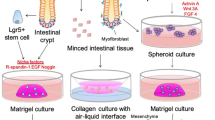
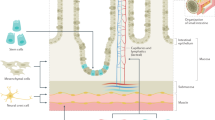
Abstract
Currently, many gastrointestinal diseases are a major reason for the increased mortality rate of children and adults every year. Additionally, these patients may cope with the high cost of the parenteral nutrition (PN), which aids in the long-term survival of the patients. Other treatment options include surgical lengthening, which is not sufficient in many cases, and intestinal transplantation. However, intestinal transplantation is still accompanied by many challenges, including immune rejection and donor availability, which may limit the transplant’s success. The development of more safe and promising alternative treatments for intestinal diseases is still ongoing. Stem cell-based therapy (SCT) and tissue engineering (TE) appear to be the next promising choices for the regeneration of the damaged intestine. However, suitable stem cell source is required for the SCT and TE process. Thus, in this review we discuss how intestinal stem cells (ISCs) are a promising cell source for small intestine diseases. We will also discuss the different markers were used to identify ISCs. Moreover, we discuss the dominant Wnt signaling pathway in the ISC niche and its involvement in some intestinal diseases. Additionally, we discuss ISC culture and expansion, which are critical to providing enough cells for SCT and TE. Finally, we conclude and recommend that ISC isolation, culture and expansion should be considered when SCT is a treatment option for intestinal disorders. Therefore, we believe that ISCs should be considered a cell source for SCT for many gastrointestinal diseases and should be highlighted in future clinical applications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PN:
-
Parenteral nutrition
- ISCs:
-
Intestinal stem cells
- SCT:
-
Stem cell-based therapy
- TE:
-
Tissue engineering
- CBCs:
-
Crypt base columnar cells
- DCAMKL1:
-
Doublecortin and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase-like 1
- LRCs:
-
Label-retaining cells
- Lgr5:
-
Leucin-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5
- mTert:
-
Mouse telomerase reverse transcriptase
- Fz:
-
7-Transmembrane Frizzled
- LRP:
-
Single-span transmembrane protein
- APC:
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli
- CKI:
-
Axin displace β-catenin allowing casein kinaseI
- GSK3 β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase3 β
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- NEC:
-
Necrotizing enterocolitis
- SBS:
-
Short bowel syndrome
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- OU:
-
Organoid units
- TESI:
-
Tissue-engineered small intestine
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- TrCP:
-
Transducin repeat-containing protein
References
Agopian VG, Chen DC, Avansino JR, Stelzner M (2009) Intestinal stem cell organoid transplantation generates neomucosa in dogs. J Gastrointest Surg 13:971–982
Albert MR, Foster RA, Vogel JC (2001) Murine epidermal label-retaining cells isolated by flow cytometry do not express the stem cell markers CD34, Sca-1, or Flk-1. J Invest Dermatol 117:943–948
Almond S, Lindley RM, Kenny SE, Connell MG, Edgar DH (2007) Characterisation and transplantation of enteric nervous system progenitor cells. Gut 56:489–496
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H (2007) Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449:1003–1007
Barker N, van de Wetering M, Clevers H (2008) The intestinal stem cell. Genes Dev 22:1856–1864
Barker N, Rookmaaker MB, Kujala P, Ng A, Leushacke M, Snippert H, van de Wetering M, Tan S, Van Es JH, Huch M, Poulsom R, Verhaar MC, Peters PJ, Clevers H (2012) Lgr5(+ve) stem/progenitor cells contribute to nephron formation during kidney development. Cell Rep 2:540–552
Beaulieu JF, Ménard D (2012) Isolation, characterization, and culture of normal human intestinal crypt and villus cells. Methods Mol Biol 806:157–173
Belkind-Gerson J, Carreon-Rodriguez A, Benedict LA, Steiger C, Pieretti A, Nagy N, Dietrich J, Goldstein AM (2013) Nestin-expressing cells in the gut give rise to enteric neurons and glial cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:61–69
Bickenbach JR, Chism E (1998) Selection and extended growth of murine epidermal stem cells in culture. Exp Cell Res 244:184–195
Bisceglie V (1933) Über die antineoplastische Immunität; heterologe Einpflanzung von Tumoren in Hühner-embryonen. Ztschr Krebsforsch 40:122–140
Bitar KN, Raghavan S (2012) Intestinal tissue engineering: current concepts and future vision of regenerative medicine in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24:7–19
Bixby S, Kruger GM, Mosher JT, Joseph NM, Morrison SJ (2002) Cell-intrinsic differences between stem cells from different regions of the peripheral nervous system regulate the generation of neural diversity. Neuron 35:643–656
Bondurand N, Natarajan D, Thapar N, Atkins C, Pachnis V (2003) Neuron and glia generating progenitors of the mammalian enteric nervous system isolated from foetal and postnatal gut cultures. Development 130:6387–6400
Byrne TA, Wilmore DW, Iyer K, Dibaise J, Clancy K, Robinson MK, Chang P, Gertner JM, Lautz D (2005) Growth hormone, glutamine, and an optimal diet reduces parenteral nutrition in patients with short bowel syndrome. Ann Surg 242:655–661
Carletti E, Motta A, Migliaresi C (2011) Scaffolds for tissue engineering and 3D cell culture. Methods Mol Biol 695:17–39
Chan RW, Gargett CE (2006) Identification of label-retaining cells in mouse endometrium. Stem Cells 24:1529–1538
Chan BP, Leong KW (2008) Scaffolding in tissue engineering: general approaches and tissue-specific considerations. Eur Spine J 17:467–479
Chen MK, Beierle EA (2004) Animal models for intestinal tissue engineering. Biomaterials 25:1675–1681
Chen Y, Lee SH, Tsai YH, Tseng SH (2014) Ischemic preconditioning increased the intestinal stem cell activities in the intestinal crypts in mice. J Surg Res 187:85–93
Choi RS, Vacanti JP (1997) Preliminary studies of tissue-engineered intestine using isolated epithelial organoid units on tubular synthetic biodegradable scaffolds. Transplant Proc 29:848–851
Christgen M, Ballmaier M, Lehmann U, Kreipe H (2012) Detection of putative cancer stem cells of the side population phenotype in human tumor cell cultures. Methods Mol Biol 878:201–215
Day RM (2006) Epithelial stem cells and tissue engineered intestine. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 1:113–120
Dekaney CM, Rodriguez JM, Graul MC, Henning SJ (2005) Isolation and characterization of a putative intestinal stem cell fraction from mouse jejunum. Gastroenterology 129:1567–1580
Ekema G, Milianti S, Boroni G (2009) Total parenteral nutrition in patients with short bowel syndrome. Minerva Pediatr 61:283–291
Evans GS, Flint N, Somers AS, Eyden B, Potten CS (1992) The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures. J Cell Sci 101:219–231
Farlie PG, McKeown SJ, Newgreen DF (2004) The neural crest: basic biology and clinical relationships in the craniofacial and enteric nervous systems. Birth Defects Res C 72:173–189
Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta M, Paolucci E, Stornaiuolo A, Cossu G, Mavilio F (1998) Muscle regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Science 279:1528–1530
Fukuda K (2003) Regeneration of cardiomyocytes from bone marrow: use of mesenchymal stem cell for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Cytotechnology 41:165–175
Garcia MI, Ghiani M, Lefort A, Libert F, Strollo S, Vassart G (2009) LGR5 deficiency deregulates Wnt signaling and leads to precocious Paneth cell differentiation in the fetal intestine. Dev Biol 331:58–67
Gracz AD, Fuller MK, Wang F, Li L, Stelzner M, Dunn JC, Martin MG, Magness ST (2013) CD24 and CD44 mark human intestinal epithelial cell populations with characteristics of active and facultative stem cells. Stem Cells 31:2024–2030
Grikscheit TC, Siddique A, Ochoa ER, Srinivasan A, Alsberg E, Hodin RA, Vacanti JP (2004) Tissue-engineered small intestine improves recovery after massive small bowel resection. Ann Surg 240:748–754
Gupta A, Dixit A, Sales KM, Winslet MC, Seifalian AM (2006) Tissue engineering of small intestines—current status. Biomacromolecules 7:2701–2709
Haegebarth A, Clevers H (2009) Wnt signaling, lgr5, and stem cells in the intestine and skin. Am J Pathol 174:715–721
Hall BK, Hörstadius S (1988) The neural crest. Oxford University Press, London
Haramis AP, Begthel H, van den Born M, van Es J, Jonkheer S, Offerhaus GJ, Clevers H (2004) De novo crypt formation and juvenile polyposis on BMP inhibition in mouse intestine. Science 303:1684–1686
Heanue TA, Pachnis V (2007) Enteric nervous system development and Hirschsprung’s disease: advances in genetic and stem cell studies. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:466–479
Hori Y, Nakamura T, Kimura D, Kaino K, Kurokawa Y, Satomi S, Shimizu Y (2002) Experimental study on tissue engineering of the small intestine by mesenchymal stem cell seeding. J Surg Res 102:156–160
Huelsken J, Behrens J (2002) The Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci 115:3977–3978
Jiang H, Edgar BA (2012) Intestinal stem cell function in Drosophila and mice. Curr Opin Genet Dev 22:354–360
Kassem M, Abdallah BM, Yu Z, Ditzel N, Burns JS (2004) The use of hTERT-immortalized cells in tissue engineering. Cytotechnology 45:39–46
Kawamoto S, Niwa H, Tashiro F, Sano S, Kondoh G, Takeda J, Tabayashi K, Miyazaki J (2000) A novel reporter mouse strain that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein upon Cre-mediated recombination. FEBS Lett 470:263–268
Kayahara T, Sawada M, Takaishi S, Fukui H, Seno H, Fukuzawa H, Suzuki K, Hiai H, Kageyama R, Okano H, Chiba T (2003) Candidate markers for stem and early progenitor cells, Musashi-1 and Hes1, are expressed in crypt base columnar cells of mouse small intestine. FEBS Lett 535:131–135
Kim KA, Kakitani M, Zhao J, Oshima T, Tang T, Binnerts M, Liu Y, Boyle B, Park E, Emtage P, Funk WD, Tomizuka K (2005) Mitogenic influence of human R-spondin1 on the intestinal epithelium. Science 309:1256–1259
Kirkman RL (1984) Small bowel transplantation. Transplantation 37:429–433
Kruger GM, Mosher JT, Bixby S, Joseph N, Iwashita T, Morrison SJ (2002) Neural crest stem cells persist in the adult gut but undergo changes in self-renewal, neuronal subtype potential, and factor responsiveness. Neuron 35:657–669
Langer R (2000) Tissue engineering. Mol Ther 1:12–15
Levin DE, Barthel ER, Speer AL, Sala FG, Hou X, Torashima Y, Grikscheit TC (2013) Human tissue-engineered small intestine forms from postnatal progenitor cells. J Pediatr Surg 48:129–137
Li L, Clevers H (2010) Coexistence of quiescent and active adult stem cells in mammals. Science 327:542–545
Li L, Milner LA, Deng Y, Iwata M, Banta A, Graf L, Marcovina S, Friedman C, Trask BJ, Hood L, Torok-Storb B (1998) The human homolog of rat Jagged1 expressed by marrow stroma inhibits differentiation of 32D cells through interaction with Notch1. Immunity 8:43–55
Lindley RM, Hawcutt DB, Connell MG, Almond SL, Vannucchi MG, Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Edgar DH, Kenny SE (2008) Human and mouse enteric nervous system neurosphere transplants regulate the function of aganglionic embryonic distal colon. Gastroenterology 135:205–216
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Markel TA, Crisostomo PR, Lahm T, Novotny NM, Rescorla FJ, Tector J, Meldrum DR (2008) Stem cells as a potential future treatment of pediatric intestinal disorders. J Pediatr Surg 43:1953–1963
May R, Sureban SM, Hoang N, Riehl TE, Lightfoot SA, Ramanujam R, Wyche JH, Anant S, Houchen CW (2009) Doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1 and leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor mark quiescent and cycling intestinal stem cells, respectively. Stem Cells 27:2571–2579
Metzger M, Caldwell C, Barlow AJ, Burns AJ, Thapar N (2009) Enteric nervous system stem cells derived from human gut mucosa for the treatment of aganglionic gut disorders. Gastroenterology 136:2214–2225
Mohamed MS, Chen Y, Yao CL (2014) A serum-free medium developed for in vitro expansion of murine intestinal stem cells. Biotechnol J. doi:10.1002/biot.201400016
Montgomery RK, Breault DT (2008) Small intestinal stem cell markers. J Anat 213:52–58
Montgomery RK, Carlone DL, Richmond CA, Farilla L, Kranendonk ME, Henderson DE, Baffour-Awuah NY, Ambruzs DM, Fogli LK, Algra S, Breault DT (2011) Mouse telomerase reverse transcriptase (mTert) expression marks slowly cycling intestinal stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:179–184
Morris RJ, Potten CS (1999) Highly persistent label-retaining cells in the hair follicles of mice and their fate following induction of anagen. J Invest Dermatol 112:470–475
Mosher JT, Yeager KJ, Kruger GM, Joseph NM, Hutchin ME, Dlugosz AA, Morrison SJ (2007) Intrinsic differences among spatially distinct neural crest stem cells in terms of migratory properties, fate determination, and ability to colonize the enteric nervous system. Dev Biol 303:1–15
Nagoshi N, Shibata S, Kubota Y, Nakamura M, Nagai Y, Satoh E, Morikawa S, Okada Y, Mabuchi Y, Katoh H, Okada S, Fukuda K, Suda T, Matsuzaki Y, Toyama Y, Okano H (2008) Ontogeny and multipotency of neural crest-derived stem cells in mouse bone marrow, dorsal root ganglia, and whisker pad. Cell Stem Cell 2:392–403
Najdi R, Holcombe RF, Waterman ML (2011) Wnt signaling and colon carcinogenesis: beyond APC. J Carcinog 10:5
Natarajan D, Grigoriou M, Marcos-Gutierrez CV, Atkins C, Pachnis V (1999) Multipotential progenitors of the mammalian enteric nervous system capable of colonising aganglionic bowel in organ culture. Development 126:157–168
Pietersen AM, Evers B, Prasad AA, Tanger E, Cornelissen-Steijger P, Jonkers J, van Lohuizen M (2008) Bmi1 regulates stem cells and proliferation and differentiation of committed cells in mammary epithelium. Curr Biol 18:1094–1099
Pinto D, Gregorieff A, Begthel H, Clevers H (2003) Canonical Wnt signals are essential for homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium. Genes Dev 17:1709–1713
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Plaks V, Brenot A, Lawson DA, Linnemann JR, Van Kappel EC, Wong KC, de Sauvage F, Klein OD, Werb Z (2013) Lgr5-expressing cells are sufficient and necessary for postnatal mammary gland organogenesis. Cell Rep 3:70–78
Potten CS, Kovacs L, Hamilton E (1974) Continuous labelling studies on mouse skin and intestine. Cell Tissue Kinet 7:271–283
Potten CS, Owen G, Booth D (2002) Intestinal stem cells protect their genome by selective segregation of template DNA strands. J Cell Sci 115:2381–2388
Potten CS, Booth C, Tudor GL, Booth D, Brady G, Hurley P, Ashton G, Clarke R, Sakakibara S, Okano H (2003) Identification of a putative intestinal stem cell and early lineage marker; musashi-1. Differentiation 71:28–41
Reya T, Clevers H (2005) Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 434:843–850
Reyes J, Mazariegos GV, Bond GM, Green M, Dvorchik I, Kosmach-Park B, Abu-Elmagd K (2002) Pediatric intestinal transplantation: historical notes, principles and controversies. Pediatr Transplant 6:193–207
Rocha FG, Whang EE (2004) Intestinal tissue engineering: from regenerative medicine to model systems. J Surg Res 120:320–325
Sangiorgi E, Capecchi MR (2008) Bmi1 is expressed in vivo in intestinal stem cells. Nat Genet 40:915–920
Sansom OJ, Reed KR, Hayes AJ, Ireland H, Brinkmann H, Newton IP, Batlle E, Simon-Assmann P, Clevers H, Nathke IS, Clarke AR, Winton DJ (2004) Loss of Apc in vivo immediately perturbs Wnt signaling, differentiation, and migration. Genes Dev 18:1385–1390
Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, van de Wetering M, Barker N, Stange DE, van Es JH, Abo A, Kujala P, Peters PJ, Clevers H (2009) Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 459:262–265
Scoville DH, Sato T, He XC, Li L (2008) Current view: intestinal stem cells and signaling. Gastroenterology 134:849–864
Serbedzija GN, Bronner-Fraser M, Fraser SE (1989) A vital dye analysis of the timing and pathways of avian trunk neural crest cell migration. Development 106:809–816
Serbedzija GN, Fraser SE, Bronner-Fraser M (1990) Pathways of trunk neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo as revealed by vital dye labelling. Development 108:605–612
Shaker A, Rubin DC (2010) Intestinal stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the crypt and stem cell niche. Transl Res 156:180–187
Shibata S, Yasuda A, Renault-Mihara F, Suyama S, Katoh H, Inoue T, Inoue YU, Nagoshi N, Sato M, Nakamura M, Akazawa C, Okano H (2010) Sox10-Venus mice: a new tool for real-time labeling of neural crest lineage cells and oligodendrocytes. Mol Brain 3:31
Simons BD, Clevers H (2011) Stem cell self-renewal in intestinal crypt. Exp Cell Res 317:2719–2724
Slorach EM, Campbell FC, Dorin JR (1999) A mouse model of intestinal stem cell function and regeneration. J Cell Sci 112:3029–3038
Sureban SM, May R, Lightfoot SA, Hoskins AB, Lerner M, Brackett DJ, Postier RG, Ramanujam R, Mohammed A, Rao CV, Wyche JH, Anant S, Houchen CW (2011) DCAMKL-1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic cells through a miR-200a-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 71:2328–2338
Uchida H, Yamazaki K, Fukuma M, Yamada T, Hayashida T, Hasegawa H, Kitajima M, Kitagawa Y, Sakamoto M (2010) Overexpression of leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 101:1731–1737
van de Wetering M, Sancho E, Verweij C, de Lau W, Oving I, Hurlstone A, van der Horn K, Batlle E, Coudreuse D, Haramis AP, Tjon-Pon-Fong M, Moerer P, van den Born M, Soete G, Pals S, Eilers M, Medema R, Clevers H (2002) The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 111:241–250
van der Flier LG, Clevers H (2009) Stem cells, self-renewal, and differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol 71:241–260
van der Flier LG, Haegebarth A, Stange DE, van de Wetering M, Clevers H (2009) OLFM4 is a robust marker for stem cells in human intestine and marks a subset of colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 137:15–17
Vanuytsel T, Senger S, Fasano A, Shea-Donohue T (2013) Major signaling pathways in intestinal stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:2410–2426
von Furstenberg RJ, Gulati AS, Baxi A, Doherty JM, Stappenbeck TS, Gracz AD, Magness ST, Henning SJ (2011) Sorting mouse jejunal epithelial cells with CD24 yields a population with characteristics of intestinal stem cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G409–G419
Wada M, Kato T, Hayashi Y, Selvaggi G, Mittal N, Thompson J, Gonzalez M, Nishida S, Madariaga J, Tzakis A (2006) Intestinal transplantation for short bowel syndrome secondary to gastroschisis. J Pediatr Surg 41:1841–1845
Watanabe K, Ueno M, Kamiya D, Nishiyama A, Matsumura M, Wataya T, Takahashi JB, Nishikawa S, Nishikawa S, Muguruma K, Sasai Y (2007) A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 25:681–686
Wulkersdorfer B, Kao KK, Agopian VG, Dunn JC, Wu BM, Stelzner M (2011) Growth factors adsorbed on polyglycolic acid mesh augment growth of bioengineered intestinal neomucosa. J Surg Res 169:169–178
Xu Q, Mellitzer G, Robinson V, Wilkinson DG (1999) In vivo cell sorting in complementary segmental domains mediated by Eph receptors and ephrins. Nature 399:267–271
Yamauchi Y, Abe K, Mantani A, Hitoshi Y, Suzuki M, Osuzu F, Kuratani S, Yamamura K (1999) A novel transgenic technique that allows specific marking of the neural crest cell lineage in mice. Dev Biol 212:191–203
Yen TH, Wright NA (2006) The gastrointestinal tract stem cell niche. Stem Cell Rev 2:203–212
Zakhem E, Raghavan S, Gilmont RR, Bitar KN (2012) Chitosan-based scaffolds for the support of smooth muscle constructs in intestinal tissue engineering. Biomaterials 33:4810–4817
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science Council, Taiwan (101-2221-E-155-044-MY3).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests in relation to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mahmoud Shaaban Mohamed and Yun Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, M.S., Chen, Y. & Yao, CL. Intestinal stem cells and stem cell-based therapy for intestinal diseases. Cytotechnology 67, 177–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9753-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9753-9