Abstract
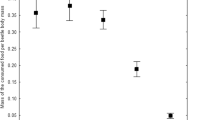
The aim of the work was to study effects of suboptimal temperature on nickel toxicity under chronic exposure and to apply the Multispecies Freshwater Biomonitor® (MFB®) for the first time to soil organisms in order to link behavioral to physiological endpoints. Ground beetles Pterostichus oblongopunctatus were reared at 10 or 20°C on control or Ni-contaminated (2500 mg Ni kg−1) food. After 64 days half of the Ni-exposed beetles were transferred to uncontaminated food (elimination phase). The remaining Ni-exposed beetles were left on the contaminated food to the end of the experiment (96 days). After completing the experiment, respiration rate and locomotor activity were measured in Ni-contaminated beetles (Ni), Ni-contaminated ones after elimination (E), and controls (C). Then, the beetles were analyzed for Ni body loads. The respiration rate, which was always measured at 20°C for all experimental groups, was highest in Ni beetles reared at 10°C and did not differ between groups C and E. Similarly, locomotor activity was highest in Ni beetles, and marginally significant temperature effect was found. The study indicated thus that exposure to elevated Ni concentrations increased the maintenance costs in P. oblongopunctatus and that rearing the beetles at suboptimal temperature increased the respiration rate even further. However, the effects observed in both respiration rate and locomotor activity were reversible after decontamination. The study demonstrated also the potential of MFB® for assessing the behavior of soil-dwelling organism in environmental toxicology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley M (2002) Basic behaviour: the use of animal locomotion in behavioural ecotoxicology. In: Dell’Omo G (ed) Behavioural ecotoxicology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 211–230
Bayley M, Baatrup E, Heimbach U, Bjerregaard P (1995) Elevated copper levels during larval development cause altered locomotor behavior in the adult carabid beetle Pterostichus cupreus L. (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 32:166–170
Bayley M, Baatrup E, Bjerregaard P (1997) Woodlouse locomotor behavior in the assessment of clean and contaminated field sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:2309–2314
Bednarska AJ, Laskowski R (2008) Effects of nickel and temperature on the ground beetle, Pterostichus oblongopunctatus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Ecotoxicology 17:189–198
Brunsting AMH (1981) Distribution patterns, life cycle and phenology of Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F. (Col., Carabidae) and Philonthus decorus grav. (Col., Staphylinidae). Neth J Zool 31:418–452
Brunsting AMH, Heessen HJL (1984) Density regulation in the carabid beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus. J Anim Ecol 53:751–760
Butler CD, Beckage NE, Trumble JT (2009) Effects of terrestrial pollutants on insect parasitoids. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1111–1119
Chaabane K, Josens G, Loreau M (1999) Respiration of Abax ater (Coleoptera, Carabidae): a complex parameter of the energy budget. Pedobiologia 43:305–318
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech J-M (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Donker MH, Abdel-Lateif HM, Khalil MA, Bayoumi BM, Van Straalen NM (1998) Temperature physiological time, and zinc toxicity in the isopod Porcelio scaber. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:1558–1563
Engenheiro EL, Hankard PK, Sousa JP, Lemos MF, Weeks JM, Soares AMVM (2005) Influence of dimethoate on acetylcholinesterase activity and locomotor function in terrestrial isopods. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:603–609
Ermler U, Grabarse W, Shima S, Goubeaud M, Thauer R (1998) Active sites of transition-metal enzymes with focus on nickel. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8:749–758
Everhart JL, McNear D, Peltier E, Van der Lelie D, Chaney RL, Sparks DL (2006) Assessing nickel bioavailability in smelter-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 367:732–744
Gerhardt A, Clostermann M, Fridlund B, Svensson E (1994) Monitoring of behavioral patterns of aquatic organisms with an impedance conversion technique. Environ Int 20:209–219
Gerhardt A, Carlsson A, Ressemann C, Stich KP (1998) A new online biomonitoring system for Gammarus pulex (L.) (Crustacea): in situ test below a copper effluent in South Sweden. Environ Sci Technol 32:150–156
Gerhardt A, Schmidt S, Höss S (2002) Measurement of movement patterns of Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda) with the Multispecies Freshwater Biomonitor® (MFB) a potential new method to study a behavioural toxicity parameter of nematodes in sediments. Environ Pollut 120:513–516
Gerhardt A, Janssens de Bisthoven L, Soares AMVM (2005) Evidence for the stepwise stress model: Gambusia holbrooki and Daphnia magna under AMD and ACID stress. Environ Sci Technol 39:4150–4158
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in invertebrates. Elsevier, Applied Science, London, England
Janczur M, Kozłowski J, Laskowski R (2000) Optimal allocation, life history and metal accumulation: a dynamic programming model. In: Kammenga J, Laskowski R (eds) Demography in ecotoxicology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 179–197
Jensen CS, Garsdal L, Baatrup E (1997) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition and altered locomotor behavior in the carabid beetle Pterostichus cupreus. A linkage between biomarkers at two levels of biological complexity. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1727–1732
Khan MAQ, Ahmed SA, Salazar A, Gurumendi J, Khan A, Vargas M, von Catalin B (2007) Effect of temperature on heavy metal toxicity to earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Annelida: Oligochaeta). Environ Toxicol 22:487–494
Kienle C, Gerhardt A (2008) Behavior of Corophium volutator (Crustacea, Amphipoda) exposed to the water-accommodated fraction of oil in water and sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:599–604
Kramarz P (1999) Dynamics of accumulation and decontamination of cadmium and zinc in carnivorous invertebrates. 1. The ground beetle, Poecilus cupreus L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63:531–537
Lagisz M, Kramarz P, Niklińska M (2005) Metal kinetics and respiration rates in F1 generation of carabid beetles (Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F.) originating from metal-contaminated and reference areas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:484–489
Laskowski R, Maryański M, Pyza E, Wojtusiak J (1996) Sublethal toxicity tests for long-lived invertebrates: searching for a solution. In: Van Straalen NM, Krivolutsky DA (eds) Bioindicator systems for soil pollution NATO ASI Series, 2: Environment. Kluwer, Dordrecht/Boston/London, pp 45–55
Lock K, Janssen CR (2002) Ecotoxicity of nickel to Eisenia fetida, Enchytraeeus albidus and Folsomia candida. Chemosphere 46:197–200
Lukasik P, Laskowski R (2007) Increased respiration rate as a result of adaptation to copper in confused flour beetle, Tribolium confusum Jacquelin du Val. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:311–314
Migula P (1989) Combined and separate effects of cadmium, lead and zinc on respiratory metabolism during the last larval stage of the house cricket, Acheta domesticus. Biologia (Bratislava) 44:513–521
Perrin N, Sibly RM (1993) Dynamic models of energy allocation and investment. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 24:379–410
Potvin C, Roff DA (1993) Distribution-free and robust statistical methods—viable alternatives to parametric statistics. Ecology 74:1617–1628
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Zehnder C, Congdon JD (2001) Metabolic costs incurred by crayfish (Procambarus acutus) in a trace element-polluted habitat: further evidence of similar responses among diverse taxonomic groups. Comp Biochem Physiol C 129:275–283
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Krogh PH, Hopkin SP (1999) Toxicity of nickel to a soil-dwelling springtail, Folsomia fimetaria (Collembola: Isotomidae). Ecotox Environ Safe 43:57–61
Sibly RM, Calow P (1989) A life-cycle theory of responses to stress. Biol J Linn Soc 37:101–116
Sjursen H, Holmstrup M (2004) Cold and drought stress in combination with pyrene exposure: studies with Protaphorura armata (Collembola: Onychiuridae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:145–152
Slotkin TA, MacKillop EA, Ryde JT, Tate CA, Seidler FJ (2007) Screening for development neurotoxicity using PC12 cells: comparisons of organophosphates with carbamate, an organochlorine, and divalent nickel. Environ Health Perspect 115:93–101
Smit CE, Van Gestel CAM (1997) Influence of temperature on the regulation and toxicity of zinc in Folsomia candida (Collembola). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 37:213–222
Sørensen FF, Bayley M, Baatrup E (1995) The effects of sublethal dimethoate exposure on the locomotor behavior of the collembolan Folsomia candida (Isotomidae). Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1587–1590
Sørensen FF, Weeks JM, Baatrup E (1997) Altered locomotory behavior in woodlice (Oniscus Asellus (L.)) collected at a polluted site. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:685–690
Spurgeon DJ, Tomlin MA, Hopkin SP (1997) Influence of temperature on the toxicity of zinc to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58:283–290
S.-Rózsa K, Salánki J (1990) Heavy metals regulate physiological and behavioral events by modulation ion channels in neuronal membranes of molluscs. Environ Monit Assess 14:363–375
Walker CH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2006) Principles of ecotoxicology, 3rd edn. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the EU NoMiracle project (Novel Methods for Integrated Risk Assessment of Cumulative Stressors in Europe, No. 003956 GOCE) to LimCo International and Jagiellonian University, SPUB (No. 158/E-338/6. PR UE/DIE 279/2005-2008), and the Jagiellonian University (DS 758). We thank Michael Jacobs for language adjustments. We also thank the Olkusz Forest Service for permission to collect animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
“Capsule”: Activity and respiration increased in Ni-intoxicated beetles but returned to normal levels after decontamination.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bednarska, A.J., Gerhardt, A. & Laskowski, R. Locomotor activity and respiration rate of the ground beetle, Pterostichus oblongopunctatus (Coleoptera: Carabidae), exposed to elevated nickel concentration at different temperatures: novel application of Multispecies Freshwater Biomonitor® . Ecotoxicology 19, 864–871 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0467-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0467-2