Abstract
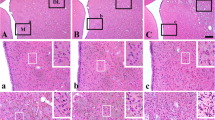
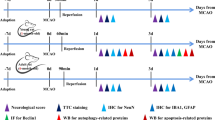
Focal brain lesions such as transient focal cerebral ischemia can lead to neuronal damage in remote areas, including the ipsilateral substantia nigra and hippocampus, as well as in the ischemic core. In this study, we investigated acute changes in the ipsilateral hippocampus from 1 up to 7 days after 90 min of transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats, using anti-NeuN (neuronal nuclei), anti-Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), anti-Mn-SOD, anti-neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), anti-inducible NOS (iNOS), anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), anti-ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1(Iba 1) and anti-2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase (CNPase) antibodies. In our western blot and histochemical analyses, present results show that transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats can cause a severe and acute damage of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the ipsilateral hippocampal CA1 sector. The present findings also demonstrate that the expression of iNOS produced by Iba 1-immunopositive microglia precedes the damage of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the ipsilateral hippocampal CA1 sector after transient focal cerebral ischemia. In contrast, our results suggest that increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production during reperfusion cannot lead to damage of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the ipsilateral hippocampal CA1 sector after transient focal cerebral ischemia, because of an insufficient expression of Cu/Zn-SOD and Mn-SOD. Our double-labeled immunohistochemical study demonstrates that the overexpression of iNOS produced by Iba 1-immunopositive microglia may play a pivotal role in the damage of neurons and oligodendrocytes in the ipsilateral hippocampal CA1 sector at an acute stage after transient focal cerebral ischemia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Araki T, Kogure K (1988) Recovery from edema and of protein synthesis differs between in the cortex and caudate following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurochem 51:1470–1476
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U (2009) Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 4:461–470
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31:571–591
Araki T, Kato H, Kogure K, Kanai Y (1992) Long-term changes in gerbil brain neurotransmitter receptors following transient cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol 107:437–442
Araki T, Kato H, Kanai Y, Kogure K (1993) Postischemic changes of intracellular second messengers in the gerbil brain after long-term survival: an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 53:829–836
Araki T, Kato H, Shuto K, Itoyama Y (1998) Alterations in [3H]L-NG-nitroarginine binding in brain after transient global or transient focal ischemia in gerbils and rats. Eur J Pharmacol 354:153–159
Araki T, Tanji H, Fujihara K, KatoH Itoyama Y (1999) Increases in [3H]FK-506 and [3H]L-N(G)-nitro-arginine binding in the rat brain after nigrostriatal dopaminergic denervation. Metab Brain Dis 14:21–31
Aronowski J, Strong R, Grotta JC (1997) Reperfusion injury: demonstration of brain damage produced by reperfusion after transient focal ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:1048–1056
ArunaDevi R, Ramteke VD, Kumar S, Shukla MK, Jaganathan S, Kumar D, Sharma AK, Tandan SK (2010) Neuroprotective effect of s-methylisothiourea in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Nitric Oxide 22:1–10
Block F, Dihné M, Loos M (2005) Inflammation in areas of remote changes following focal brain lesion. Prog Neurobiol 75:342–365
Chan PH (1996) Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke 27:1124–1129
Chan PH, Kawase M, Murakami K, Chen SF, Li Y, Calagui B, Reola L, Carlson E, Epstein CJ (1998) Overexpression of SOD1 in transgenic rats protects vulnerable neurons against ischemic damage after global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Neurosci 18:8292–8299
Collino M, Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Gallicchio M, Rosa AC, Dianzani C, Danni O, Theiememann C, Fantozzi R (2006) Modulation of the oxidative stress and inflammatory response by PPAR-gamma agonists in the hippocampus of rats exposed to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol 530:70–80
Domercq M, Perez-Samartin A, Aparicio D, Alberdi E, Pampliega O, Matute C (2010) P2X7 receptors mediate ischemic damage to oligodendrocytes. Glia 58:730–740
Endres M, Laufs U, Huang Z, Nakamura T, Huang P, Moskowitz MA et al (1998) Stroke protection by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors mediated by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8880–8885
Fujie W, Kirino T, Tomukai N, Iwasawa T, Tamura A (1990) Progressive shrinkage of the thalamus following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 21:1485–1488
Halliwell B (2001) Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging 18:685–716
Hara H, Huang PL, Panahian N, Fishman MC, Moskowitz MA (1996) Reduced brain edema and infarction volume in mice lacking the neuronal isoform of nitric oxide synthase after transient MCA occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:605–611
Himeda T, Watanabe Y, Tounai H, Hayakawa N, Kato H, Araki T (2006) Time dependent alterations of co-localization of S100beta and GFAP in the MPTP-treated mice. J Neural Transm 113:1887–1894
Himeda T, Tounai H, Hayakawa N, Araki T (2007) Postischemic alterations of BDNF, NGF, HSP 70 and ubiquitin immunoreactivity in the gerbil hippocampus: pharmacological approach. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:229–250
Huang Z, Huang PL, Panahian N, Dalkara T, Fishman MC, Moskowitz MA (1994) Effects of cerebral ischemia in mice deficient in neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science 265:1883–1885
Huang Z, Huang PL, Ma J, Meng W, Ayata C, Fishman MC, Moskowitz MA (1996) Enlarged infarcts in endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice are attenuated by nitro-l-arginine. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:981–987
Hudgins WR, Garcia JH (1970) Transorbital approach to the middle cerebral artery of the squirrel monkey: a technique for experimental cerebral infarction applicable to ultrastructural studies. Stroke 1:107–111
Iadecola C, Zhang F, Casey R, Nagayama M, Ross ME (1997) Delayed reduction of ischemic brain injury and neurological deficits in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. J Neurosci 17:9157–9164
Keller JN, Kindy MS, Holtsberg FW, St Clair DK, Yen HC, Germeyer A, Steiner SM, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hutchins JB, Mattson MP (1998) Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurosci 18:687–697
Kelly PJ, Morrow JD, Ning M, Koroshetz W, Lo EH, Terry E, Milne GL, Hubbard J, Lee H, Stevenson E, Lederer M, Furie KL (2008) Oxidative stress and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in acute ischemic stroke: the Biomarker Evaluation for Antioxidant Therapies in Stroke (BEAT-Stroke) study. Stroke 39:100–104
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Matsuda S, Umeda M, Uchida H, Kato H, Araki T (2009) Alterations of oxidative stress markers and apoptosis markers in the striatum after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neural Transm 116:395–404
Muramatsu Y, Kurosaki R, Watanabe H, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Imai Y, Araki T (2003) Expression of S-100 protein is related to neuronal damage in MPTP-treated mice. Glia 42:307–313
Nagasawa H, Kogure K (1990) Exo-focal postischemic neuronal death in the rat brain. Brain Res 524:196–202
Neumar RW (2000) Molecular mechanisms of ischemic neuronal injury. Ann Emerg Med 36:483–506
O’Brien RG, Waltz AG (1973) Transorbital approach for occluding the middle cerebral artery without craniectomy. Stroke 4:201–206
Ookubo M, Yokoyama H, Kato H, Araki T (2009) Gender differences on MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) neurotoxicity in C57BL/6 mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 311:62–68
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Ridnour LA, Thomas DD, Mancardi D, Espey MG, Miranda KM, Paolocci N, Feelisch M, Fukuto J, Wink DA (2004) The chemistry of nitrosative stress induced by nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen oxide species. Putting perspective on stressful biological situations. Biol Chem 385:1–10
Robinson RG (1981) A model for the study of stroke using the rat. Surgical ligation of the middle cerebral artery in the rat. Am J Pathol 104:103–105
Saito A, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Nishi T, Song YS, Yu F, Liu J, Lee YS, Nito C, Kamada H, Dodd RL, Hsieh LB, Hassid B, Kim EE, Gonzalez M, Chan PH (2005) Oxidative stress and neuronal death/survival signaling in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 31:105–116
Sakuma M, Hayakawa N, Kato H, Araki T (2008) Time dependent changes of striatal interneurons after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neural Transm 115:413–422
Samdani AF, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (1997) Nitric oxide synthase in models of focal ischemia. Stroke 28:1283–1288
Sims NR, Anderson MF (2002) Mitochondrial contributions to tissue damage in stroke. Neurochem Int 40:511–526
Smith ML, Auer RN, Siesjö BK (1984) The density and distribution of ischemic brain injury in the rat following 2–10 min of forebrain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 64:319–332
States BA, Honkaniemi J, Weinstein PR, Sharp FR (1996) DNA fragmentation and HSP70 protein induction in hippocampus and cortex occurs in separate neurons following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:1165–1175
Tamura A, Kirino T, Sano K, Takagi K, Oka H (1990) Atrophy of the ipsilateral substantia nigra following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Brain Res 510:154–157
Wu HW, Li HF, Wu XY, Zhao J, Guo J (2008) Reactive oxygen species mediate ERK activation through different Raf-1-dependent signaling pathways following cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett 432:83–87
Yamada K, Goto S, Yoshikawa M, Okamura A, Ushio Y (1996) Involvement of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor in the delayed transneuronal regression of substantia nigra neurons in rats. Brain Res 743:233–239
Yang G, Chan PH, Chen J, Carlson E, Chen SF, Weinstein P, Epstein CJ, Kamii H (1994) Human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice are highly resistant to reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 25:165–170
Yokoyama H, Takagi S, Watanabe Y, Kato H, Araki T (2008) Role of reactive nitrogen and reactive oxygen species against MPTP neurotoxicity in mice. J Neural Transm 115:831–842
Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Liu XS, Hozeska-Solgot A, Chopp M (2007) The PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the neuroprotective effect of atorvastatin in extending thrombolytic therapy after embolic stroke in the rat. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2470–2475
Zhao X, Haensel C, Araki E, Ross ME, Iadecola C (2000) Gene-dosing effect and persistence of reduction in ischemic brain injury in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Brain Res 872:215–218
Zhu CZ, Auer RN (1995) Graded hypotension and MCA occlusion duration: effect in transient focal ischemia. J Cerebral Blood flow Metab 15:980–988
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21790376 and 22590935) from the Ministry of Science and Education in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchida, H., Fujita, Y., Matsueda, M. et al. Damage to Neurons and Oligodendrocytes in the Hippocampal CA1 Sector after Transient Focal Ischemia in Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 1125–1134 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9545-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9545-5