Abstract
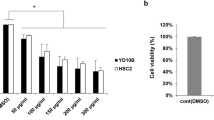
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors of the oral cavity. Probiotics have often been considered as effective anti-tumoral candidates. This study aimed to investigate the role of Pichia fermentans YSH secretion metabolites on the induction of apoptosis in SCC. Cytotoxicity, apoptotic effects, and visualization DNA damage were evaluated by MTT, flow cytometry, and DAPI staining assays, respectively. Real-time PCR was employed for evaluation of the mechanism of cellular apoptosis. P. fermentans YSH secretions (IC50) showed cellular cytotoxicity in human tongue squamous carcinoma (HSC4, RRID:CVCL_1289) cells (85% apoptosis) similar to the cytotoxicity of cisplatin whereas only 21% apoptosis was observed in human epithelial normal (KDR, RRID:CVCL_9V14) cells. The prophylactic efficacy of reference yeast, which regarded as a reference, was not comparable to P. fermentans YSH illustrating strain-dependent properties of bioactivities on oral disease control and prevention. According to our result, the main cytotoxicity is related to apoptosis mechanisms induced by apoptosis genes inducing BAX and CASP. However, follow-up researches should be performed to recognize the compounds to be utilized as effective anticancer therapeutics.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Please contact the author for data requests.
References
Ashkenazi A (2002) Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat Rev Cancer 2:420–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc821
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Investig 104:155–162
Bairoch A (2018) The cellosaurus, a cell-line knowledge resource. J Biomol Technol 29:25–38. https://doi.org/10.7171/jbt.18-2902-002
Bolz J, Dosa E, Schubert J, Eckert AW (2014) Bacterial colonization of microbial biofilms in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Oral Investig 18:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1007-2
Burns A, Rowland I (2000) Anti-carcinogenicity of probiotics and prebiotics. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol 1:13–24
Chong ES (2014) A potential role of probiotics in colorectal cancer prevention: review of possible mechanisms of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:351–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1499-6
Ciorba MA, Hallemeier CL, Stenson WF, Parikh PJ (2015) Probiotics to prevent gastrointestinal toxicity from cancer therapy: an interpretive review and call to action. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 9:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1097/SPC.0000000000000134
Consoli ML, da Silva RS, Nicoli JR, Bruna-Romero O, da Silva RG, de Vasconcelos Generoso S, Correia MI (2015) Randomized clinical trial: impact of oral administration of Saccharomyces boulardii on gene expression of intestinal cytokines in patients undergoing colon resection. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607115584387
Desboeufs J, Ralambosoa C, Astoin J, Joram C, Salhi SL, Bastide JM (1988) Structural characterization of pichilan, a beta-d-glucan immunostimulant from Pichia fermentans. Chem Pharm Bull 36:2766–2771. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.36.2766
Ghoneum MHJ, Brown J, Gollapudi S (2005) Human squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and colon undergoes apoptosis upon phagocytosis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the baker’s yeast, in vitro. Anticancer Res 25:981–989
Ghoneum M, El-Din NKB, Noaman E, Tolentino L (2008) In vivo tumor inhibitory effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Ehrlich carcinoma-bearing mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:581–592
Habil N, Abate W, Beal J, Foey AD (2014) Heat-killed probiotic bacteria differentially regulate colonic epithelial cell production of human beta-defensin-2: dependence on inflammatory cytokines. Benef Microbes 5:483–495. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2013.0061
Haghshenas B, Nami Y, Abdullah N, Radiah D, Rosli R, Khosroushahi AY (2015) Anticancer impacts of potentially probiotic acetic acid bacteria isolated from traditional dairy microbiota. LWT-Food Sci Technol 60:690–697
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y, Sakuragi N (2014) Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in cancer. Biomed Res Int 2014:150845. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/150845
Herman MP, Dagan R, Amdur RJ, Morris CG, Werning JW, Vaysberg M, Mendenhall WM (2015) Postoperative radiotherapy for patients at high risk of recurrence of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope 125:630–635. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24938
Jee-Youn K, Su-Mi K, Jeong-Hun K, Ji-Hye Y, Jin-Hae P, Jae-Hoon P (2006) Interaction of pro-apoptotic protein HGTD-P with heat shock protein 90 is required for induction of mitochondrial apoptotic cascades. FEBS Lett. 580:3270–3275
Karasawa T, Steyger PS (2015) An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett 237:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.06.012
Khodadadi H, Karimi L, Jalalizand N, Adin H, Mirhendi H (2017) Utilization of size polymorphism in ITS1 and ITS2 regions for identification of pathogenic yeast species. J Med Microbiol 66:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.000426
Lee CH, Chang JS, Syu SH, Wong TS, Chan JY, Tang YC, Yang ZP, Yang WC, Chen CT, Lu SC, Tang PH, Yang TC, Chu PY, Hsiao JR, Liu KJ (2015) IL-1beta promotes malignant transformation and tumor aggressiveness in oral cancer. J Cell Physiol 230:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24816
Marttila E, Uittamo J, Rusanen P, Lindqvist C, Salaspuro M, Rautemaa R (2015) Site-specific acetaldehyde production and microbial colonization in relation to oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral lichenoid disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 119:697–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2015.01.019
Mee YH, Navindra PS, Yanjun Z, David H (2008) Anticancer effects of Chinese red yeast rice versus monacolin K alone on colon cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem 19:448–458
Moslehi-Jenabian S, Lindegaard L, Jespersen L (2010) Beneficial effects of probiotic and food borne yeasts on human health. Nutrients 2:449–473
Nami Y, Abdullah N, Haghshenas B, Radiah D, Rosli R, Khosroushahi AY (2014) Probiotic potential and biotherapeutic effects of newly isolated vaginal Lactobacillus acidophilus 36YL strain on cancer cells. Anaerobe 28:29–36
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45–e45
Phuphanich S, Baker SD, Grossman SA, Carson KA, Gilbert MR, Fisher JD, Carducci MA (2005) Oral sodium phenylbutyrate in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas: a dose escalation and pharmacologic study. Neuro Oncol 7:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1215/S1152851704000183
Pinpimai K, Rodkhum C, Chansue N, Katagiri T, Maita M, Pirarat N (2015) The study on the candidate probiotic properties of encapsulated yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae JCM 7255, in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Res Vet Sci 102:103–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2015.07.021
Ren Y, Zhu H, Chi C, Yang F, Xu X (2015) MiRNA-139 regulates oral cancer Tca8113 cells apoptosis through Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:4588–4594
Saber A, Alipour B, Faghfoori Z, Khosroushahi AY (2017a) Secretion metabolites of dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus AS41 isolated as probiotic, induces apoptosis in different human cancer cell lines and exhibit anti-pathogenic effects. J Funct Foods 34:408–421
Saber A, Alipour B, Faghfoori Z, Mousavi Jam A, Yari Khosroushahi A (2017b) Secretion metabolites of probiotic yeast, Pichia kudriavzevii AS-12, induces apoptosis pathways in human colorectal cancer cell lines. Nutr Res 41:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2017.04.001
Satheeshkumar PS, Mohan MP (2014) Malignant potential of oral submucous fibrosis due to intraoral extraction wounds and poor oral hygiene. Oral Oncol 50:e5–e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.10.011
Tripathi R, Samadder T, Gupta S, Surolia A, Shaha C (2011) Anticancer activity of a combination of cisplatin and fisetin in embryonal carcinoma cells and xenograft tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 10:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0606
Udeabor SE, Rana M, Wegener G, Gellrich NC, Eckardt AM (2012) Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and the oropharynx in patients less than 40 years of age: a 20-year analysis. Head Neck Oncol 4:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-3284-4-28
Yang B, McCullough ML, Gapstur SM, Jacobs EJ, Bostick RM, Fedirko V, Flanders WD, Campbell PT (2014) Calcium, vitamin D, dairy products, and mortality among colorectal cancer survivors: the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort. J Clin Oncol 32:2335–2343. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.55.3024
Acknowledgements
The facilities support of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HBS performed the experiment; ZA participated in the protocol design and provided help; AS and HBS prepared the manuscript; AYKH participated in the discussion, protocol design, edit and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
This study has “Not applicable” any individual person’s data.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study has “Not applicable” any individual person’s data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamloo, H.B., Shahabi, A., Aghazadeh, Z. et al. Pichia fermentans originates apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma by over-expressing BAX and CASP 9 genes. Cytotechnology 72, 445–454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00392-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-020-00392-w