Abstract
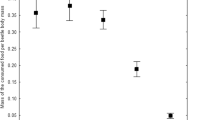
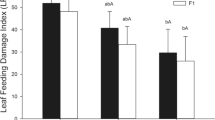
We investigated resistance to metals in carabid beetles inhabiting metal-polluted and reference areas. Chronic multigeneration exposure to toxic metal concentrations may potentially result in adaptation through decreased metal uptake rate and/or increased excretion rate. The cost of resistance to pollution could be associated with increased metabolic rate. To test these predictions, laboratory cultured F1-generation beetles originating from metal-polluted and reference sites were exposed to food contaminated with zinc and/or cadmium for 10 weeks. After that, uncontaminated food was offered to the animals for another 3 weeks. During the experiment, internal concentrations of Cd and Zn were measured as were respiration rates of the animals. The results obtained show no significant differences in metal accumulation and excretion patterns or respiration rates between the populations. This may suggest that adaptation has not occurred in the beetles chronically exposed to toxic metal concentrations. The possible explanations for the lack of differences between the populations are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
VM Devi (1997) ArticleTitleBioaccumulation and metabolic effects of cadmium on marine fouling dressinid bivalve, Mytilopsis sallei (Recluz) Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31 47–53 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002449900077
MH Donker (1992) Phsyiology of metal adaptation in the isopod Porcellio scaber Doctrol thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands
SP Hopkin (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in invertebrates Elsevier Applied Science London, England
WA Hopkins CL Rowe JD Congdon (1999) ArticleTitleElevated trace element concentrations and standard metabolic rate in banded water snakes (Nerodia fascinata) exposed to coal combustion wastes Environ Toxicol Chem 18 1258–1263 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjt1SrtLY%3D
MPM Janssen (1991) Comparison of cadmium kinetics in four soil arthropod species Doctrol thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, The Netherlands
DT Jones SP Hopkin (1998) ArticleTitleReduced survival and body size in the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber from a metal-polluted environment Environ Pollut 99 215–223 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktFeltLY%3D Occurrence Handle15093314
MA Khalil MH Donker NM Straalen ParticleVan (1995) ArticleTitleLong-term and short-term changes in the energy budget of Porcellio scaber Latreille (Crustacea) exposed to cadmium polluted food Eur J Soil Biol 31 163–172 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xhs1Sns70%3D
P Kramarz (1999) ArticleTitleDynamic of accumulation and decontamination of cadmium and zinc in carnivorous invertebrates. 1. The ground beetle, Poecilus cupreus L Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63 538–546 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmslOitrY%3D Occurrence Handle10501734
Kramarz P, Laskowski R, Stone D, Zygmunt P, Wojewodzic M (2001) Influence of chronic metal pollution on survival of carabid beetles exposed to additional intoxication. Proceedings of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Europe 11th Annual Meeting, Madrid, Spain, May 6–10, 2001, p 136
P Kramarz A Kafel (2003) ArticleTitleThe respiration rate of the beet armyworm pupae (Spodoptera exigua) after multi-generation intoxication with cadmium and zinc Environ Pollut 126 1–3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlt1eitro%3D Occurrence Handle12860096
M Lagisz R Laskowski (2002a) ArticleTitleRespiratory metabolism in Pterostichus oblongopunctatus originating from metal contaminated and reference area Fresenius Environ Bull 11 74–77 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XisFOgtb0%3D
Lagisz M, Laskowski R (2002b) Effects of metal pollution on the ground beetle—Linking population parameters and metabolic characteristics. Proceedings of the Society of Environmental Europe 12th Annual Meeting, Vienna, Austria, May 12–17, 2002, p 177
M Lagisz R Laskowski P Kramarz M Tobor (2002) ArticleTitlePopulation parameters of the beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F. from metal contamined and reference areas Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69 243–249 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmt1WjurY%3D Occurrence Handle12107701
R Laskowski (1991) ArticleTitleAre the top carnivores endangered by heavy metal biomagnification? Oikos 60 387–390
R Laskowski M Maryański E Pyza J Wojtusiak (1996) Sublethal toxicity tests for long-lived invertebrates: Searching for a solution NM Straalen Particlevan DA Krivolutsky (Eds) Bioindicator Systems for soil pollution NATO ASI Series, 2: Environment. Volume 16 Kluwer Dordrecht/Boston/London 45–55
P Migula (1986) ArticleTitleCombined and separate effects of cadmium, lead and zinc on respiratory metabolism during the last larval stage of the house cricket, Acheta domesticus Biologia (Bratisl) 44 513–521
TJ Mozdzer P Kramarz A Piśkiewicz M Niklińska (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of cadmium and zinc on larval growth and survival in the ground beetle, Pterostichus oblongopunctatus Environ Int 28 737–742 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsVymsLY%3D Occurrence Handle12605922
SL Pandeswara PR Yallaprogada (2000) ArticleTitleTolerance, accumulation and depuration in an intertidal gastropod, Turbo intercostalis, exposed to cadmium Mar Environ Res 50 103–106 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0141-1136(00)00165-3
L Posthuma NM Straalen ParticleVan (1993) ArticleTitleHeavy-metal adaptation in terrestrial invertebrates: A review of occurrence, genetics, physiology and ecological consequences Comp Biochem Physiol 106 11–38
CL Rowe (1998) ArticleTitleElevated standard metabolic rate in a freshwater shrimp (Palaemonetes paludosus) exposed to trace element-rich coal combustion waste Comp Biochem Physiol 121 299–304 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0305-0491(98)10103-7
CL Rowe OM Kinney RD Nagle JD Congdon (1998) ArticleTitleElevated maintenance costs in an anuran (Rana catesbeiana) exposed to a mixture of trace elements during the embryonic and early larval periods Physiol Zool 71 27–35 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7jt1WmsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9472810
GH Schmidt NMM Ibrahim MD Abdallah (1992) ArticleTitleLong-term effects of heavy metals in food on development of Aioolopus thalassinus (Saltatoria: Acrididae) Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 23 375–382 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlvVKgsbc%3D Occurrence Handle1456784
RM Sibly P Calow (1989) ArticleTitleA life-cycle theory of responses to stress Biol J Linn Soc Lond 37 101–116
D Stone P Jepson P Kramarz R Laskowski (2001) ArticleTitleTime to death response in carabid beetles exposed to multiple stressors along a gradient of heavy metal pollution Environ Pollut 113 239–244 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvFGhsLY%3D Occurrence Handle11383341
D Stone P Jepson R Laskowski (2002) ArticleTitleTrends in detoxification enzymes and heavy metal accumulation in ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) inhabiting a gradient of pollution Comp Biochem Physiol 32 105–112
CH Walker SP Hopkin RM Sibly DB Peakall (2001) Principles of ecotoxicology. Taylor Francis
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to R. Laskowski, M. Maryanski, A. Piskiewicz, and M. Wojewodzic for their assistance and advice. Financial support came from National Committee for Scientific Research (Grant no. 6 P04F 072 20) and Jagiellonian University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lagisz, M., Kramarz, P. & Niklinska, M. Metal Kinetics and Respiration Rates in F1 Generation of Carabid Beetles (Pterostichus oblongopunctatus F.) Originating From Metal-Contaminated and Reference Areas. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48, 484–489 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0023-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0023-2