Abstract
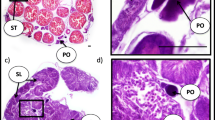
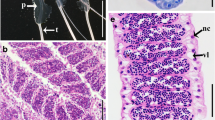
The reproductive anatomy of gobiid fishes (Family Gobiidae) exhibits remarkable morphological diversity and complexity. However, there has been little in the way of detailed anatomical descriptions of species-specific reproductive anatomy among gobiid fishes that could be used to generate hypotheses of homology. Consequently, identifying valid reproductive synapomorphies among extant gobiid lineages remains problematic. Gobiodon oculolineatus, an obligate coral-dwelling fish, exhibits several unusual modifications of the reproductive complex associated with its hermaphroditic sexual pattern and with the production and storage of secretory material. All post-indifferent individuals had either an ovariform gonad or an ovotestis. In addition, all individuals had fully developed secretory structures derived from the gonoduct wall with secretory activity being greatest among male-active fish. Among male-active fish, part of the ovotestis was modified for the storage of secreted material. Based on current reportage, the combination of features seen in G. oculolineatus is unique, with the exception of a congener, G. okinawae, the only other species in the genus for which detailed information on reproductive anatomy is available. This study represents the first step towards identifying and characterizing the functional and anatomical components of the reproductive system in a gobiid taxon in order to develop testable hypotheses regarding homology and the nature of adaptive modifications of various components of the gobiid reproductive system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akihito [Prince], Iwata A, Kobayashi T, Ikeo K, Imanishi T, Ono H, Umehara Y, Hamamatsu C, Sugiyama K, Ikeda Y, Sakamoto K, Fumihito A, Ohno S, Gojobori T (2000) Evolutionary aspects of gobioid fishes based upon a phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial cytochrome b genes. Gene 259:5–15. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00488-1
Arai R (1964) Sex characters of Japanese gobioid fishes. Bull Natl Sci Mus, Tokyo 7:295–306
Asahina K, Suzuki K, Aida K, Hibiya T, Tamaoki B (1985) Relationship between the structures and steroidogenic functions of the testes of the urohaze-goby (Glossogobius olivaceus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 57:281–292. doi:10.1016/0016-6480(85)90273-4
Arbuckle WJ, Bélangera AJ, Corkum LD, Zielinski BS, Li W, Yun S-S, Bachynski S, Scott AP (2005) In vitro biosynthesis of novel 5β-reduced steroids by the testis of the round goby, Neogobius melanostomus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 140:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.09.014
Bonnin PJ (1975) Organotype culture of glandular tissue of the testis of Gobius niger L. Association with hypophysis. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 169:548–552. (Comptes rendus des séances de la Société de biologie et de ses filiales)
Brusléa S (1987) Sex-inversion of the hermaphroditic, protogynous teleost Coris julis L. (Labridae). J Fish Biol 30:605–616. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1987.tb05788.x
Bruslé S, Bruslé J (1978) An ultrastructural study of early germ cells in Mugil (Liza) auratus Risso, 1810 (Teleostei : Mugilidae). Ann Biol anim Bioch Biophys 18:1141–1153
Bruslé-Sicard S, Debas L, Fourcault B, Fuchs J (1992) Ultrastructural study of sex inversion in a protogynous hermaphrodite, Epinephelus microdon (Teleostei, Serranidae). Reprod Nutr Dev 32:393–406. doi:10.1051/rnd:19920409
Cole KS (1988) Predicting the potential for sex-change on the basis of ovarian structure in gobiid fishes. Copeia 1988:1082–1086. doi:10.2307/1445741
Cole KS (1990) Patterns of gonad structure in hermaphroditic gobies. Environ Biol Fishes 28:125–142. doi:10.1007/BF00751032
Cole KS (2008) Transient ontogenetic expression of hermaphroditic gonad morphology within the Gobiosoma group of the Neotropical seven-spined gobies (Teleostei: Gobiidae). Mar Biol (Berl) 154:943–951. doi:10.1007/s00227-008-0986-z
Cole KS, Shapiro DY (1992) Gonadal structure and population characteristics of the protogynous goby Coryphopterus glaucofraenum. Mar Biol (Berl) 113:1–9. doi:10.1007/BF00367632
Cole KS, Robertson DR (1988) Protogyny in the Caribbean reef goby, Coryphopterus personatus: gonad ontogeny and social influences on sex change. Bull Mar Sci 42:317–333
Cole KS, Hoese DF (2001) Gonad morphology, colony demography and evidence for hermaphroditism in Gobiodon okinawae (Teleostei, Gobiidae). Environ Biol Fishes 61:161–173. doi:10.1023/A:1011032228716
Cole KS, Robertson DR, Cedeño AA (1994) Does gonad structure reflect sexual pattern in all gobiid fishes? Environ Biol Fishes 41:301–309
Colombo L, Burighel P (1974) Fine structure of the testicular gland of the black goby, Gobius jozo L. Cell Tissue Res 154:39–49. doi:10.1007/BF00221070
Colombo L, Marconato A, Belvedere PC, Friso C (1980) Endocrinology of teleost reproduction: a testicular steroid pheromone in the black goby, Gobius jozo L. Boll Zool 47:355–364
Doitsidou M, Reichman-Fried M, Stebler J, Köprunner M, Dörries J, Meyer D, Esguerra CV, Leung T, Raz E (2002) Guidance of PGC migration by the chemokine SDF-1. Cell 111:647–659. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01135-2
Egami N (1960) Comparative morphology of the sex characters in several species of Japanese gobies, with reference to the effects of sex steroids on the characters. J Fac Sci, Univ Tokyo. Sec IV 9:67–100
Essenberg JM (1923) Sex-differentiation in the viviparous teleost Xiphophorus helleri Heckel. Biol Bull 45:46–97. doi:10.2307/1536637
Harold AS, Winterbottom R, Munday PL, Chapman RW (2008) Phylogenetic relationships of Indo-pacific coral gobies of the genus Gobiodon (Teleostei: Gobiidae), based on morphological and molecular data. Bull Mar Sci 82:119–136
Hiatt RW, Strasburg DW (1960) Ecological relationships of the fish fauna on croal reefs of the Marshall Islands. Ecol Monogr 30:65–127. doi:10.2307/1942181
Hoese DF, Gill AC (1993) Phylogenetic relationships of eleotrid fishes (Perciformes: Gobioidei). Bull Mar Sci 52:415–440
Kroon FJ, Munday PL, Westcott DA, Hobbs JP, Liley NR (2005) Aromatase pathway mediates sex change in each direction. Proc Royal Soc London. Biol Sci 272:1399–1405. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3097
Kurokawa H, Aoki Y, Nakamura S, Ebe Y, Kobayash D, Tanaka M (2006) Time-lapse analysis reveals different modes of primordial germ cell migration in the medaka Oryzias latipes. Dev Growth Differ 48:209–221. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169X.2006.00858.x
Lee Y-H, Du J-L, Yueh W-S, Lin B-Y, Huang J-D, Lee C-Y, Lee M-F, Lau E-L, Lee F-Y, Morrey C, Nagahama Y, Chang C-F (2001) Sex change in the protandrous black porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegeli: a review in gonadal development, estradiol, estrogen receptor, aromatase activity and gonadotropin. J Exp Zool 290:715–726. doi:10.1002/jez.1122
Lo Nostro F, Grier H, Andreone L, Guerrero GA (2003) Involvement of the gonadal germinal epithelium during sex reversal and seasonal testicular cycling in the protogynous swamp eel, Synbranchus marmoratus Bloch 1795 (teleostei, synbranchidae). J Morphol 257:107–126. doi:10.1002/jmor.10105
Miller PJ (1984) The tokology of gobioid fishes. In: Potts GW, Wootton RJ (eds) Fish reproduction: strategies and tactics. Academic Press, London, England, pp 119–153
Miller PJ (1986) Reproductive biology and systematic problems in gobioid fishes. In: Uyeno T, Arai R, Taniuchi T, Matsuura K (eds) Indo-Pacific fish biology. Tokai Univ Press, Tokyo, Japan, pp 640–647
Miller PJ (1992) The sperm duct gland: a visceral synapomorphy for gobioid fishes. Copeia 1992:253–256. doi:10.2307/1446565
Munday PL (2002) Bi-directional sex change: testing the growth-rate advantage model. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 52:247–254. doi:10.1007/s00265-002-0517-8
Munday PL, Jones GP, Caley MJ (1997) Habitat specialisation and the distribution and abundance of coral-dwelling gobies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 152:227–239. doi:10.3354/meps152227
Munday PL, Caley MJ, Jones GP (1998) Bi-directional sex change in a coral-dwelling goby. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 43:371–377. doi:10.1007/s002650050504
Munday PL, Harold AS, Winterbottom R (1999) Guide to the coral-dwelling gobies, genus Gobiodon (Gobiidae) from Papua New Guinea and the Great Barrier Reef. Rev Fr Aquariol 26:49–54
Munday PL, Cardoni AM, Syms C (2006) Cooperative growth regulation in coral-dwelling fishes. Biol Lett 2:355–358. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2006.0488
Nakashima Y, Kuwamua T, Yogo Y (1996) Both-ways sex change in monogamous coral gobies, Gobiodon spp. Environ Biol Fishes 46:281–288. doi:10.1007/BF00005004
Parmentier HK, Timmermans LPM (1985) The differentiation of germ cells and gonads during development of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). A study with anti-carp sperm monoclonal antibodies. J Embryol Exp Morphol 90:13–32
Pezold F (1993) Evidence for monophyletic Gobiinae. Copeia 1993:634–643. doi:10.2307/1447224
Rasotto MB, Mazzoldi C (2002) Male traits associated with alternative reproductive tactics in Gobius niger. J Fish Biol 61:173–184. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb01744.x
Stanley H, Chieffi G, Botte V (1965) Histological and histochemical observations on the testis of Gobius paganellus. Zeit. Zellforsch 65:350–362. doi:10.1007/BF00345636
Suzuki A, Tanaka M, Shibata N (2004) Expression of aromatase mRNA and effects of aromatase inhibitor during ovarian development in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. J Exp Zool 310A:266–273. doi:10.1002/jez.a.20027
Thacker CE (2003) Molecular phylogeny of the gobioid fishes (Teleostei: Perciformes: Gobioidei). Mol Phylogenet Evol 26:354–368. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00361-5
Timmermans LPM, Taverne N (1983) Origin and differentiation of primordial germ cells (PGC’s) in the rosy barb, Barbus conchonius, (Cyprinidae, Teleostei). Acta Morphol Neerl Scand 21:182
Tyler JC (1971) Habitat preferences of the fishes that dwell in shrub corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Proc Acad Nat Sci 123:1–26
Young RT, Fox DL (1937) The seminal vesicles of the goby, with preliminary chemical and physiological studies of the vesicular fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 23:461–467. doi:10.1073/pnas.23.8.461
Xia L, Cheng H, Yu H, Guo Y, Zhou R (2004) Molecular cloning and expression of the osteoclast-stimulating-factor-like gene from the rice field eel. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol 302:174–181. doi:10.1002/jez.b.20008
Acknowledgments
Portions of this study were supported by an Australian Museum Curatorial Fellowship to the author and from funds provided by the University of Hawaii at Manoa. I thank D. Hoese for his sponsorship and innumerable helpful conversations, S. Reader for field collection assistance, Ellyn Tong for the artwork for Figure 1, B. Vine for help with digital imaging, A. Dewan for statistical assistance, T. Harold for information on Gobiodon phylogenetics, F. Pezold for insightful comments on the manuscript and informative discussions and two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, K.S. Modifications of the reproductive complex and implications for the reproductive biology of Gobiodon oculolineatus (Teleostei: Gobiidae). Environ Biol Fish 84, 261–273 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-008-9433-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-008-9433-8