Total Environ 367:924–931. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.01.006
Tsumura A, Yamasaki IM (1993) Behaviour of uranium, thorium and lanthanides in paddy fields. Radioisotopes 42:265–272
UNSCEAR (1993) United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, Exposure from Natural Sources of Radiation 1993. Report to the General Assembly
van Kauwenbergh SJ (2002) Cadmium content of phosphate rocks and fertilizers. IFA technical conference, Chennai, India 24–27 September 2002, p 31
Wang XC, Yan WD, An Z, Lu Q, Shi WM, Cao ZH, Wong MH (2003) Status of trace elements in paddy soil and sediment in Taihu Lake region. Chemosphere 50:707–710. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00209-6
Zamora ML, Tracy BL, Zielinski JM, Meyerhof DP, Moss MA (1998) Chronic ingestion of uranium in drinking water: a study of kidney bioeffects in humans. Toxicol Sci 43:68–77. doi:10.1093/toxsci/43.1.68
Zielinski RA, Asher-Bolinder S, Meier AL, Johnson CA, Szabo BJ (1997) Natural or fertilizer-derived uranium in irrigation drainage: a case study in southeastern Colorado, USA. Appl Geochem 12:9–21. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(96)00050-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrajith, R., Seneviratna, S., Wickramaarachchi, K. et al. Natural radionuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environ Earth Sci 60, 193–201 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0179-1