Summary
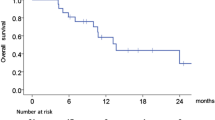
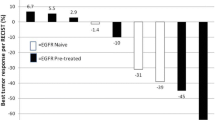
Background The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase pathway is often altered in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), and is involved in the resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Objective We investigated the dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs), maximum tolerated dose, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of the combination of copanlisib, an intravenous, pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, with the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab in recurrent and/or metastatic HNSCC patients in a phase I dose-escalation trial. Patients and methods Copanlisib was given intravenously on days 1, 8, and 15 of 28-day cycles at the dose of 45 mg and 30 mg, in combination with standard doses of weekly cetuximab (400 mg/m2 loading dose followed by 250 mg/m2 on days 8, 15, and 22, and weekly thereafter). Results Three patients received copanlisib 45 mg, of whom two experienced grade 3 hyperglycemia during Cycle 1 that met the DLT criteria. Eight patients were then treated with copanlisib at the dose of 30 mg. Because of the occurrence of hyperglycemia, a premedication with metformine was introduced on the day of the injections. No DLTs were reported at this dose level. The trial was stopped early because of the unfavourable toxicity profile of the combination. Among eight evaluable patients for response, four patients (50%) had disease stabilization according to RECIST1.1 as best response. Conclusion Copanlisib combined with cetuximab demonstrated unfavorable toxicity and limited efficacy in heavily pretreated recurrent and/or metastatic HNSCC patients.
Trial registration NCT02822482, Date of registration: June 2016.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ (2009) Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:627–644. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2926
Lui VWY, Hedberg ML, Li H et al (2013) Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov 3:761–769. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0103
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2015) Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 517:576–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14129
Rebucci M, Peixoto P, Dewitte A et al (2011) Mechanisms underlying resistance to cetuximab in the HNSCC cell line: role of AKT inhibition in bypassing this resistance. Int J Oncol 38:189–200
D’Amato V, Rosa R, D’Amato C et al (2014) The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PKI-587 enhances sensitivity to cetuximab in EGFR-resistant human head and neck cancer models. Br J Cancer 110:2887–2895. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.241
Soulières D, Faivre S, Mesía R et al (2017) Buparlisib and paclitaxel in patients with platinum-pretreated recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (BERIL-1): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30064-5
Patnaik A, Appleman LJ, Tolcher AW et al (2016) First-in-human phase I study of copanlisib (BAY 80–6946), an intravenous pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Ann Oncol 27:1928–1940. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw282
Dreyling M, Santoro A, Mollica L et al (2020) Long-term safety and efficacy of the PI3K inhibitor copanlisib in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of the CHRONOS-1 study. Am J Hematol 95:362–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25711
Klinghammer K, Politz O, Eder T et al (2020) Combination of copanlisib with cetuximab improves tumor response in cetuximab-resistant patient-derived xenografts of head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 11:3688–3697. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27763
Dreyling M, Santoro A, Mollica L et al (2017) Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibition by Copanlisib in Relapsed or Refractory Indolent Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 35:3898–3905. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.75.4648
Shepherd PR, Withers DJ, Siddle K (1998) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: the key switch mechanism in insulin signalling. Biochem J 333:471–490. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3330471
Knight ZA, Gonzalez B, Feldman ME et al (2006) A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for p110alpha in insulin signaling. Cell 125:733–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.035
Bøje CR, Dalton SO, Primdahl H et al (2014) Evaluation of comorbidity in 9388 head and neck cancer patients: a national cohort study from the DAHANCA database. Radiother Oncol 110:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2013.11.009
Flinn IW, Kahl BS, Leonard JP et al (2014) Idelalisib, a selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-δ, as therapy for previously treated indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 123:3406–3413. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-11-538546
Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S et al (2014) PI3Kδ inhibition by idelalisib in patients with relapsed indolent lymphoma. N Engl J Med 370:1008–1018. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1314583
Drug Approval Package: ALIQOPA (copanlisib) (2021) https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/209936Orig1_toc.cfm. Accessed 1 Jun 2021
Jimeno A, Shirai K, Choi M et al (2015) A randomized, phase II trial of cetuximab with or without PX-866, an irreversible oral phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with relapsed or metastatic head and neck squamous cell cancer. Ann Oncol 26:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu574
Acknowledgements
We thank the participating patients, the UNICANCER Head and Neck research team, Marta Jimenez, Celia Dupain, and Linda Larbi Cherif.
Funding
The study was funded by Bayer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
CLT, MA, KR, JG, and MC wrote the protocol. CLT, NI, ESB, FR, EB, MA, and DV contributed to the recruitment and treatment of patients in the trial. All authors contributed to the acquisition of data, the analysis, and the interpretation of data. CLT and GM designed the figures and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflicts of interest
CLT participated in advisory boards from MSD, BMS, Merck Serono, Astra Zeneca, Celgene, Seattle Genetics, Roche, Novartis, Rakuten, Nanobiotix, and GSK. JG participated in advisory boards from Astra Zeneca, BMS, Innate Pharma, Merck Serono, Roche, and as invited speaker for Merck SD and Merck Serono. All other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marret, G., Isambert, N., Rezai, K. et al. Phase I trial of copanlisib, a selective PI3K inhibitor, in combination with cetuximab in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Invest New Drugs 39, 1641–1648 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01152-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01152-z