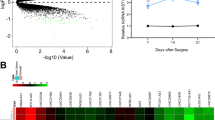
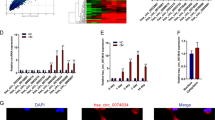
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) is an endogenous regulatory small molecule RNA. Growing evidence shows that miRNA plays an important regulatory role in gene expression. Although miRNA is a more intensive regulatory noncoding RNA in recent years, few studies have investigated the regulation of targeting genes involved in bone repair. Meanwhile, as a negative bone regulator, previous studies showed that casein kinase 2-interacting protein 1 (CKIP-1) is closely associated with bone formation and regeneration. However, the gene knockout method may not be suitable for clinical application. Therefore, it was hypothesized that miRNA molecules can inhibit the expression of CKIP-1 and ultimately promote the osteogenesis process. The present study revealed that let-7i-5p plays an important role in the process of fracture healing by inhibiting the expression of CKIP-1. Related research provides a novel gene target for fracture healing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek WY, Lee MA, Jung JW, Kim SY, Akiyama H, de Crombrugghe B, Kim JE (2009) Positive regulation of adult bone formation by osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix. J Bone Miner Res 24:1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.081248
Center JR, Bliuc D, Nguyen TV, Eisman JA (2007) Risk of subsequent fracture after low-trauma fracture in men and women. JAMA 297:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.297.4.387
Chu ZM, Li HB, Sun SX, Jiang YC, Wang B, Dong YF (2017) Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in aged rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:4446–4456
Collison J (2018) Osteoporosis: teriparatide preferable for fracture prevention. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14:4. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2017.194
Cooper C (2005) Epidemiology of osteoporotic fracture: looking to the future. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:iv36–iv40. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei060
Hu L, Su P, Yin C, Zhang Y, Li R, Yan K, Chen Z, Li D, Zhang G, Wang L (2018) Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by promoting β-catenin/TCF1/Runx2 signaling axis. J Cell Physiol 233:1574
Huang Z, Cheng C, Wang J, Liu X, Wei H, Han Y, Yang S, Wang X (2018) Icariin regulates the osteoblast differentiation and cell proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells through microRNA?153 by targeting Runt related transcription factor 2. Exp Ther Med 15:5159
Jethva R, Otsuru S, Dominici M, Horwitz EM (2009) Cell therapy for disorders of bone. Cytotherapy 11:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240902753477
Jia Y, Ding X, Zhou L, Zhang L, Yang X (2020) Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-139-5p restrains tumorigenesis in bladder cancer by targeting PRC1. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01486-7
Kim KM, Park SJ, Jung SH, Kim EJ, Jogeswar G, Ajita J, Rhee Y, Kim CH, Lim SK (2012) miR-182 is a negative regulator of osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and skeletogenesis through targeting FoxO1. J Bone Miner Res 27:1669–1679. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1604
Ling S, Sun Q, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang P, Wang X, Tian C, Li Q, Song J, Liu H (2012) CKIP-1 inhibits cardiac hypertrophy by regulating class II histone deacetylase phosphorylation through recruiting PP2A. Circulation 126:3028–3040
Liu J, Lu C, Wu X, Zhang Z, Li J, Guo B, Li D, Liang C, Dang L, Pan X (2017) Targeting osteoblastic casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 to enhance Smad-dependent BMP signaling and reverse bone formation reduction in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Sci Rep 7:41295
Liu J, Liang C, Guo B, Wu X, Li D, Zhang Z, Zheng K, Dang L, He X, Lu C, Peng S, Pan X, Zhang BT, Lu A, Zhang G (2017) Increased PLEKHO1 within osteoblasts suppresses Smad-dependent BMP signaling to inhibit bone formation during aging. Aging Cell 16:360–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12566
Liu Q, Guo Y, Wang Y, Zou X, Yan Z (2018) miR-98–5p promotes osteoblast differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells by targeting CKIP-1. Mol Med Rep 17:4797
Lu K, Yin X, Weng T, Xi S, Li L, Xing G, Cheng X, Yang X, Zhang L, He F (2008) Targeting WW domains linker of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat Cell Biol 10:994–1002
Mei L, Chi Z, Xinhan L, Zeheng L, Yao C, Jiyuan Z (2019) Isoquercitrin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts and BMSCs via the RUNX2 or BMP-pathway. Connect Tissue Res 60:189–199
Murata K, Ito H, Yoshitomi H, Yamamoto K, Fukuda A, Yoshikawa J, Furu M, Ishikawa M, Shibuya H, Matsuda S (2014) Inhibition of miR-92a enhances fracture healing via promoting angiogenesis in a model of stabilized fracture in young mice. J Bone Miner Res 29:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2040
Orimo H (2010) The mechanism of mineralization and the role of alkaline phosphatase in health and disease. J Nippon Med Sch 77:4–12. https://doi.org/10.1272/jnms.77.4
Palvanen M, Kannus P, Parkkari J, Pitkajarvi T, Pasanen M, Vuori I, Jarvinen M (2000) The injury mechanisms of osteoporotic upper extremity fractures among older adults: a controlled study of 287 consecutive patients and their 108 controls. Osteoporos Int 11:822–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001980070040
Peng X, Wu X, Zhang J, Zhang G, Li G, Pan X (2018) The role of CKIP-1 in osteoporosis development and treatment. Bone Joint Res 7:173–178
Riggs BL, Melton LJ III (1995) The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insights afforded by epidemiology. Bone 17:505S-511S. https://doi.org/10.1016/8756-3282(95)00258-4
Rongyao X, Xiang S, Yameng S, Yu F, Weiwen Z, Tao X, Zongyun F, Ping Z, Jie C, Hongbing J (2018) MicroRNA-31a-5p from aging BMSCs links bone formation and resorption in the aged bone marrow microenvironment. Aging Cell 17:e12794
Shan Z, Cheng N, Huang R, Zhao B, Zhou Y (2018) Puerarin promotes the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via microRNA-106b by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand. Exp Ther Med 15:55–60
Shen H, Yao X, Li H, Li X, Zhang T, Sun Q, Ji C, Chen G (2018) Role of exosomes derived from miR-133b modified MSCs in an experimental rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. J Mol Neurosci 64:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1041-2
Shuid AN, Mohamad S, Muhammad N, Fadzilah FM, Mokhtar SA, Mohamed N, Soelaiman IN (2011) Effects of alpha-tocopherol on the early phase of osteoporotic fracture healing. J Orthop Res 29:1732–1738. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.21452
Sun X, Li X, Qi H, Hou X, Zhao J, Yuan X, Ma X (2020) MiR-21 nanocapsules promote early bone repair of osteoporotic fractures by stimulating the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Translat 24:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jot.2020.04.007
Tian Y, Cui LH, Xiang SY, Xu WX, Chen DC, Fu R, Zhou CL, Liu XQ, Wang YF, Wang XT (2017) Osteoblast-oriented differentiation of BMSCs by co-culturing with composite scaffolds constructed using silicon-substituted calcium phosphate, autogenous fine particulate bone powder and alginate in vitro. Oncotarget 8:88308–88319. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19015
Tu M, Tang J, He H, Cheng P, Chen C (2017) MiR-142-5p promotes bone repair by maintaining osteoblast activity. J Bone Miner Metab 35:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0757-8
Unnanuntana A, Gladnick BP, Donnelly E, Lane JM (2010) The assessment of fracture risk. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:743–753. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.I.00919
Wang T, Xu Z (2010) miR-27 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Wnt signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402:186–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.08.031
Wu M, Hesse E, Morvan F, Zhang JP, Correa D, Rowe GC, Kiviranta R, Neff L, Philbrick WM, Horne WC, Baron R (2009) Zfp521 antagonizes Runx2, delays osteoblast differentiation in vitro, and promotes bone formation in vivo. Bone 44:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2008.11.011
Xu D, Gao Y, Hu N, Wu L, Chen Q (2017) miR-365 ameliorates dexamethasone-induced suppression of osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 cells by targeting HDAC4. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18050977
Yang M, Lin L, Sha C, Li T, Zhao D, Wei H, Chen Q, Liu Y, Chen X, Xu W, Li Y, Zhu X (2020) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-144-5p improves rat ovarian function after chemotherapy-induced ovarian failure by targeting PTEN. Lab Invest 100:342–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-019-0321-y
Zhang JF, Fu WM, He ML, Xie WD, Lv Q, Wan G, Li G, Wang H, Lu G, Hu X, Jiang S, Li JN, Lin MC, Zhang YO, Kung HF (2011) MiRNA-20a promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by co-regulating BMP signaling. RNA Biol 8:829–838. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.8.5.16043
Zhang X, Wang Q, Wan Z, Li J, Liu L, Zhang X (2016) CKIP-1 knockout offsets osteoporosis induced by simulated microgravity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 122:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.09.007
Zhao R, Li Y, Lin Z, Wan J, Xu C, Zeng Y, Zhu Y (2016) miR-199b-5p modulates BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477:749–754
Zhou ZC, Che L, Kong L, Lei DL, Liu R, Yang XJ (2016) CKIP-1 silencing promotes new bone formation in rat mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Oral surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 123:e1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.11432016, No.31370942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10616_2020_444_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary material 1 (JPEG 2193 kb). Figure S1. Detection of cell surface markers and evaluation of multi-directional ability to identify BMSCs. (A) Cell surface markers CD29, CD44 and CD45 were detected by flow cytometry. (B) Detection of the cell surface marker CD90 (200X). (C) BMSCs stained with alkaline phosphatase following osteogenic induction at days 7, 14 and 21(200X). (D) BMSCs stained with oil red O following adipogenic induction at day 7 (200X). (E) BMSCs stained with Alcian blue following chondrogenic induction at day 14 (200X).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Cheng, W., Han, B. et al. Let-7i-5p functions as a putative osteogenic differentiation promoter by targeting CKIP-1. Cytotechnology 73, 79–90 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00444-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00444-1